What is a Marketing Environment? Definition And Importance
The marketing environment is the backdrop against which businesses operate, and comprehending its dynamics is fundamental to crafting effective marketing strategies. In this article, we delve into the heart of the matter by exploring the definition and importance of the marketing environment.
Understanding the Marketing Environment
The concept of a marketing environment encompasses the external factors that directly or indirectly influence a company’s marketing efforts. It’s crucial to comprehend this environment to tailor strategies that resonate with the target audience. The marketing environment is multifaceted and includes:
- Macro Environment: This includes broad societal forces that impact the market, such as economic, technological, political, and cultural factors. Analyzing macro trends helps businesses anticipate changes and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
- Micro Environment: This pertains to factors directly linked to the company, like suppliers, competitors, distributors, and customers. A deep understanding of the microenvironment aids in forming strategic partnerships and differentiating from rivals.
- Internal Environment: The company’s internal resources, capabilities, and structure play a significant role in shaping marketing strategies. Identifying strengths and weaknesses assists in leveraging resources effectively.
- Customer Environment: Understanding the needs, preferences, and behaviors of the target audience is at the heart of successful marketing. In-depth customer analysis enables the creation of personalized experiences that resonate with consumers.
- Market Environment: This involves analyzing the market size, growth potential, and segmentation. Identifying the most promising market segments helps in optimizing resource allocation.
Navigating the marketing environment requires a proactive and adaptive approach. Businesses need to continuously monitor and assess these factors to make informed decisions and stay ahead in the competitive landscape. By recognizing the interplay between these various environments, companies can craft strategies that align with their goals and cater to the ever-changing needs of their audience.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into each aspect of the marketing environment, exploring strategies to harness its potential and stay agile in the face of change.
What is a Marketing Environment?

The marketing environment serves as the intricate web of external and internal factors that collectively shape a brand’s ability to establish meaningful connections with its existing and potential customers. This dynamic landscape, also referred to as the business environment, holds significant sway over a company’s research, development, and market positioning efforts. Understanding the marketing environment is the cornerstone of a successful marketing strategy, as it lays the foundation for tailoring campaigns that resonate with specific demographics while adapting to the ever-changing forces of the market.
The analysis of the marketing environment is a multidimensional endeavor that aids companies in gauging how well a marketing campaign might perform under the influence of various internal and external dynamics. As businesses strive to secure their foothold in the market and expand their reach, this comprehensive assessment becomes essential for informed decision-making.
At its core, comprehending the marketing environment empowers a company’s marketing team and stakeholders to ascertain the demands of their target demographic. It reveals the needs, preferences, and behaviors of consumers, providing a roadmap for crafting tailored marketing strategies that align with these intricate nuances. Moreover, the marketing environment sheds light on how marketing operations and advertising agencies can seamlessly adapt to these needs, fortify their brand identity, and venture into new and unexplored markets.
By gaining insights into the multifaceted layers of the marketing environment, businesses can unlock several key advantages:
- Informed Innovation: As the cultural and technological landscape evolves, so do consumer expectations. Staying attuned to the marketing environment empowers companies to innovate, adopting novel strategies that leverage cutting-edge technologies to enhance their marketing efforts.
- Competitive Edge: A deep dive into the marketing environment encompasses more than customer insights; it extends to understanding the broader economic environment and how competitors operate within it. This understanding allows companies to differentiate themselves, outshining competitors and amplifying their influence on consumer buying decisions.
- Precision in Targeting: The analysis of consumer behavior and market trends empowers marketers and retailers to refine their decision-making processes. This insight ensures that campaigns and strategies are aligned with customer preferences, maximizing the likelihood of success.
In the following sections, we will delve into the internal and external dimensions of the marketing environment. This exploration will unveil the factors that businesses can control and those beyond their influence, collectively shaping the way brands interact with their audience and adapt to the ever-evolving marketplace.
Components of the Marketing Environment
The marketing environment is a complex and dynamic system that encompasses various factors and forces that influence a company’s marketing efforts and overall business operations. To effectively navigate this environment, businesses need to understand its components and how they impact their strategies and decisions. Here are the key components of the marketing environment:
1. Internal Environment:
This includes factors within the organization that directly impact marketing decisions. It encompasses elements like company culture, organizational structure, resources, and management style. The internal environment can significantly influence marketing strategies, as a company’s capabilities and resources shape its ability to execute marketing plans.
2. Microenvironment:
The microenvironment consists of factors that are directly or closely related to the company and have a more immediate impact on its marketing activities. Key components of the microenvironment include:
- Customers: Understanding customer needs, preferences, and behaviors is crucial for marketing success. Customer feedback and market research play a vital role in shaping marketing strategies.
- Suppliers: Suppliers provide the resources and materials necessary for a company’s products or services. The quality, reliability, and pricing of these supplies can affect production and pricing decisions.
- Competitors: Monitoring and analyzing competitors’ strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning helps businesses identify opportunities and threats in the market.
- Intermediaries: Intermediaries like distributors, retailers, and wholesalers play a role in product distribution and may influence pricing and promotion strategies.
- Stakeholders: Other stakeholders, such as shareholders, employees, and regulatory bodies, can impact marketing efforts through their interests and demands.
3. Market Environment:
The market environment refers to the specific industry or sector in which a company operates. Factors within the market environment include market size, growth trends, customer segments, and market dynamics. Understanding the competitive landscape and trends within the market is essential for making informed marketing decisions.
4. Macroenvironment:
The macroenvironment encompasses broader external factors that are beyond the control of the organization but can significantly affect its operations. Key components of the macroenvironment include:
- Economic Factors: Economic conditions, such as inflation rates, interest rates, and consumer spending, impact consumer purchasing power and overall demand for products and services.
- Technological Factors: Advances in technology can create opportunities for innovation and efficiency in marketing and operations. They can also disrupt industries and change consumer behaviors.
- Social and Cultural Factors: Societal values, cultural norms, demographic trends, and lifestyle changes influence consumer preferences and the way products and services are marketed.
- Political and Legal Factors: Government regulations, trade policies, taxation, and legal requirements can affect marketing practices, product labeling, and industry standards.
- Environmental Factors: Growing environmental concerns, sustainability trends, and consumer attitudes toward eco-friendly products impact marketing strategies and product development.
- Global Factors: International markets and global economic conditions present both opportunities and challenges for companies engaged in international marketing.
Understanding and monitoring these components of the marketing environment is essential for developing effective marketing strategies, anticipating changes, and adapting to evolving market conditions. Successful businesses regularly analyze and respond to the various forces at play in their marketing environment to stay competitive and achieve their goals.
Microenvironment: Closest Influences
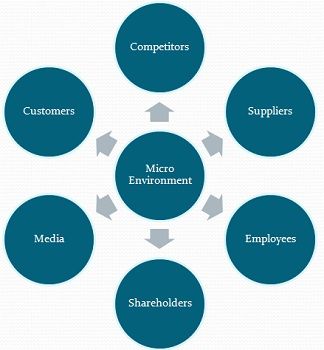
The microenvironment, comprising the closest influences, is a critical layer of the marketing environment that directly impacts a company’s day-to-day operations and strategies. It’s a network of interconnected entities and factors that have an immediate and tangible effect on a business’s interactions within the market. Understanding the microenvironment is instrumental for crafting effective marketing campaigns, building strong customer relationships, and maintaining a competitive edge in the industry.
Within this intimate sphere, businesses engage with various stakeholders who play pivotal roles in shaping their operations and success. The microenvironment provides insights into these relationships, enabling companies to tailor their strategies according to the unique dynamics of each element.
Key Factors within the Microenvironment
The microenvironment consists of several key factors, each with its distinct influence on a company’s operations. Let’s explore these factors and their roles within the microenvironment:
1. Customers
Customers lie at the heart of any business. Understanding their preferences, needs, and behaviors is crucial for delivering products and services that resonate. By analyzing customer data and feedback, companies can refine their offerings and tailor their marketing messages to better connect with their target audience.
2. Suppliers
Suppliers are essential partners in a company’s supply chain. They provide the necessary resources and materials for production, manufacturing, and delivery of products or services. Maintaining strong relationships with reliable suppliers ensures a consistent flow of high-quality resources.
3. Competitors
Competitors are other businesses operating within the same market or industry. Analyzing their strategies, strengths, and weaknesses helps companies identify gaps and opportunities in the market. Understanding competitor behavior can inform marketing decisions and give a competitive edge to a business.
4. Intermediaries
Intermediaries are entities that facilitate the distribution and delivery of products from manufacturers to consumers. They include distributors, wholesalers, retailers, and other intermediaries. Collaborating effectively with intermediaries ensures that products reach the right markets and target audiences efficiently.
5. Publics
Publics encompass groups or individuals that have an interest in or impact on a company’s operations. These may include media, investors, advocacy groups, and local communities. Maintaining positive relationships with various publics is essential for reputation management and building a favorable brand image.
Understanding these key factors within the microenvironment empowers businesses to make informed decisions and develop strategies that align with the dynamics of their immediate market surroundings. By closely analyzing and adapting to the influences of customers, suppliers, competitors, intermediaries, and various publics, companies can build a strong foundation for successful marketing endeavors.
Macroenvironment: Broader Influences
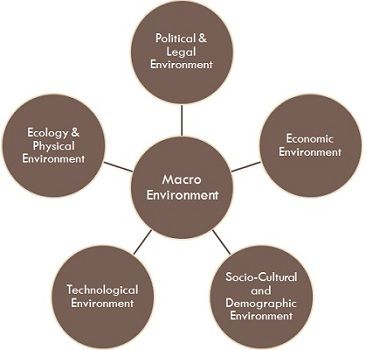
The macroenvironment encompasses a spectrum of broader influences that shape a company’s operations and strategies on a larger scale. It comprises external factors that extend beyond immediate interactions and have a profound impact on businesses operating within a specific industry or market. Understanding the macro environment is crucial for aligning a company’s approach with prevailing trends, regulations, and societal shifts, allowing businesses to adapt and thrive in a dynamic landscape.
Within the macro environment, businesses engage with a complex interplay of forces that influence industry dynamics, consumer behavior, and market conditions. By gaining insights into these external factors, companies can develop strategies that not only cater to current demands but also position them advantageously for future growth.
Key Factors within the Macroenvironment
The macroenvironment consists of several key factors, each exerting a distinct influence on a company’s operations and strategic decisions. Let’s delve into these factors and their roles within the macroenvironment:
1. Demographic Factors
Demographic factors encompass population characteristics such as age, gender, ethnicity, income levels, and geographic location. These factors have a direct impact on consumer preferences, needs, and purchasing power. Understanding demographic shifts allows businesses to tailor their offerings and marketing strategies to effectively target specific segments of the population.
2. Economic Factors
Economic factors encompass elements like inflation, unemployment rates, economic growth, and consumer spending patterns. Fluctuations in these factors impact consumer purchasing power, which in turn affects demand for products and services. By monitoring economic indicators, businesses can adjust their pricing strategies, product offerings, and marketing efforts to align with prevailing economic conditions.
3. Socio-cultural Factors
Socio-cultural factors encompass societal norms, values, beliefs, and cultural trends. These factors shape consumer preferences, attitudes, and behaviors. Adapting marketing messages and products to align with sociocultural shifts allows businesses to resonate with their target audience and build stronger connections.
4. Technological Factors
Technological factors pertain to advancements in technology and their impact on industries. Innovations such as automation, artificial intelligence, and digital platforms can disrupt traditional business models and open up new opportunities. Embracing technological advancements enables businesses to enhance operational efficiency, engage with customers through digital channels, and stay ahead of the curve.
5. Political and Legal Factors
Political and legal factors include governmental regulations, policies, and political stability. Changes in regulations can influence industries through shifts in trade policies, taxation, and industry-specific regulations. Businesses need to navigate these factors to ensure compliance and adapt their strategies accordingly.
6. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors encompass ecological considerations, sustainability, and the impact of businesses on the environment. Increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues has led to a demand for eco-friendly products and practices. Companies that incorporate sustainability into their operations can appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and contribute positively to society.
Understanding these key factors within the macroenvironment allows businesses to anticipate changes, make informed strategic decisions, and navigate the complexities of the external landscape. By closely analyzing and adapting to the influences of demographic, economic, socio-cultural, technological, political and legal, and environmental factors, companies can position themselves for long-term success and resilience in the face of evolving industry trends and challenges.
In the subsequent sections, we will explore each of these macroenvironmental factors in greater detail, shedding light on their significance and strategies to effectively navigate their influence and thrive in a dynamic business environment.
Importance of Understanding the Marketing Environment
Understanding the marketing environment is crucial for businesses of all sizes and industries. It provides essential insights that enable organizations to make informed decisions, tailor their marketing strategies, and adapt to changing conditions.
Impact of Environmental Factors on Marketing Strategies
Understanding the marketing environment is paramount for businesses as it enables them to navigate the complexities of external influences and tailor their marketing strategies accordingly. Environmental factors have a profound impact on how businesses engage with their target audience, develop products, and communicate their brand messages. Here’s a closer look at the impact of environmental factors on marketing strategies:
- Target Audience Alignment: Environmental factors, including demographic, socio-cultural, and technological shifts, shape the preferences and behaviors of the target audience. By staying attuned to these factors, businesses can craft marketing messages and campaigns that resonate with their audience’s values and needs.
- Product Development: Environmental changes often drive shifts in consumer demands and expectations. Businesses that monitor these changes can adapt their product offerings to meet evolving consumer needs and preferences, ensuring that their products remain relevant and desirable.
- Communication Channels: Technological advancements and changes in media consumption habits influence the most effective communication channels for reaching target audiences. By understanding these shifts, businesses can allocate their marketing resources to channels that provide the greatest impact.
Adaptation to Changing Market Conditions
The marketing landscape is dynamic, with environmental factors constantly evolving. Businesses that understand and anticipate these changes can proactively adjust their strategies to remain competitive. Here’s how adaptation to changing market conditions plays a vital role:
- Agility and Flexibility: Environmental changes can lead to sudden shifts in consumer behavior or industry dynamics. Businesses that can swiftly adapt their strategies are better equipped to seize emerging opportunities and mitigate potential threats.
- Innovation: A thorough understanding of the marketing environment allows businesses to identify gaps in the market and innovative solutions. By staying ahead of trends, businesses can develop new products or services that cater to emerging customer needs.
- Competitive Edge: Adapting to changing conditions enables businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors. Brands that stay responsive to market shifts often gain a competitive edge by offering unique value propositions.
Mitigating Risks and Seizing Opportunities
The marketing environment is characterized by both opportunities and risks. Businesses that comprehend external influences can navigate potential pitfalls and capitalize on favorable circumstances. Here’s how understanding the marketing environment helps in mitigating risks and seizing opportunities:
- Risk Assessment: By analyzing the macro and microenvironments, businesses can identify potential risks and challenges that may arise. This proactive approach allows them to develop contingency plans and strategies to manage risks effectively.
- Strategic Planning: Understanding the marketing environment aids businesses in developing well-informed and comprehensive strategic plans. This includes considering how various factors may impact their operations and adjusting strategies accordingly.
- Exploiting Trends: Businesses that can spot emerging trends early can position themselves to take advantage of new market opportunities. Whether it’s capitalizing on technological innovation or aligning with a cultural shift, understanding the environment helps businesses act swiftly.
Understanding the marketing environment is not only crucial but also integral to a business’s success. It provides insights that guide decision-making, helps businesses adapt to changing conditions, and enables them to proactively address risks and opportunities. By recognizing the impact of environmental factors on marketing strategies, adapting to changing market conditions, and leveraging opportunities, businesses can build strong, customer-centric brands that thrive in a dynamic and competitive marketplace.
Navigating the Marketing Environment

Navigating the marketing environment is a critical aspect of strategic marketing management. It involves understanding and responding to various external and internal factors that can impact a business’s marketing efforts and overall success. To effectively navigate the marketing environment, businesses must adopt a proactive and adaptive approach.
Market Research as a Tool for Understanding the Environment
Market research plays a pivotal role in helping businesses gain insights into the marketing environment. It involves the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data related to consumers, competitors, and other environmental factors. Here’s how market research serves as a valuable tool for understanding the environment:
- Consumer Insights: Market research helps businesses understand consumer behavior, preferences, and needs. By gathering data on consumer demographics, buying habits, and attitudes, companies can tailor their marketing strategies to effectively target and engage their audience.
- Competitive Analysis: Examining the strategies, strengths, and weaknesses of competitors provides businesses with a competitive edge. Market research allows companies to identify gaps in the market, differentiate themselves, and capitalize on opportunities that competitors might have missed.
- Trend Identification: Market research helps identify emerging trends and shifts in the market. This information guides businesses in making informed decisions about product development, communication channels, and branding strategies.
Monitoring and Analysis of Environmental Trends
Staying informed about environmental trends is crucial for businesses to remain competitive and responsive to changing conditions. Continuous monitoring and analysis of these trends allow businesses to stay ahead of the curve:
- Technological Advances: Rapid technological changes impact consumer behavior and expectations. By tracking technological trends, businesses can adopt new tools and platforms to enhance their marketing efforts and reach their target audience effectively.
- Cultural Shifts: Societal changes and cultural shifts influence consumer values and preferences. Monitoring these shifts helps businesses create marketing messages that resonate with cultural sentiments and reflect changing norms.
- Economic Indicators: Economic factors such as inflation, employment rates, and consumer spending directly impact purchasing behavior. Monitoring economic trends enables businesses to adjust pricing strategies and adapt to changing consumer budgets.
Flexibility and Agility in Adjusting Strategies
In a dynamic marketing environment, businesses must be adaptable and agile in their strategies. Flexibility allows businesses to respond promptly to unforeseen changes and capitalize on emerging opportunities:
- Scenario Planning: Businesses can create multiple scenarios to anticipate various outcomes based on environmental changes. This enables them to be prepared with strategies that align with different possibilities.
- Real-time Adjustments: Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of marketing strategies and making real-time adjustments based on performance data is essential. This approach allows businesses to optimize campaigns and pivot when necessary.
- Experimentation: Embracing experimentation enables businesses to test new approaches and tactics. By trying out innovative strategies, businesses can uncover new avenues for growth and engagement.
Navigating the marketing environment requires a combination of market research, trend monitoring, and strategic agility. Market research provides critical insights into consumer behavior and competitor strategies, while trend monitoring ensures businesses are prepared to adapt to changing conditions. Finally, strategic flexibility and agility empower businesses to adjust strategies in response to real-time data and emerging opportunities. By leveraging these practices, businesses can effectively navigate the marketing landscape, stay relevant, and achieve their marketing objectives.
Case Studies
A. Examples of Companies Impacted by Changes in Their Marketing Environment
Several companies have experienced significant impacts due to changes in their marketing environment. These examples highlight the importance of understanding and adapting to the dynamic business landscape:
- Kodak: Kodak, once a leader in the photography industry, struggled to adapt to the digital revolution. The shift from film to digital photography disrupted its business model, leading to a decline in market share and financial struggles.
- Blockbuster: Blockbuster, a prominent video rental chain, faced challenges from streaming services like Netflix. Blockbuster’s failure to embrace digital distribution and adapt to changing consumer preferences ultimately led to its bankruptcy.
- Nokia: Nokia was a dominant player in the mobile phone industry but failed to anticipate the rise of smartphones. The company’s slow response to changing technological trends resulted in a loss of market share to competitors like Apple and Samsung.
B. Success Stories of Businesses That Effectively Adapted to Environmental Shifts
Several businesses have successfully navigated changes in their marketing environment by embracing innovation and adapting their strategies:
- Netflix: Netflix started as a DVD rental service but recognized the shift to digital streaming early on. The company invested in original content and developed a user-friendly platform, positioning itself as a leader in online streaming entertainment.
- Amazon: Amazon initially focused on selling books online but expanded its offerings to include a wide range of products. The company’s commitment to customer-centricity, efficient logistics, and innovative technology propelled it to become a global e-commerce giant.
- Apple: Apple transformed itself from a computer company into a leader in consumer electronics. The introduction of innovative products like the iPod, iPhone, and iPad allowed Apple to diversify its product portfolio and capture new market segments.
In these success stories, companies recognized the importance of staying ahead of environmental shifts, embracing new technologies, and understanding evolving consumer preferences. Their ability to adapt and innovate allowed them to not only survive but thrive in dynamic marketing environments.
Case studies of both struggling companies and successful businesses serve as valuable lessons in the importance of understanding and responding to the marketing environment. Adapting to changes, embracing innovation, and staying customer-focused are key factors in determining a company’s success or failure in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.
Strategies for Responding to Environmental Changes
A. Reactive vs. Proactive Approaches
Companies facing environmental changes can adopt either reactive or proactive strategies:
- Reactive Approach: This involves responding to changes after they occur. While it may help address immediate challenges, it can lead to a lack of preparedness and missed opportunities.
- Proactive Approach: This involves anticipating changes and planning ahead. Proactive companies are better positioned to seize opportunities and mitigate risks.
B. Innovation and Differentiation to Stay Competitive
- Innovation: Embrace innovation by developing new products, services, or technologies. This can help capture new market segments and maintain relevance in a changing environment.
- Differentiation: Differentiate your brand by offering unique value to customers. Highlight what sets your business apart from competitors, whether it’s through quality, features, or customer experience.
C. Collaborations and Partnerships for Addressing Challenges
- Collaborations: Collaborate with other businesses, organizations, or experts to tackle challenges. Partnerships can lead to shared knowledge, resources, and innovative solutions.
- Strategic Alliances: Form strategic alliances with complementary businesses to create mutual benefits, expand reach, and access new markets.
To navigate changes in the marketing environment successfully, businesses must choose between reactive and proactive strategies. Embracing innovation, differentiation, collaborations, and strategic partnerships can help companies address challenges, remain competitive, and thrive in dynamic markets.
Ethical and Sustainability Considerations
Balancing Environmental Factors with Ethical and Sustainable Practices
As businesses navigate the marketing environment, it’s crucial to balance environmental factors with ethical and sustainable practices:
- Environmental Impact: Consider the environmental impact of your marketing strategies. Minimize waste, energy consumption, and pollution to contribute to a more sustainable future.
- Social Responsibility: Acknowledge your responsibility towards society. Ensure that your marketing efforts do not exploit vulnerable populations or harm the environment.
Importance of Aligning with Societal Values and Expectations
- Public Perception: Aligning with societal values and expectations enhances your brand’s reputation. Consumers are more likely to support businesses that prioritize ethics and sustainability.
- Long-Term Viability: Sustainable practices ensure the long-term viability of your business. Adapting to societal changes ensures continued relevance and customer trust.
Incorporating ethical and sustainable practices into your marketing strategies demonstrates your commitment to both the environment and society. Balancing environmental factors with ethical considerations not only benefits your business but also contributes to a better world for all.
Future Trends in the Marketing Environment
The marketing environment is continually evolving due to technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and economic shifts. To stay competitive, businesses must anticipate and adapt to future trends in the marketing environment.
Anticipated Shifts in the Marketing Landscape
- Personalization: The marketing landscape is expected to continue emphasizing personalized experiences. Advanced data analytics and AI-driven insights will enable brands to tailor their messages and offerings to individual preferences.
- Sustainability and Ethics: Consumers’ increasing awareness of environmental and ethical concerns will drive brands to integrate sustainability and ethical practices into their marketing strategies.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: Virtual and augmented reality technologies will reshape customer engagement, offering immersive experiences for product exploration and interaction.
- Influencer Marketing Evolution: Influencer marketing will evolve, with a focus on authenticity and long-term partnerships rather than short-term endorsements.
The Role of Technology and Digitalization
- Digital Transformation: Technology will continue to drive digital transformation, leading to enhanced customer experiences, streamlined processes, and improved targeting.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI will play a central role in marketing, from predictive analytics to chatbots that offer real-time customer support.
- Data Privacy: The importance of data privacy will rise, with brands needing to navigate stricter regulations while maintaining effective data-driven strategies.
- E-commerce Growth: E-commerce will flourish, with mobile shopping and social commerce becoming integral to customer buying journeys.
The marketing environment is rapidly evolving, driven by changing consumer behaviors and technological advancements. Brands that anticipate these trends and adapt their strategies accordingly will be well-positioned to thrive in the future marketing landscape.
Conclusion
Understanding the marketing environment is a critical factor for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s dynamic marketplace. Analyzing both internal and external factors that impact customers and the industry is essential for developing effective marketing strategies. This comprehensive understanding enables brands to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and make informed decisions that align with market trends and customer behaviors.


