What Are Distribution Channels In Marketing
What lies at the heart of successfully delivering products to customers, expanding market reach, and ensuring seamless accessibility? The answer lies in understanding the intricate web of “distribution channels” in marketing. In this article, we will embark on a journey to unravel the significance and mechanics of distribution channels and explore how they play a pivotal role in connecting producers and consumers in the ever-evolving landscape of business. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or a curious newcomer to the world of marketing, join us as we demystify the world of distribution channels and uncover the key strategies that drive business success.
Purpose of the Article
In this section, we will focus on the key objectives of this article, which are:
Clarifying the Role of Distribution Channels in Marketing Strategies:
- Defining the concept of distribution channels and their significance in marketing strategies.
- Highlighting the benefits of using distribution channels for businesses.
- Discussing how distribution channels contribute to market reach and product availability.
Exploring Different Types of Distribution Channels:
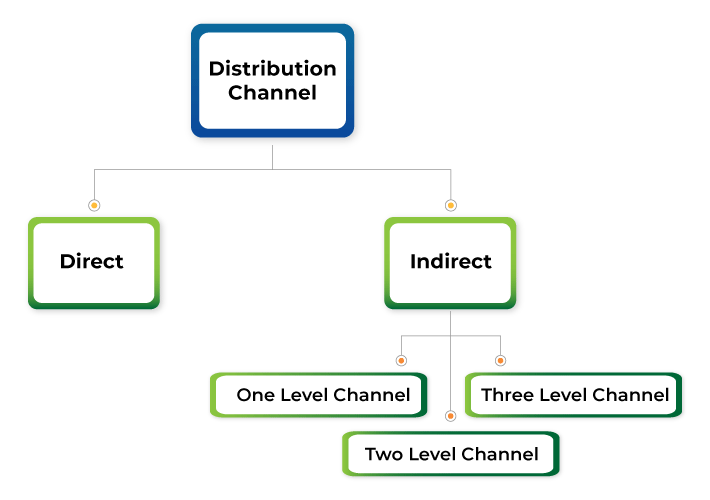
- Distinguishing between direct, indirect, and hybrid distribution channels.
- Understanding the characteristics and applications of each type of distribution channel.
- Providing real-world examples of businesses using different types of distribution channels.
Analyzing the Impact of Effective Distribution Channels on Business Success:
- Examining case studies of companies that have successfully leveraged distribution channels to their advantage.
- Discussing how the choice of distribution channels can impact sales, market penetration, and customer satisfaction.
- Identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of distribution channels in achieving business goals.
By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of distribution channels and their pivotal role in shaping marketing strategies. They will gain insights into selecting the right distribution channels, optimizing partner relationships, and maximizing the impact of distribution channels on business success.
Understanding Distribution Channels
Distribution channels play a pivotal role in the world of marketing, serving as a crucial bridge between businesses and their customers. In this section, we will delve into the fundamental concepts of distribution channels, exploring their definition, significance, and overall distribution process.
What are Distribution Channels in Marketing?
Distribution channels, also known as marketing channels or trade channels, refer to the pathways through which products or services travel from the producer to the end consumer. It is the route taken by a product as it moves through various stages of distribution until it reaches the hands of the final buyer. These channels can be direct, where products are sold directly from the producer to the consumer, or indirect, involving intermediaries such as wholesalers, retailers, and distributors.
Importance of Distribution Channels for Businesses
Distribution channels are of paramount importance for businesses across industries, as they serve several critical functions that facilitate the efficient movement of goods and services. Here are some key reasons why distribution channels matter:
- Market Reach: Distribution channels enable businesses to access a broader customer base by extending their presence into multiple geographic locations. Through strategic partnerships with intermediaries, businesses can tap into markets they may not have been able to reach on their own.
- Product Availability: Distribution channels ensure that products are readily available to consumers when and where they need them. This accessibility improves customer satisfaction and brand reputation, as customers are more likely to choose products that are easily accessible.
- Cost Efficiency: By leveraging existing distribution networks, businesses can achieve economies of scale, reducing transportation and storage costs. This efficiency translates into competitive pricing, making products more attractive to price-conscious consumers.
- Focus on Core Competencies: By outsourcing certain distribution functions to intermediaries, businesses can concentrate on their core competencies, such as product innovation and marketing. This specialization leads to improved overall efficiency and effectiveness.
- Risk Mitigation: Diversifying distribution channels helps mitigate risks associated with relying heavily on a single channel. Market fluctuations, disruptions, or changing consumer preferences may impact one channel, but having multiple channels spreads the risk and safeguards the business.
Overview of the Distribution Process
The distribution process encompasses a series of steps that facilitate the movement of products from production to consumption. While the specifics may vary based on the industry and product type, the general distribution process involves the following stages:
- Product Creation: The journey begins with product creation, where manufacturers or producers design, develop, and produce goods or services.
- Transportation and Warehousing: Once the products are ready, they are transported to distribution centers or warehouses, where they are stored until they are ready for shipment to retailers or end consumers.
- Distribution to Intermediaries: In an indirect distribution model, products are distributed to intermediaries like wholesalers or retailers who purchase goods in bulk and resell them to retailers or end consumers.
- Retailing: In the final stage, products reach retailers or end consumers, where they are made available for purchase.
In conclusion, understanding distribution channels is vital for businesses aiming to optimize their supply chain, expand market reach, and enhance customer satisfaction. The efficient management of distribution channels contributes significantly to a business’s overall success and competitive advantage in the marketplace.
The Fundamentals of Distribution Channels
The fundamentals of distribution channels refer to the various pathways through which products or services move from producers to end-users or consumers. Distribution channels play a critical role in ensuring that products are available, accessible, and delivered efficiently to the target market. Understanding these fundamentals helps businesses optimize their distribution strategies and reach customers effectively.
Types of Distribution Channels
Distribution channels are essential for businesses to reach their target customers efficiently. There are three main types of distribution channels: direct, indirect, and hybrid. Each type comes with its unique characteristics and considerations.
1. Direct Distribution Channels
Direct distribution channels involve the company selling its products or services directly to the end customers without the involvement of intermediaries. This approach offers both advantages and challenges.
Pros of Selling Directly to Customers:
- Control Over Customer Experience: Companies have complete control over how their products are presented and delivered to customers, ensuring a consistent and positive customer experience.
- Higher Profit Margins: Eliminating intermediaries means the company retains the entire profit margin from each sale, leading to potentially higher profitability.
- Direct Customer Feedback: Companies can gather direct feedback from customers, helping them understand their needs and preferences better.
Cons of Selling Directly to Customers:
- Higher Operational Costs: Establishing and maintaining a direct distribution channel can be costly, as it requires building and managing an in-house sales force or e-commerce operation.
- Limited Market Reach: Companies might face challenges in reaching a broader customer base without the support of intermediaries who have established distribution networks.
- Resource and Expertise Requirements: Companies need to invest in hiring and training a competent sales team or developing and managing an efficient e-commerce platform.
Examples of Businesses Utilizing Direct Distribution:
- Boutique Retailers: Small boutique stores that produce and sell their own products directly to customers without third-party involvement.
- Craftsmen and Artisans: Individual craftsmen and artisans who market and sell their handmade products directly to consumers through their own websites or physical stores.
2. Indirect Distribution Channels
Indirect distribution channels involve the use of intermediaries to distribute products from the producer to the end customers. These intermediaries can be wholesalers, retailers, or other entities that connect the producer to the final consumers.
Understanding Intermediaries: Wholesalers and Retailers
- Wholesalers: Wholesalers purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers and sell them to retailers or other businesses. They play a critical role in bridging the gap between producers and retailers by offering storage, logistics, and bulk purchasing benefits.
- Retailers: Retailers buy products from wholesalers or directly from manufacturers and sell them to consumers through brick-and-mortar stores, online platforms, or both.
Selecting the Right Intermediaries for Your Product
- Market Analysis: Understanding the target market and its preferences is crucial in selecting the right intermediaries who can effectively reach the intended customer base.
- Product Characteristics: The complexity, size, and perishability of the product can influence the choice of intermediaries. For instance, highly technical products may require specialized retailers with product expertise.
- Geographical Reach: If the target market is widespread, choosing intermediaries with an extensive distribution network becomes essential.
- Competitive Landscape: Analyzing the competition and existing distribution channels in the industry can help identify opportunities and gaps in the market.
Understanding the types of distribution channels is essential for businesses to make informed decisions about their distribution strategy. Each type of channel comes with its benefits and challenges, and choosing the right distribution approach can significantly impact a company’s success in the marketplace.
Factors Influencing Distribution Channel Choice
Selecting the right distribution channel is a critical decision for businesses, as it directly impacts how products or services reach the target customers. Several factors influence the choice of distribution channels, and understanding these factors is essential for devising an effective distribution strategy.
1. Target Market Analysis
Understanding the target market is fundamental to making informed decisions about distribution channels. The characteristics and preferences of the target customers play a significant role in shaping the distribution approach.
Key Considerations:
- Demographics: Analyzing the age, gender, income level, and other demographic factors of the target audience helps in identifying the most suitable distribution channels.
- Behavioral Patterns: Understanding how the target customers shop and make purchasing decisions helps in aligning the distribution strategy with their preferences.
- Market Segmentation: Identifying specific segments within the target market and tailoring distribution channels for each segment can enhance market penetration.
Example: If the target market consists of tech-savvy individuals who prefer online shopping, utilizing e-commerce platforms may be an effective distribution channel choice.
2. Product Characteristics and Complexity
The nature of the product or service being offered also plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate distribution channels. Certain products may require specialized handling or expertise, influencing the choice of intermediaries.
Key Considerations:
- Technical Complexity: High-tech products may require knowledgeable intermediaries capable of providing technical support to customers.
- Perishability: Perishable goods may necessitate a distribution channel with efficient and time-sensitive logistics to maintain product freshness.
- Fragility or Sensitivity: Delicate products may require careful handling and specialized packaging during distribution.
Example: A company selling complex industrial machinery might opt for distribution through authorized dealers who can provide installation and maintenance services.
3. Geographical Reach and Customer Accessibility
The geographical location of the target market and the accessibility of customers are crucial factors in distribution channel decisions. The distribution approach should ensure efficient product availability to customers in different regions.
Key Considerations:
- Regional Demand: Assessing the demand for the product in various regions helps in designing a distribution network that optimizes availability.
- Logistics and Infrastructure: Consideration of transportation and distribution infrastructure is essential for delivering products to remote or difficult-to-access areas.
- Local Regulations and Laws: Complying with local laws and regulations may influence the choice of intermediaries or the direct approach.
Example: Companies with a global customer base may utilize a combination of direct and indirect channels, with direct sales in key markets and distributors in remote regions.
4. Competitive Landscape and Industry Norms
Analyzing the competitive landscape and industry practices helps in identifying opportunities and differentiating the distribution strategy from competitors.
Key Considerations:
- Competitors’ Channels: Studying how competitors distribute similar products can offer insights into effective distribution methods and potential gaps in the market.
- Industry Standards: Understanding common distribution practices within the industry can guide the selection of intermediaries and distribution models.
- Value-Added Services: Offering unique value-added services through distribution partners can set a company apart from its competitors.
Example: In a highly competitive consumer electronics industry, offering value-added services like product customization through retailers can attract more customers.
Multiple factors influence the choice of distribution channels, and businesses must carefully analyze their target market, product characteristics, geographical reach, and competitive environment to make informed decisions. The right distribution strategy can enhance market reach, customer satisfaction, and overall business success.
Evaluating the Efficiency of Distribution Channels
Once a distribution channel strategy is implemented, it is crucial for businesses to regularly evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of their distribution channels. This evaluation enables them to identify strengths and weaknesses, make informed decisions, and optimize the distribution process for better results.
1. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Distribution Channels
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable metrics that provide insights into the performance of distribution channels. By tracking these indicators, businesses can assess the success of their distribution strategy and identify areas that require improvement.
Common KPIs for Distribution Channels:
- Sales Volume: The total quantity of products or services sold through each distribution channel.
- Revenue and Profitability: The amount of revenue generated and the profitability of each distribution channel.
- Market Penetration: The percentage of the target market reached through each channel.
- Customer Reach: The number of unique customers reached through each channel.
- Inventory Turnover: The rate at which inventory is sold and replaced within each channel.
- Order Fulfillment Time: The time taken to fulfill orders and deliver products to customers through each channel.
- Customer Satisfaction: Feedback and ratings from customers regarding their satisfaction with the purchasing experience from each channel.
- Return and Refund Rate: The percentage of products returned and refunds issued for each distribution channel.
2. Measuring Sales and Distribution Channel Performance
Accurate measurement of sales and distribution channel performance is essential for identifying successful channels and understanding customer preferences.
Steps to Measure Performance:
- Data Collection: Gather data on sales, revenue, customer feedback, and other relevant metrics for each distribution channel.
- Data Analysis: Analyze the collected data to identify trends, patterns, and areas of strength or weakness for each channel.
- Comparison: Compare the performance of different channels against each other and against predefined goals and benchmarks.
- Identify Successful Channels: Determine which channels are driving the most sales and revenue, and identify the factors contributing to their success.
- Underperforming Channels: Identify underperforming channels and investigate the reasons behind their lack of success.
- Customer Feedback: Gather feedback from customers to understand their preferences and satisfaction levels with different channels.
3. Identifying Areas for Improvement
Continuous improvement is key to optimizing distribution channels and enhancing overall business performance. Identifying areas for improvement enables businesses to take corrective actions and maximize the potential of their distribution strategy.
Areas for Improvement:
- Underperforming Channels: Address the issues with underperforming channels, such as inadequate marketing or poor customer support.
- Market Reach: Explore opportunities to expand the market reach of successful channels and enter new geographic regions or customer segments.
- Channel Mix: Assess the effectiveness of the channel mix (direct, indirect, hybrid) and consider adjustments based on market trends and customer preferences.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Optimize the supply chain to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery of products to customers.
- Channel Partner Collaboration: Strengthen collaboration with channel partners and provide necessary training and support to improve their performance.
- Customer Experience: Focus on enhancing the customer experience in all channels to improve customer retention and loyalty.
Evaluating the efficiency of distribution channels is a continuous process that involves monitoring KPIs, analyzing data, and making data-driven decisions to optimize distribution strategies. Regular assessments and improvements can lead to increased sales, customer satisfaction, and overall business success.
Developing an Effective Distribution Strategy

Developing an effective distribution strategy is essential for businesses to ensure that their products or services reach the target market efficiently and profitably. A well-designed distribution strategy helps maximize market coverage, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Here are the key steps to developing an effective distribution strategy:
1. Creating a Channel Strategy
A channel strategy, also known as a distribution channel strategy, is a crucial element of the overall marketing plan. It outlines how a company will reach its target customers and get its products or services to market efficiently. Creating a well-defined channel strategy is essential for optimizing distribution channels and achieving business objectives.
Setting Distribution Objectives
Distribution objectives are specific goals that a company aims to achieve through its distribution channels. These objectives should align with the overall business goals and contribute to the company’s success.
Common Distribution Objectives:
- **Market Penetration:**Expand the market reach by targeting new customer segments or geographic regions.
- Sales Growth: Increase sales volume and revenue through effective distribution.
- Market Expansion: Enter new markets or product categories through distribution channels.
- Customer Convenience: Enhance the customer buying experience by offering multiple distribution options.
- Brand Awareness: Improve brand visibility and recognition through strategic distribution.
- Cost Efficiency: Optimize the distribution process to reduce operational costs and improve profitability.
- Customer Service: Provide excellent customer service and support through distribution partners.
Channel Structure and Design
The channel structure refers to the organization and arrangement of distribution channels to achieve the distribution objectives effectively. The channel design involves making decisions about the type and number of intermediaries involved in the distribution process.
Considerations for Channel Structure and Design:
- Target Market: Understand the characteristics and preferences of the target market to choose the most suitable distribution channels.
- Product Characteristics: Consider the nature of the product or service being offered and its complexity, perishability, and size, as these factors can influence the choice of channels.
- Geographic Reach: Determine the geographic areas where the product will be distributed and select channels that can efficiently cover those regions.
- Channel Partners: Identify potential channel partners that align with the company’s values and can effectively reach the target market.
- Competition: Analyze the distribution strategies of competitors to identify gaps or opportunities in the market.
- Channel Flexibility: Design a channel structure that can adapt to changing market conditions and business needs.
- Channel Control: Assess the level of control the company wants to have over distribution activities and select channels accordingly.
Developing a Channel Mix
A channel mix, also known as a distribution mix, involves choosing the most appropriate combination of direct and indirect channels to reach the target market. The right channel mix can help maximize market coverage and sales opportunities.
Factors to Consider in Developing a Channel Mix:
- Product Complexity: Complex products may require direct channels with more control over the sales process.
- Customer Preferences: Understand how customers prefer to purchase products and select channels that align with those preferences.
- Geographic Reach: Choose channels that can efficiently cover the target market’s geographic areas.
- Market Presence: Consider the existing distribution channels in the market and how they can complement the company’s channel strategy.
- Resource Availability: Assess the company’s resources and capabilities to support different types of channels effectively.
- Channel Partner Relationships: Build strong relationships with channel partners to ensure a smooth distribution process.
Developing a channel strategy is a critical step in creating an effective distribution strategy. Setting clear distribution objectives, designing an appropriate channel structure, and developing the right channel mix is essential to reaching target customers, maximizing sales opportunities, and achieving business success. A well-designed channel strategy can also adapt to changing market conditions and provide a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
2. Managing Distribution Relationships
Managing distribution relationships is a crucial aspect of a successful distribution strategy. Effective collaboration with channel partners, ensuring their loyalty and commitment, and resolving conflicts that may arise in distribution channels are essential for achieving business objectives and maximizing sales opportunities.
Collaborating with Channel Partners
Channel partners, such as distributors, wholesalers, retailers, VARs, and MSPs, play a significant role in the distribution process. Collaborating effectively with these partners can lead to increased market reach, improved customer service, and higher sales.
Key Considerations for Collaborating with Channel Partners:
- Communication: Maintain open and regular communication with channel partners to stay informed about market trends, customer feedback, and potential opportunities.
- Shared Goals: Align the goals and objectives of the company with those of channel partners to ensure a mutual focus on success.
- Training and Support: Provide adequate training and support to channel partners to enhance their product knowledge and selling capabilities.
- Marketing Support: Offer marketing materials, co-branded collateral, and promotional incentives to help channel partners effectively market products.
- Incentive Programs: Implement incentive programs, such as commissions or performance-based rewards, to motivate channel partners to achieve sales targets.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Create mechanisms for gathering feedback from channel partners and use it to improve the distribution process.
- Regular Performance Review: Regularly review the performance of channel partners and provide constructive feedback for continuous improvement.
Ensuring Channel Partner Loyalty and Commitment
Loyalty and commitment from channel partners are essential for a strong and sustainable distribution network. Building strong relationships with channel partners and offering value-added benefits can enhance their loyalty and commitment.
Strategies to Ensure Channel Partner Loyalty and Commitment:
- Transparency and Fairness: Be transparent in business dealings and maintain fairness in all aspects of the partnership.
- Exclusive Deals: Offer exclusive deals, discounts, or special promotions to channel partners to incentivize them to stay committed.
- Recognition: Acknowledge the efforts and achievements of channel partners to boost their motivation and loyalty.
- Training and Development: Invest in the training and development of channel partners to build their skills and expertise.
- Co-marketing Opportunities: Provide opportunities for joint marketing initiatives to strengthen the partnership and create a sense of collaboration.
- Timely Payments: Ensure timely and accurate payments to channel partners for their efforts and contributions.
- Problem Resolution: Address any issues or concerns raised by channel partners promptly and find mutually beneficial solutions.
Conflict Resolution in Distribution Channels
Conflicts can arise in distribution channels due to various reasons, such as competition, conflicting interests, or resource constraints. Effective conflict resolution is crucial to maintain a harmonious and productive distribution network.
Steps for Conflict Resolution in Distribution Channels:
- Identify the Source: Identify the root cause of the conflict and the parties involved to understand the nature of the disagreement.
- Open Communication: Encourage open and honest communication between the parties to express their concerns and viewpoints.
- Mediation: If necessary, involve a neutral third party as a mediator to facilitate communication and find a resolution.
- Negotiation: Encourage the parties to negotiate and find common ground to resolve the conflict mutually.
- Contractual Clauses: Refer to the contractual agreements and terms between the company and channel partners to address the conflict.
- Collaborative Problem-Solving: Promote a collaborative approach to problem-solving, focusing on finding win-win solutions.
- Reevaluation and Adaptation: Periodically reevaluate the distribution strategy and make necessary adaptations to prevent conflicts in the future.
Managing distribution relationships is critical for a successful distribution strategy. Collaborating effectively with channel partners, ensuring their loyalty and commitment, and resolving conflicts in a constructive manner can lead to a strong and efficient distribution network. By maintaining positive and productive relationships with channel partners, companies can enhance their market reach, optimize sales opportunities, and achieve their distribution objectives.
3. Leveraging Technology in Distribution
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern distribution strategies, enabling businesses to reach a wider audience, streamline operations, and make informed decisions. Leveraging technology in distribution involves using tools such as e-commerce platforms, online marketplaces, data analytics, and omnichannel integration to enhance efficiency and improve customer experience.
The Role of E-commerce and Online Marketplaces
E-commerce platforms and online marketplaces have revolutionized the way products and services are distributed to customers. These digital channels provide a convenient and accessible way for businesses to reach a global audience and facilitate direct sales to consumers.
Benefits of E-commerce and Online Marketplaces in Distribution:
- Wider Market Reach: E-commerce platforms and online marketplaces allow businesses to reach customers beyond their local markets, expanding their customer base.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike physical stores with fixed operating hours, online channels remain accessible to customers 24/7, enabling purchases at any time.
- Reduced Costs: Online selling can often be more cost effective than traditional retail, as it eliminates the need for physical store locations and associated expenses.
- Personalization: E-commerce platforms can utilize customer data to offer personalized product recommendations and promotions, enhancing the shopping experience.
- Efficient Order Fulfillment: Automated order processing and fulfillment systems streamline operations, leading to faster delivery times.
- Customer Insights: E-commerce platforms generate valuable data on customer behavior, preferences, and buying patterns, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions.
Integrating Offline and Online Channels for Omnichannel Success
Omnichannel distribution involves seamlessly integrating offline and online channels to provide a consistent and unified customer experience. By offering customers the flexibility to interact with the brand across various touchpoints, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Strategies for Omnichannel Success in Distribution:
- Single View of Inventory: Implement systems that provide real-time visibility of inventory across all channels to prevent stockouts and optimize inventory levels.
- Unified Customer Data: Integrate customer data from various touchpoints to gain a comprehensive understanding of customer preferences and behavior.
- Cross-Channel Fulfillment: Enable customers to order online and pick up in-store or return online purchases in physical locations, providing convenience and choice.
- Consistent Branding: Maintain consistent branding and messaging across all channels to reinforce brand identity and create a cohesive customer experience.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure that all online channels are mobile-friendly, as mobile devices are increasingly used for online shopping.
- Customer Support Integration: Integrate customer support across channels to provide seamless assistance and address customer inquiries effectively.
Using Data Analytics for Informed Distribution Decisions
Data analytics plays a vital role in distribution by providing valuable insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency. By leveraging data analytics tools, businesses can make informed decisions and optimize their distribution strategies.
Ways Data Analytics Enhances Distribution:
- Demand Forecasting: Analyze historical sales data to predict future demand and plan inventory levels accordingly, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
- Customer Segmentation: Segment customers based on preferences, demographics, and behavior to tailor marketing efforts and product offerings.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Analyze supply chain data to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, allowing for better resource allocation and cost reduction.
- Pricing Strategies: Use pricing analytics to optimize pricing strategies based on market dynamics and competitor analysis.
- Marketing ROI: Measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns through data analytics to allocate resources to the most impactful initiatives.
Leveraging technology in distribution is essential for modern businesses to stay competitive and meet customer expectations. E-commerce platforms and online marketplaces enable wider market reach and enhanced customer experiences. Integrating offline and online channels through omnichannel strategies ensures a consistent and unified customer journey. Data analytics empowers businesses to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and enhance overall distribution efficiency. By embracing technology in distribution, businesses can adapt to the changing market landscape and achieve long-term success.
Distribution Channel Selection and Management

Distribution channel selection and management are crucial aspects of a business’s overall distribution strategy. Choosing the right distribution channels and effectively managing them is essential for ensuring that products or services reach the target market efficiently and cost-effectively. Here are the key steps to distribution channel selection and management:
1. Selecting the Right Distribution Partners
Selecting the right distribution partners is a crucial step in building a successful distribution channel. It involves identifying potential channel partners, negotiating contractual agreements, and evaluating their performance.
Identifying Potential Channel Partners
When identifying potential channel partners, businesses should consider several factors to ensure a good fit for their distribution strategy. Some key considerations include:
- Alignment with Target Market: Channel partners should have a customer base that aligns with the target market for the product or service. Understanding the partner’s customer demographics and needs is essential.
- Geographic Coverage: Assess the geographic coverage of potential partners to ensure they can effectively reach the target regions or territories.
- Reputation and Trustworthiness: Research the reputation and track record of potential partners to ensure they are reliable and trustworthy.
- Competencies and Resources: Evaluate the partner’s competencies and available resources, such as sales and marketing capabilities, distribution networks, and customer support.
- Compatibility with Brand Image: Ensure that the partner’s values and brand image align with the brand identity of the business.
- Commitment to Collaboration: Look for partners who are willing to collaborate and work closely with the business to achieve mutual success.
- Financial Stability: Verify the financial stability of potential partners to minimize the risk of partnership disruptions.
Negotiation and Contractual Agreements
Once potential channel partners are identified, the next step is to negotiate and establish contractual agreements. Effective negotiation is crucial to building a mutually beneficial partnership. Key aspects of the negotiation process include:
- Defining Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each party in the distribution channel. This includes outlining sales targets, marketing efforts, and support obligations.
- Pricing and Margins: Discuss pricing strategies and profit margins for both the business and the channel partner. Determine how profits will be shared, and ensure the pricing is competitive in the market.
- Exclusive vs. Non-Exclusive Arrangements: Decide whether the partnership will be exclusive (restricted to one channel partner) or non-exclusive (allowing multiple partners).
- Contract Terms and Duration: Establish the terms of the contract, including its duration, renewal options, termination clauses, and any specific performance metrics.
- Intellectual Property and Brand Usage: Address issues related to the use of intellectual property and brand assets in marketing and sales activities.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: Include mechanisms for dispute resolution to handle any potential conflicts that may arise during the partnership.
- Legal Review: Seek legal review and counsel to ensure that the contractual agreements comply with relevant laws and regulations.
Evaluating Channel Partner Performance
Continuous evaluation of channel partner performance is essential to maintain a successful distribution channel. Regular assessments help identify areas of improvement and potential issues. Key aspects of evaluating channel partner performance include:
- Sales Performance: Measure the partner’s sales performance against set targets and track sales growth over time.
- Customer Satisfaction: Collect feedback from customers to assess their satisfaction with the partner’s services and support.
- Market Reach and Penetration: Evaluate the partner’s effectiveness in reaching the target market and expanding market penetration.
- Compliance with Contractual Obligations: Ensure that the partner is adhering to the terms and obligations outlined in the contractual agreement.
- Channel Support and Training: Assess the level of support and training provided to the channel partner to help them succeed.
- Inventory and Order Management: Monitor inventory levels and the partner’s ability to manage orders efficiently.
- Communication and Collaboration: Evaluate the level of communication and collaboration between the business and the partner.
Based on the evaluation, businesses can provide feedback, offer additional support or resources, or make necessary adjustments to the partnership to optimize channel performance.
Selecting the right distribution partners is crucial for the success of a distribution channel. By carefully identifying potential partners, negotiating favorable contractual agreements, and regularly evaluating partner performance, businesses can build strong and effective distribution channels that contribute to overall business growth and success.
2. Channel Expansion and Diversification
After selecting the right distribution partners, businesses may explore channel expansion and diversification to reach a wider customer base and increase market penetration. This involves assessing market expansion opportunities, adding new distribution channels to the mix, and balancing channel diversity and complexity.
Assessing Market Expansion Opportunities
Market expansion opportunities refer to identifying new markets or customer segments that the business can target with its products or services. When considering market expansion, businesses should focus on the following aspects:
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand the needs, preferences, and buying behaviors of potential customers in the new markets.
- Competitive Analysis: Evaluate the competitive landscape in the new markets to determine the level of competition and identify unique selling points that can differentiate the business from competitors.
- Market Entry Strategy: Develop a clear market entry strategy that outlines how the business plans to enter and establish a presence in the new markets.
- Resource Allocation: Assess the resources required for market expansion and ensure the business has the necessary infrastructure, distribution capabilities, and support to cater to new markets.
- Risk Assessment: Analyze the risks associated with market expansion, such as regulatory challenges, cultural differences, and economic uncertainties.
- Partner Identification: If channel partners are involved in the expansion, identify potential partners in the new markets that can effectively distribute the products or services.
Adding New Distribution Channels to the Mix
Adding new distribution channels allows businesses to reach different customer segments and provide alternative ways for customers to access their products or services. Key considerations when adding new distribution channels include:
- Channel Relevance: Ensure that the new distribution channels are relevant to the target markets and customer preferences.
- Channel Fit: Assess whether the business has the necessary capabilities and resources to support the new distribution channels effectively.
- Channel Integration: Plan for seamless integration between existing and new distribution channels to avoid conflicts and ensure a consistent customer experience.
- Channel Partner Selection: If channel partners are involved, carefully select partners with experience in the new distribution channels and a track record of success.
- Training and Support: Provide training and support to channel partners to ensure they are equipped to effectively represent and sell the products or services.
- Pricing and Margins: Determine pricing strategies and profit margins for the new distribution channels, considering factors such as market demand and partner incentives.
Balancing Channel Diversity and Complexity
As businesses expand and diversify their distribution channels, they must strike a balance between channel diversity and complexity. Too much complexity can lead to inefficiencies, higher operational costs, and potential conflicts between channels. Key steps to balance channel diversity and complexity include:
- Channel Strategy Alignment: Ensure that the distribution channel strategy aligns with the overall business objectives and long-term growth plans.
- Clear Communication: Establish clear communication channels and guidelines to facilitate collaboration and coordination between different distribution channels and partners.
- Channel Performance Evaluation: Regularly evaluate the performance of each distribution channel to identify areas for improvement and optimize channel efficiency.
- Adaptability: Remain adaptable to changing market conditions and customer preferences. Continuously assess the effectiveness of each distribution channel and be prepared to make adjustments if needed.
- Customer Experience Focus: Keep the customer experience at the forefront of channel decisions. Ensure that customers receive consistent and satisfactory experiences, regardless of the distribution channel they choose.
- Data and Analytics: Utilize data and analytics to gain insights into channel performance, customer behavior, and market trends. This information can guide strategic decisions and resource allocation.
By carefully assessing market expansion opportunities, adding new distribution channels strategically, and managing channel diversity and complexity effectively, businesses can maximize their reach, optimize distribution efficiency, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Channel expansion and diversification are essential for businesses looking to grow their market presence and adapt to changing customer needs. Through thorough market research, partner selection, and continuous evaluation, businesses can build a robust and adaptable distribution ecosystem that drives business success and fosters strong relationships with customers and channel partners.
3. Distribution Channel Risk Management
Distribution channel risk management involves identifying potential risks and implementing strategies to mitigate them. It aims to safeguard the efficiency and effectiveness of distribution channels, ensuring a smooth flow of products or services from the producer to the customer. Key aspects of distribution channel risk management include mitigating channel dependency risks, addressing channel conflict and cannibalization, and creating contingency plans for channel disruptions.
Mitigating Channel Dependency Risks
Channel dependency refers to the level of reliance a business has on a particular distribution channel or partner. High channel dependency can lead to vulnerabilities if that channel or partner faces challenges or disruptions. To mitigate channel dependency risks, businesses can consider the following steps:
- Diversification: Explore multiple distribution channels to reduce over-reliance on a single channel. This strategy spreads the risk and provides alternative routes to reach customers.
- Multi-Channel Strategy: Adopt a multi-channel approach, utilizing both direct and indirect channels, to cater to different customer segments. This ensures that no single channel has an excessive influence on the business’s revenue.
- Partner Performance Evaluation: Continuously assess the performance of channel partners to identify potential issues early on. Address any underperforming partners and collaborate closely with high-performing ones.
- Develop Partner Relationships: Cultivate strong relationships with channel partners to foster loyalty and commitment. Transparent communication and mutual support can strengthen partnerships.
- Incentives and Support: Offer incentives and support to channel partners to encourage them to promote the business’s products or services effectively.
Addressing Channel Conflict and Cannibalization
Channel conflict arises when different distribution channels or partners compete or clash with each other for the same customers. Cannibalization occurs when a new channel or product offering reduces sales from an existing channel or product. To address channel conflict and cannibalization, businesses can take the following measures:
- Clear Channel Roles: Define distinct roles and responsibilities for each distribution channel to avoid overlapping and conflict.
- Channel Communication: Facilitate communication and collaboration among channels to ensure they work together harmoniously.
- Pricing Strategy: Implement pricing strategies that minimize cannibalization, such as differentiating prices based on channels or products.
- Market Segmentation: Segment the target market to direct different channels toward specific customer segments, minimizing competition for the same customers.
- Performance Incentives: Align incentives for channel partners to collaborate rather than compete. Reward collaboration and joint efforts.
Contingency Planning for Channel Disruptions
Disruptions in distribution channels can occur due to various factors, such as economic changes, natural disasters, or changes in regulations. To create contingency plans for channel disruptions, businesses can consider the following:
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in each distribution channel and assess their potential impact on the business.
- Backup Channels: Have backup distribution channels or partners in place to ensure continuity in case of disruptions.
- Communication Plan: Establish a clear communication plan to keep channel partners informed of any changes, disruptions, or contingency measures.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Build a resilient supply chain that can quickly adapt to disruptions and changes in demand.
- Financial Preparedness: Maintain sufficient financial reserves to weather any unforeseen challenges in the distribution network.
- Scenario Planning: Conduct scenario planning exercises to anticipate potential disruptions and devise strategies to address them proactively.
By actively managing distribution channel risks, businesses can minimize potential disruptions, optimize distribution efficiency, and maintain strong relationships with channel partners. A well-executed risk management strategy enhances the overall stability and sustainability of the distribution network, contributing to the success of the business’s go-to-market strategy.
Case Studies: Successful Distribution Channel Strategies
Case Study 1: Company A – Direct-to-Consumer Dominance
Overview of Company A’s Business Model: Company A is a successful consumer goods manufacturer that has achieved dominance through its direct-to-consumer distribution strategy. Rather than relying on intermediaries, Company A sells its products directly to end customers. This approach allows the company to maintain full control over its brand, customer experience, and pricing.
How Company A Built and Sustained Its Distribution Channels:
- E-commerce Platform: Company A invested in building a robust and user-friendly e-commerce platform. This platform became the primary channel through which customers could browse, purchase, and receive support for their products.
- Digital Marketing and Branding: To attract customers and drive traffic to its e-commerce site, Company A focused on digital marketing and branding efforts. They utilized social media, influencer marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO) to enhance their online presence and reach a wider audience.
- Exceptional Customer Experience: Company A prioritized providing an exceptional customer experience. This included fast and reliable shipping, hassle-free returns, and prompt customer support.
- Product Innovation and Quality: The company consistently introduced innovative products and maintained high product quality. This helped build customer trust and loyalty, leading to repeat purchases.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Company A used data analytics to understand customer preferences, identify trends, and optimize its marketing and distribution strategies accordingly.
Key Takeaways and Lessons Learned:
- Direct-to-consumer distribution can provide greater control over the brand and customer experience.
- Investing in a strong e-commerce platform and digital marketing is essential for success in the direct-to-consumer model.
- Providing exceptional customer experience and high-quality products fosters customer loyalty and drives repeat business.
- Utilizing data analytics helps in making informed decisions and adapting to changing market dynamics.
Case Study 2: Company B – Mastering Indirect Channels
Understanding Company B’s Distribution Approach: Company B is a leading technology manufacturer that has achieved success by mastering indirect distribution channels. Rather than selling directly to end customers, Company B leverages a network of intermediaries to reach a wider market.
Leveraging Intermediaries for Wider Market Reach:
- Channel Partner Relationships: Company B carefully selects and nurtures strong relationships with channel partners, including distributors, value-added resellers (VARs), and managed service providers (MSPs).
- Training and Support: To ensure that channel partners effectively promote and sell their products, Company B provides comprehensive training, marketing materials, and ongoing support.
- Market Segmentation: Company B segments its target market and assigns specific products to different channel partners based on their expertise and customer base. This avoids channel conflict and ensures each partner can focus on their strengths.
- Channel Incentives: To motivate channel partners, Company B offers attractive incentives, such as discounts, rebates, and rewards for achieving sales targets.
- Collaborative Marketing: Company B collaborates with its channel partners on joint marketing initiatives, including co-branded campaigns and events.
Best Practices from Company B’s Success:
- Mastering indirect channels requires building strong relationships with channel partners and providing them with the necessary tools and support.
- Market segmentation helps in assigning products to the right partners and maximizing market coverage.
- Incentives and collaborative marketing efforts encourage channel partners to actively promote and sell the company’s products.
These case studies illustrate how different companies can achieve distribution success by tailoring their strategies to their unique business models and market dynamics. Whether through direct-to-consumer dominance or mastering indirect channels, effective distribution channel strategies can significantly impact a company’s market position and growth.
Conclusion
Distribution channels, the unsung heroes of successful businesses, serve as vital bridges between producers and customers. They ensure products reach the right hands at the right time, driving sales, market reach, and customer satisfaction. In this article, we delved into the significance of distribution channels, explored key takeaways, and glimpsed into the future of these essential pathways. From direct and indirect channels to data-driven decisions and sustainable practices, join us on this journey of unraveling the secrets behind effective distribution strategies for thriving in a dynamic business landscape.

