Importance Of Product In The Development Of Marketing Strategy
Amidst the myriad of factors that influence this strategic concoction, the role of the product itself stands as a linchpin, pivotal in determining the overall efficacy of a marketing campaign. In this article, we delve into the profound significance of the product in the development of a marketing strategy, exploring how its attributes, positioning, and evolution can shape the trajectory of a business’s success. By illuminating the symbiotic relationship between product and strategy, we aim to elucidate why astute product considerations are at the core of every flourishing marketing endeavor.
What is a Marketing Strategy?
A marketing strategy can be likened to a meticulously crafted blueprint that outlines an organization’s approach to achieving its marketing objectives. It encompasses a comprehensive plan that amalgamates various elements, such as market research, target audience identification, and promotional tactics. However, the linchpin of this strategy is undoubtedly the products a company brings forth.
Overview of the Role of Products in Marketing Strategy Development
Products are the embodiment of a company’s value proposition, encapsulating the essence of what it offers to consumers. They are not merely physical entities or digital commodities; rather, products are the conduits through which brands connect with their customers on an emotional, functional, and aspirational level. In the intricate tapestry of marketing strategy development, products are the threads that weave the story of a brand’s identity, differentiating it from the competition.
To delve deeper, products play a multifaceted role:
1. Value Creation and Proposition
Products are the conduits through which value is delivered to customers. An effective marketing strategy hinges on identifying and articulating this value proposition clearly. Whether it’s addressing a pain point, fulfilling a desire, or enhancing convenience, products serve as the primary vehicle to communicate the inherent benefits a brand offers.
2. Target Audience Alignment
Understanding the target audience is indispensable for crafting a successful marketing strategy. Products, tailored to meet the specific needs and preferences of the target demographic, become the catalyst for resonating with customers. When products align seamlessly with the aspirations of the audience, it forges a deeper emotional connection, fostering brand loyalty and advocacy.
3. Competitive Differentiation
In an overcrowded marketplace, differentiation is paramount. Products, when infused with unique features, innovations, or qualities, carve a niche for the brand. A well-differentiated product can act as a competitive advantage, setting the stage for a marketing strategy that revolves around highlighting these distinctive attributes.
4. Channel and Pricing Strategies
Products often dictate the channels through which they are distributed and the pricing strategies employed. Whether a product is positioned as a luxury item, a mid-range staple, or an affordable solution influences the marketing channels chosen and the pricing structures set. Therefore, a harmonious integration of product attributes with distribution and pricing strategies is central to an effective marketing plan.
Understanding “Product”

In the intricate tapestry of marketing, a “product” transcends its mere physical form; it encapsulates the very essence of a brand’s value proposition. Beyond the tangible attributes, a product encompasses the intangible experiences, solutions, and emotions that it evokes in consumers. It’s the embodiment of a brand’s promise, a conduit that connects the brand’s essence with the consumer’s needs and desires.
At its core, a product is the sum of its features, benefits, and unique attributes that cater to the diverse expectations of its target audience. It’s the synthesis of practicality, aesthetics, functionality, and emotional resonance. Whether it’s a physical item, a digital service, or an immersive experience, a product carries the mantle of representing a brand’s identity, values, and the solutions it brings to its customers.
A product in the marketing context is not confined to a single dimension. It’s the culmination of innovation, craftsmanship, and customer-centricity. From the inception of an idea to its design, development, and eventual delivery, every facet contributes to the holistic product experience. A product should not merely meet a need; it should exceed expectations and create a lasting impact that resonates with consumers.
In essence, a product in marketing is the bridge that connects the intangible aspirations of a brand with the tangible desires of consumers. It’s the vessel through which value is exchanged, emotions are triggered, and loyalty is cultivated. This understanding transforms a product from a functional commodity to an integral part of a brand’s narrative, amplifying its ability to shape consumer perceptions, fuel engagement, and foster enduring relationships.
Types of Products: Tangible, Intangible, Services, Experiences
In the vibrant realm of commerce, products span a kaleidoscope of forms, each weaving a unique thread in the tapestry of consumer engagement. As we embark on an exploration of these diverse product categories, we uncover a spectrum that embraces the tactile, the intangible, the experiential, and the transformative.
1. Tangible Products:
Tangible products stand as the pillars of consumer engagement, offering palpable solutions to real-world needs. From smartphones that seamlessly connect us to the digital realm, to clothing that mirrors our personality, tangible products engage our senses and enhance our daily lives. Their physical presence invites touch, ignites sight, and arouses emotions, creating a profound connection between the brand and the consumer. Tangible products become canvas and conduit, expressing a brand’s essence while delivering functionality.
2. Intangible Products:
In the ethereal realm of intangible products, value transcends the confines of the physical. These offerings reside in the digital domain, encapsulating software, e-books, and online courses. They redefine convenience, offering instant access and boundless possibilities. Intangible products are the emissaries of knowledge, entertainment, and tools, traversing geographical boundaries with ease. They empower consumers to explore, learn, and evolve, all through the seamless medium of technology.
3. Services:
Services emerge as the dynamic pulse of modern commerce, where expertise and interaction converge to fulfill distinct needs. From financial consultation to spa experiences, services embody customization and personalization. It’s the therapist’s healing touch, the consultant’s strategic insight, and the instructor’s guidance. Services are an immersive journey, intertwining the tangible and the intangible, leaving an indelible imprint on the consumer’s memory.
4. Experiences:
At the zenith of the product landscape lies the realm of experiences, where transformation takes precedence over transaction. Experiential products are a symphony of moments, emotions, and interactions. From culinary adventures to music festivals, these offerings forge memories and create lasting connections. They redefine the consumer from a passive observer to an active participant, inviting engagement, emotional resonance, and shared narratives.
In the digital age, the boundaries between these categories blur, birthing hybrids that defy traditional definitions. A smartphone transcends its tangible form to offer intangible apps, seamless services, and immersive experiences. This convergence underscores the dynamism of products and the boundless innovation brands can harness. By mastering the nuances of each category, marketers can sculpt strategies that resonate, captivate, and satisfy diverse consumer desires.
Link Between Product Characteristics and Customer Needs
The characteristics of a product serve as a bridge between what a brand offers and what consumers seek. These characteristics must align harmoniously with customer needs to foster engagement and loyalty.
- Functionality: The product’s core purpose and features must address specific customer needs. A smartphone’s camera quality, for instance, directly addresses the desire for high-quality photos.
- Quality and Reliability: Ensuring that a product consistently performs as promised builds trust. A reliable product that meets or exceeds expectations enhances customer satisfaction and encourages repeat purchases.
- Customization: The ability to tailor a product to individual preferences enhances its appeal. Customizable features cater to diverse customer requirements, allowing them to shape their own experiences.
- Innovation: Products that incorporate innovative elements stand out in competitive markets. Innovation can be manifested through new technologies, materials, or novel functionalities.
- Aesthetics: Visual appeal plays a significant role in attracting customers. A well-designed product not only serves its purpose but also elevates the overall user experience.
Understanding the intricate link between product characteristics and customer needs empowers brands to create offerings that resonate deeply. By tailoring products to fulfill specific desires and aspirations, companies can forge lasting connections, positioning themselves as indispensable solutions in their customers’ lives.
Integration of Products into Marketing Strategies
In the world of marketing, the art of seamlessly integrating products into overarching marketing strategies is a pivotal undertaking that can significantly impact a company’s success. Beyond merely offering a product to the market, businesses must strategically position and promote their offerings to engage with their target audience effectively. This integration of products into marketing strategies encompasses a multifaceted approach that encompasses product development, positioning, branding, and the orchestration of various marketing channels
A. Product-Centric vs. Customer-Centric Approaches
In the intricate web of marketing strategies, the approach to product integration stands as a pivotal crossroads, with two distinct paths: the product-centric and the customer-centric. These paths encapsulate divergent philosophies that shape how brands position their offerings, interact with consumers, and ultimately drive success.
1. Product-Centric Approach: At the heart of the product-centric approach lies the product itself. This philosophy places paramount importance on the features, specifications, and functionalities of the offering. Brands adhering to this approach believe that a superior product, with its inherent qualities, will organically attract customers. Here, the product takes center stage, and marketing efforts revolve around highlighting its distinct attributes.
The product-centric approach is marked by an emphasis on innovation, quality, and uniqueness. Brands employing this strategy aim to differentiate themselves through product superiority, relying on features and functionalities to capture consumer attention. Marketing campaigns center on showcasing the product’s capabilities and advantages over competitors.
2. Customer-Centric Approach: Contrastingly, the customer-centric approach is an ode to understanding, empathy, and resonance. Brands embracing this philosophy recognize that customer needs, desires, and emotions drive purchasing decisions. The focus here shifts from the product’s intrinsic attributes to the consumer’s journey and experience.
In the customer-centric paradigm, brands immerse themselves in understanding consumer pain points, aspirations, and preferences. Marketing strategies align with these insights, aiming to create solutions that cater to consumers’ needs and emotional triggers. Personalization, engagement, and connection become the pillars of customer-centric marketing.
Navigating the Intersection: In the modern landscape, the lines between these approaches often blur. Brands recognize that the product’s merits are inseparable from the consumer’s perception and experience. The integration of both product-centric and customer-centric elements forms a dynamic tapestry that resonates with diverse audiences.
Striking the right balance entails crafting narratives that highlight the product’s unique features while weaving them into a larger story that speaks to consumer aspirations. Successful brands engage in conversations that address both the functional and emotional dimensions of their offerings. Whether it’s showcasing a product’s innovative features or narrating how it addresses specific consumer pain points, the ultimate goal is to forge a lasting connection.
In closing, the integration of products into marketing strategies necessitates a delicate balance between the product’s merits and its alignment with consumer needs. The journey traverses both rational and emotional territories, and its success lies in a cohesive narrative that resonates on every level. By artfully combining product-centric innovation with customer-centric empathy, brands can forge connections that are both enduring and impactful.
B. Identifying the Product’s Value Proposition
The value proposition of a product encapsulates the unique benefits and advantages it offers to consumers. It’s the compelling reason why customers should choose this product over competitors’ offerings. In essence, the value proposition answers the question: “What’s in it for the customer?”
To craft a strong value proposition, several factors should be considered:
- Consumer Needs: Understand the pain points, desires, and challenges of the target audience. A value proposition should address these needs directly.
- Product Differentiation: Highlight the features, attributes, or qualities that set the product apart from others in the market.
- Solving a Problem: Explain how the product solves a particular problem or fulfills a specific need for the customer.
- Benefit Emphasis: Focus on the benefits that customers will enjoy by using the product, whether they’re functional, emotional, or both.
- Clear Communication: Express the value proposition concisely and in plain language that resonates with the target audience.
- Proof of Value: Provide evidence or testimonials that demonstrate how the product has positively impacted others.
- Visual Appeal: Consider using visuals, such as graphics or videos, to convey the value proposition effectively.
Remember, a compelling value proposition can be a powerful tool in attracting and retaining customers, as it gives them a clear reason to choose your product.
C. Aligning Products with Target Market Segments
Tailoring products to specific market segments is crucial for effective marketing. Each market segment has unique characteristics, preferences, and needs, and aligning products with these segments enhances relevance and resonance.
Here’s how to align products with target market segments:
- Segment Identification: Identify and define market segments based on demographics, psychographics, behaviors, or other relevant criteria.
- Market Research: Conduct thorough research to understand the preferences, pain points, and aspirations of each segment.
- Product Customization: Modify product features, packaging, or messaging to cater to the specific preferences of each segment.
- Messaging: Craft marketing messages that resonate with the values and needs of each segment. Use language and imagery that they can relate to.
- Distribution Channels: Choose distribution channels that are accessible and preferred by the target segments. This includes online platforms, retail locations, or other relevant avenues.
- Pricing Strategy: Set pricing that aligns with the perceived value of the product within each segment.
- Promotion Tactics: Design promotion strategies that speak directly to the concerns and aspirations of the target segments.
By effectively aligning products with target market segments, brands can create a stronger connection with customers, drive engagement, and increase the likelihood of successful product adoption.
Importance of Product in Differentiation

In a competitive market, differentiation is essential to stand out and capture the attention of consumers. Creating a unique selling proposition (USP) is a strategy that focuses on highlighting distinct features or benefits of a product that set it apart from competitors. A strong USP not only attracts customers but also fosters brand loyalty and long-term success.
A. Creating Unique Selling Propositions (USPs)
A unique selling proposition (USP) is a concise statement that communicates the unique benefits or value a product offers to its target audience. It’s a compelling reason why customers should choose a particular product over alternatives. To create an effective USP, consider the following steps:
- Identify Customer Pain Points: Understand the challenges or needs your target audience faces and how your product can address them effectively.
- Analyze Competitors: Research competitors to identify what they’re offering and how your product can differentiate itself from theirs.
- Highlight Unique Features: Determine what aspects of your product make it stand out, such as innovative technology, special ingredients, or unique design.
- Quantify Benefits: Specify the quantifiable benefits customers will gain from using your product, such as saving time, money, or effort.
- Focus on Emotions: Tap into the emotional aspect by showcasing how your product can make customers’ lives better, easier, or more enjoyable.
- Be Clear and Concise: Craft a clear and concise USP that can be easily understood and remembered by consumers.
- Test and Refine: Test your USP with a sample audience and gather feedback to refine and improve it.
- Integrate into Marketing: Incorporate your USP into marketing materials, advertising campaigns, and product packaging.
Examples of well-known USPs include:
- FedEx: “When it absolutely, positively has to be there overnight.”
- M&M’s: “Melts in your mouth, not in your hands.”
- Apple iPhone: “The only phone that works seamlessly with other Apple devices.”
A strong USP not only helps differentiate your product but also resonates with your target audience, leading to increased brand recognition and customer loyalty.
B. Role of Product Features in Setting Brands Apart
Product features play a crucial role in setting brands apart in a competitive market. These features are the distinctive characteristics and attributes of a product that differentiate it from competitors and create a unique value proposition for consumers. By understanding the importance of product features, brands can create a compelling offering that resonates with their target audience and drives brand loyalty.
1. Differentiation and Competitive Advantage: Distinctive product features give brands a competitive edge by offering something that others don’t. When a brand’s product features address specific customer needs or pain points, they become a powerful tool for differentiation. This differentiation can attract customers looking for a solution that meets their requirements more effectively than alternatives.
2. Enhanced Value Proposition: Product features contribute to the overall value proposition of a brand. By offering unique benefits or functionalities, brands can communicate how their product is superior and more valuable compared to others. This can be achieved through innovative technology, better performance, added convenience, or improved user experience.
3. Addressing Specific Segments: Customizing product features to cater to specific market segments allows brands to target niche audiences effectively. This approach acknowledges that not all customers have the same needs or preferences. By tailoring features to different segments, brands can create offerings that resonate with diverse consumer groups.
4. Brand Identity and Recognition: Distinctive product features can become synonymous with a brand’s identity. When customers associate certain features with a brand, it enhances brand recognition and recall. This association fosters brand loyalty and encourages customers to choose that brand over others.
5. Emotional Connection: Certain product features can evoke emotional responses in consumers. Brands that understand their target audience’s values and desires can incorporate features that tap into these emotions. This emotional connection can create stronger bonds between consumers and the brand.
6. Premium Pricing: Unique and valuable product features can justify a premium price point. Consumers are often willing to pay more for products that offer exclusive features or enhanced benefits. Premium pricing can contribute to brand positioning and revenue generation.
7. Continuous Innovation: Product features drive innovation within a brand. Brands that consistently invest in research and development to enhance their products’ features demonstrate a commitment to meeting evolving consumer needs. This continuous innovation can keep a brand relevant and ahead of the competition.
8. Marketing and Communication: Product features provide valuable content for marketing and communication efforts. Brands can create compelling narratives around these features, emphasizing how they improve customers’ lives and solve their problems.
Examples:
- Apple’s focus is on user-friendly design and seamless integration of hardware and software.
- Tesla’s electric vehicles with cutting-edge technology and autonomous driving capabilities.
- Dyson’s vacuum cleaners are known for innovative suction technology and ergonomic design.
In conclusion, product features are a pivotal element in brand differentiation. Brands that understand their target audience, identify unique features that resonate with them, and effectively communicate these features can create a competitive advantage and cultivate lasting customer relationships.
C. How Innovative Products Contribute to Market Differentiation
Innovative products play a pivotal role in market differentiation by introducing new and unique features that set a brand apart from its competitors. When brands bring innovation to their products, they not only address unmet consumer needs but also create a distinct identity that captures the attention and loyalty of their target audience. Here’s how innovative products contribute to market differentiation:
1. Creating a Competitive Edge: Innovation allows brands to develop products that offer something novel and valuable to consumers. These unique features become a competitive edge that attracts customers looking for fresh and improved solutions.
2. Meeting Unmet Needs: Innovative products often arise from identifying unmet or underserved consumer needs. By addressing these needs, brands can carve out a niche for themselves in the market and cater to specific customer segments.
3. Changing Consumer Expectations: Innovation sets new standards and raises consumer expectations. Brands that consistently deliver innovative products can shape how customers perceive quality, functionality, and user experience, thus influencing their purchasing decisions.
4. Enhancing User Experience: Innovative products often come with improved user experiences, such as enhanced usability, convenience, and efficiency. These positive experiences create customer satisfaction and loyalty, contributing to the brand’s differentiation strategy.
5. Defining Brand Identity: Innovation becomes synonymous with a brand’s identity. Brands known for their innovative products build a reputation for being forward-thinking and cutting-edge, attracting consumers seeking the latest and best solutions.
6. Earning Media Attention: Innovative products tend to attract media attention and coverage due to their uniqueness and potential impact on the market. This exposure can generate buzz, raise awareness, and establish the brand as an industry leader.
7. Fostering Brand Loyalty: Customers who benefit from innovative products are more likely to develop brand loyalty. When a brand consistently delivers products that enhance customers’ lives, they become loyal advocates who stick with the brand through various product cycles.
8. Expanding Market Reach: Innovation can open up new market segments or demographics. Brands that offer solutions that were previously unavailable or overlooked can tap into previously untapped markets.
Examples:
- Apple’s introduction of the iPhone revolutionized the smartphone market with its touch interface and app ecosystem.
- Tesla’s electric vehicles not only addressed environmental concerns but also introduced advanced autonomous driving capabilities.
- Airbnb disrupted the hospitality industry by allowing individuals to rent out their homes to travelers, offering a unique alternative to traditional hotels.
In Conclusion: Innovation is a key driver of market differentiation. Brands that invest in research, development, and creative problem-solving can create products that stand out, cater to specific needs, and generate brand loyalty. By continuously pushing the boundaries of what is possible, brands can establish themselves as leaders in their industry and create a lasting impact on consumers’ lives.
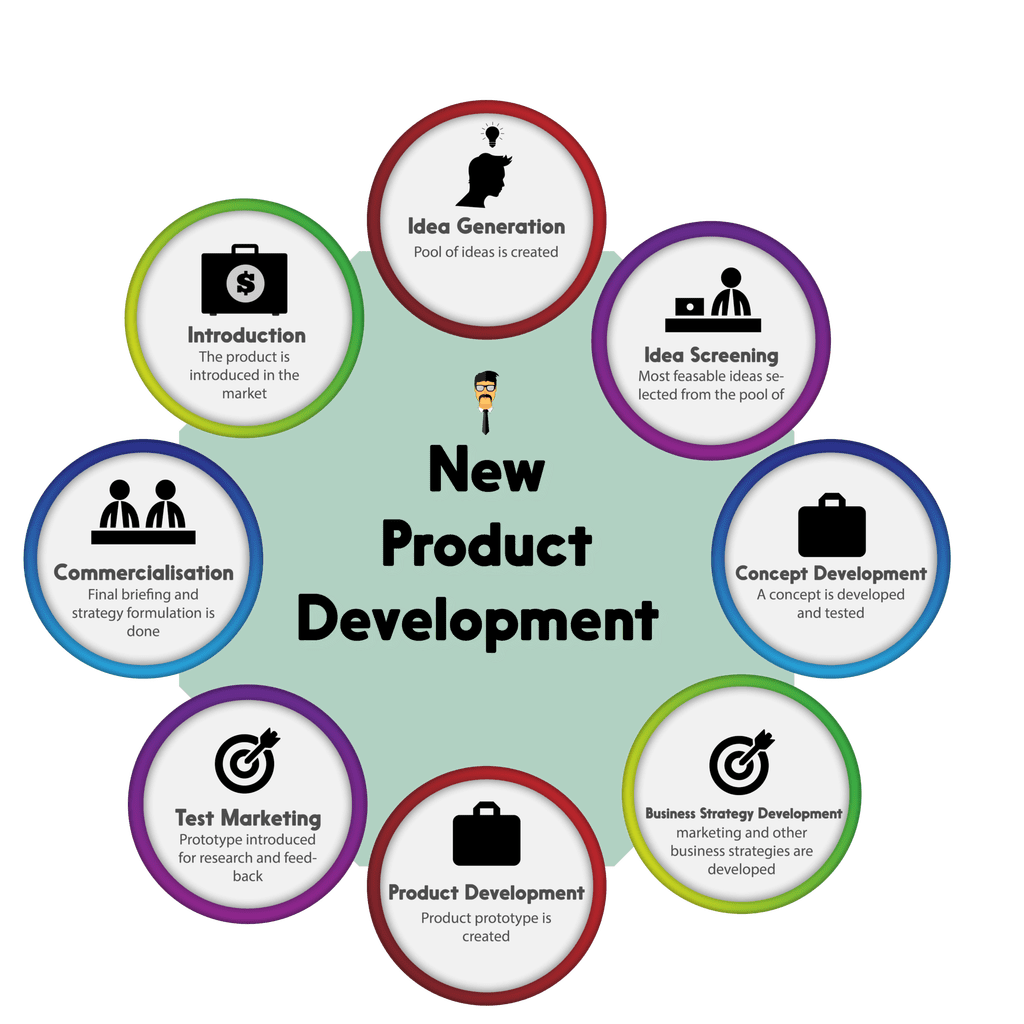
Product Lifecycle and Strategy
Understanding and effectively managing the product lifecycle is a fundamental aspect of crafting a successful marketing strategy. The product lifecycle concept provides a framework for businesses to navigate the various stages a product goes through, from its introduction to eventual decline. By aligning marketing strategies with each stage of the product lifecycle, companies can optimize their efforts and maximize profitability while meeting the evolving needs of consumers.
Introduction to the Product Lifecycle Stages: Introduction, Growth, Maturity, Decline
The product lifecycle is a fundamental concept in marketing that describes the various stages a product goes through in its journey from introduction to eventual decline. The four main stages of the product lifecycle are:
- Introduction: In this stage, a new product is introduced to the market. Sales are typically low as consumers become aware of the product’s existence. Marketing efforts focus on creating awareness and generating initial interest.
- Growth: As the product gains traction, sales start to grow rapidly. Consumer demand increases, and competitors may enter the market. Marketing strategies aim to build brand loyalty, expand market share, and differentiate the product from competitors.
- Maturity: Sales stabilize during the maturity stage, with the product reaching its peak market penetration. Competition intensifies, and growth slows down. Marketing efforts focus on maintaining market share, optimizing distribution channels, and adapting promotional strategies.
- Decline: Sales and profits start to decline as the product becomes outdated, faces strong competition, or experiences shifts in consumer preferences. Marketing efforts may involve cost reduction, discontinuing certain variants, or introducing new features to extend the product’s life.
Adapting Marketing Strategies to Match the Product’s Lifecycle Stage
Effective marketing strategies are crucial at each stage of the product lifecycle to maximize success and maintain profitability:
- Introduction Stage: Focus on building product awareness and gaining a foothold in the market. Heavy advertising, public relations, and promotions can help educate consumers about the product’s benefits.
- Growth Stage: Capitalize on the product’s success by expanding distribution, targeting new customer segments, and emphasizing brand loyalty. Continue advertising to reinforce the product’s benefits.
- Maturity Stage: Shift marketing efforts towards maintaining market share and customer loyalty. Consider introducing product variations or updates to attract new customers. Price adjustments and promotions can help maintain competitiveness.
- Decline Stage: Focus on maximizing profitability as sales decline. Consider discontinuing less profitable product variations and focusing on core offerings. Evaluate whether to invest in revitalization efforts or transition to a new product.
Revitalizing Products Through Strategic Adjustments
Revitalizing a product involves making strategic adjustments to extend its lifecycle or reintroduce it to the market. Some approaches to revitalization include:
- Product Innovation: Introducing new features, improved designs, or updated technology can rekindle interest in the product.
- Repositioning: Changing the product’s positioning, target audience, or marketing message can help it resonate with new customer segments.
- Bundle Offerings: Packaging the product with complementary items or services can add value and renew consumer interest.
- Promotions: Offering special deals, discounts, or limited-time offers can stimulate sales during a decline.
- Brand Refresh: Updating the product’s branding, packaging, and overall image can create a renewed perception among consumers.
- Expanding Distribution: Exploring new distribution channels or entering new markets can breathe new life into a product.
- Communication Campaigns: Launching a new advertising campaign or leveraging social media to highlight the product’s unique benefits can attract attention.
Understanding the product lifecycle is essential for effective marketing planning. Each stage requires tailored strategies to maximize the product’s success and adapt to changing market conditions. Revitalizing products through innovative approaches can extend their relevance and value to consumers.
Product as a Communication Tool
In the world of marketing and branding, products are more than just tangible items; they are powerful tools of communication. Beyond their utilitarian functions, products convey messages, embody brand values, and establish connections with consumers. This concept of “product as a communication tool” is fundamental to creating meaningful and lasting relationships between brands and their customers.
Conveying Brand Identity and Values Through Products
Products are not just physical entities; they also serve as powerful communication tools that convey a brand’s identity and values to consumers. When a brand creates products, it sends a message about its core principles, mission, and the type of experience it aims to provide. Here’s how products play a role in communicating brand identity and values:
- Design and Packaging: The design and packaging of a product reflect the brand’s aesthetics and values. Whether it’s sleek and minimalist, vibrant and playful, or elegant and luxurious, the design choices instantly communicate the brand’s intended image to consumers.
- Quality and Craftsmanship: The quality of a product reflects the brand’s commitment to delivering excellence. Brands that prioritize high-quality materials and craftsmanship communicate their dedication to providing customers with valuable and durable solutions.
- Functionality: How a product meets consumers’ needs and solves their problems speaks volumes about the brand’s understanding of its target audience. A product that seamlessly fits into customers’ lifestyles demonstrates that the brand values practicality and convenience.
- Innovation: Innovative features and technologies in a product indicate that the brand is forward-thinking and willing to invest in cutting-edge solutions. This can create a perception of being innovative and staying ahead of the curve.
- Sustainability: Brands that prioritize eco-friendliness and sustainability in their products show that they care about the environment and societal well-being. Sustainable packaging and materials convey a commitment to responsible business practices.
- Emotional Connection: Products can evoke emotions and create a bond between consumers and the brand. A product that resonates emotionally with customers can enhance brand loyalty and create lasting connections.
- Brand Messaging: Products can reinforce the brand’s messaging and values through their names, taglines, and descriptions. These elements provide an opportunity to directly communicate brand identity to consumers.
- User Experience: The experience of using a product, from its ease of use to the feelings it evokes, contributes to the overall brand perception. A positive user experience can lead to positive associations with the brand.
Example: Apple Inc.
Apple is a prime example of a company that uses products as a communication tool for its brand identity and values. The sleek design, premium materials, and intuitive functionality of Apple products communicate simplicity, innovation, and user-centered design. Apple’s focus on creativity and individuality is conveyed through customizable features, such as personalized device setups. The brand’s commitment to sustainability is evident in its efforts to reduce environmental impact through recycling programs and energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
In conclusion, products are not only functional items but also potent means of conveying a brand’s identity and values to consumers. Every element of a product, from its design to its functionality, contributes to the narrative a brand tells about itself, influencing consumers’ perceptions and building a connection that goes beyond the product itself.
Packaging and Its Impact on Brand Perception
Packaging is a critical element that goes beyond mere containment; it plays a significant role in shaping brand perception and influencing consumer decisions. The design, materials, and functionality of packaging can have a profound impact on how consumers perceive a brand. Here’s how packaging affects brand perception:
- First Impressions: Packaging is often the first interaction a consumer has with a product. A well-designed and visually appealing package creates a positive first impression, suggesting that the brand values quality and attention to detail.
- Consistency: Packaging design that aligns with a brand’s visual identity, colors, and logo reinforces brand consistency. This consistency builds recognition and trust among consumers.
- Differentiation: Unique and distinctive packaging helps products stand out on shelves crowded with competing offerings. Packaging that stands apart from the crowd can create a sense of intrigue and curiosity.
- Perceived Value: Premium and luxurious packaging can elevate the perceived value of a product. Consumers may associate upscale packaging with higher quality and be willing to pay more.
- Emotional Connection: Packaging design can evoke emotions and trigger memories. Brands can use packaging to tap into consumers’ emotions, creating a deeper connection between the product and the consumer.
- Storytelling: Packaging can tell a story about the brand’s history, values, and mission. It serves as a visual platform to communicate the brand’s narrative to consumers.
- Functionality: Packaging that is easy to use, transport, and store enhances the overall user experience. Functional packaging can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Environmental Consciousness: Sustainable and eco-friendly packaging reflects a brand’s commitment to environmental responsibility. Brands that prioritize sustainable packaging can attract environmentally-conscious consumers.
Leveraging Products for Storytelling and Emotional Connection
Products have the power to tell stories and create emotional connections with consumers. Brands that effectively use products as vehicles for storytelling can establish deeper relationships with their audience. Here’s how products can be leveraged for storytelling and emotional connection:
- Origin and Craftsmanship: Sharing the story of a product’s origin, craftsmanship, and production process can resonate with consumers. It humanizes the product and highlights the dedication behind its creation.
- User Scenarios: Demonstrating how a product fits into consumers’ lives through real-world scenarios or use cases can help consumers envision themselves using the product.
- Customer Testimonials: Highlighting real customer experiences and testimonials can create relatable stories that build trust and authenticity.
- Brand Values: Linking products to a brand’s core values and mission can create a sense of alignment between the brand and its customers. This emotional connection can foster brand loyalty.
- Heritage and Tradition: Brands with a rich history can use products to showcase their heritage and tradition, appealing to consumers who value nostalgia and authenticity.
- Social Impact: Products associated with social causes or philanthropic efforts can evoke emotions and make consumers feel like they are contributing to a positive change.
- Aspirations: Positioning products as tools that help consumers achieve their aspirations can create a strong emotional bond. Consumers may see the brand as a partner in their journey.
Example: Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” Campaign
Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign is a prime example of leveraging products for storytelling and emotional connection. By printing individual names on Coke bottles and cans, the campaign encouraged people to share personalized beverages with friends and loved ones. This simple act of sharing a Coke became a way to create connections and share moments, evoking positive emotions and enhancing the brand’s image as a facilitator of joy and togetherness.
In conclusion, packaging and products have a profound impact on brand perception, storytelling, and emotional connection. By strategically designing packaging and using products to convey stories and emotions, brands can forge deeper relationships with consumers and differentiate themselves in the market.
Product-Driven Market Research

In the ever-evolving world of business, market research serves as the compass guiding companies toward making informed decisions and achieving their strategic objectives. Among the myriad approaches to market research, the concept of “product-driven market research” stands out as a potent tool for businesses aiming to not only meet but exceed customer expectations.
Gathering Insights Through Product Testing and Market Feedback
Effective product-driven market research involves gathering valuable insights from product testing and market feedback. These insights help businesses refine their products, align with consumer preferences, and make informed decisions. Here’s how product testing and market feedback contribute to gathering insights:
Product Testing:
- Prototype Evaluation: Testing prototypes allows businesses to identify design flaws, functionality issues, and potential improvements before the final product is launched.
- Functionality and Performance: Testing the product’s functionality and performance ensures it meets the promised features and quality standards, building customer trust.
- Usability and User Experience: Evaluating usability helps ensure the product is user-friendly and intuitive. A positive user experience contributes to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Compatibility: Testing the product’s compatibility with different devices, systems, or software is crucial for seamless integration and user satisfaction.
- Durability and Reliability: Assessing a product’s durability and reliability ensures it can withstand regular use without frequent breakdowns, contributing to customer trust.
- Safety: Safety testing is vital, especially for products that interact closely with users. Ensuring products meet safety regulations enhances consumer confidence.
Market Feedback:
- Customer Surveys: Conducting surveys allows businesses to gather direct feedback from customers about their preferences, satisfaction levels, and suggestions for improvement.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups bring together a diverse set of consumers to discuss their opinions, perceptions, and experiences with the product, providing qualitative insights.
- Online Reviews and Social Media: Monitoring online reviews and social media discussions helps identify sentiment, trends, and areas of improvement based on real-time feedback.
- Customer Support Interactions: Analyzing customer support interactions and inquiries provides insights into common issues, helping address concerns proactively.
- Sales and Return Data: Studying sales patterns and return data can reveal which product features resonate with customers and which areas need enhancement.
Example: Apple’s Product Testing and Market Feedback
Apple is known for rigorous product testing and actively seeking market feedback to enhance its products. Before launching a new iPhone model, Apple tests prototypes extensively to ensure performance, design, and usability align with customer expectations. After product release, Apple monitors online forums, social media, and customer support interactions to gather feedback on user experiences. This feedback informs future software updates and product enhancements, demonstrating Apple’s commitment to continuous improvement based on customer insights.
In conclusion, gathering insights through product testing and market feedback is essential for creating products that resonate with consumers and meet their needs. Effective product-driven market research helps businesses identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas of improvement, leading to more successful product launches and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Adapting Products Based on Consumer Preferences and Trends
Adapting products based on consumer preferences and trends is a vital aspect of maintaining competitiveness and meeting evolving customer demands. By closely monitoring market trends and listening to consumer feedback, businesses can make informed decisions to enhance their products. Here’s how adapting products works:
Market Research:
- Consumer Insights: Collect data on consumer preferences, behaviors, and needs through surveys, focus groups, and online analytics.
- Competitor Analysis: Study competitors’ products and strategies to identify gaps in the market and areas for improvement.
- Trend Analysis: Keep track of emerging trends, technological advancements, and cultural shifts that could impact consumer preferences.
Product Adaptation:
- Feature Enhancement: Integrate new features or improvements based on identified consumer needs and desires.
- Customization Options: Offer product customization to cater to diverse preferences, such as color choices or functionality variations.
- Packaging and Design: Update packaging and design to align with current aesthetic preferences and create a more attractive product.
- Sustainability Considerations: Adapt products to be more environmentally friendly in response to the growing demand for sustainable options.
Example: Adidas and Sustainable Footwear
Adidas identified the increasing consumer preference for sustainable products and adapted their footwear offerings accordingly. They introduced the “Futurecraft Loop” sneaker, a fully recyclable shoe made from a single material. This move addressed consumer concerns about waste and sustainability while aligning with the trend of eco-friendly products.
Case Studies Demonstrating Successful Product-Driven Market Research
1. Apple’s iPhone Iterations: Apple’s consistent success can be attributed to its product-driven market research. Over the years, Apple has adapted its iPhone models based on consumer preferences and technological advancements. Features like larger screens, improved cameras, and enhanced processors were introduced in response to market trends and customer feedback. Each iteration reflects Apple’s dedication to aligning its products with evolving consumer needs.
2. Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” Campaign: Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign demonstrates the power of product-driven market research. The company replaced its logo with popular names on its cans and bottles, which increased personalization and consumer engagement. The campaign was driven by insights showing that people connect more deeply with products that are tailored to them. This approach resulted in increased sales and brand loyalty.
3. Netflix’s Content Strategy: Netflix’s data-driven content strategy is a prime example of adapting products to consumer preferences. The platform uses viewership data to create and recommend content that resonates with different audience segments. By offering personalized content suggestions, Netflix enhances the user experience and keeps subscribers engaged.
In conclusion, adapting products based on consumer preferences and trends is essential for staying competitive and meeting changing market demands. Market research helps businesses gather insights, make informed decisions, and create products that align with customer needs, ultimately leading to enhanced customer satisfaction and business success.
Product as a Foundation for Pricing Strategies
In the intricate landscape of business, pricing strategies hold a pivotal role in determining a company’s profitability, market positioning, and overall success. One often-underestimated factor that profoundly influences pricing decisions is the product itself. Indeed, the product serves as a foundation upon which pricing strategies are built. Understanding the product’s attributes, market position, and customer perception is essential for crafting effective pricing strategies.
The link between Product Quality, Features, and Pricing
The relationship between product quality, features, and pricing is a critical consideration in developing effective pricing strategies. Pricing plays a significant role in how consumers perceive a product’s value, and aligning it with product attributes can influence purchasing decisions. Here’s how these elements are interconnected:
1. Product Quality and Features:
- Quality Impact: The perceived quality of a product is closely linked to its features, functionality, and overall performance. A high-quality product is more likely to offer superior features and a better user experience.
- Features Influence: Product features, such as advanced technology or innovative design, can enhance the perceived value of a product and justify a higher price point.
2. Pricing Strategies:
- Value-Based Pricing: This strategy prices a product based on the value it offers to customers. A high-quality product with advanced features can command a higher price due to its perceived value.
- Skimming Pricing: Setting an initially high price for a product with unique features or high quality to capitalize on early adopters and premium-seeking customers.
- Penetration Pricing: Introducing a product at a lower price to quickly gain market share, especially if the product’s features provide a competitive advantage.
3. Perceived Value:
- Perceived Benefits: Consumers assess whether the product’s quality and features align with the price being asked. If the perceived benefits match or exceed the price, they are more likely to make a purchase.
- Luxury and Premium Perception: High-quality products with advanced features are often associated with luxury or premium status, allowing businesses to charge higher prices.
Example: Apple’s Pricing Strategy for iPhones
Apple’s iPhones exemplify the link between product quality, features, and pricing. iPhones are known for their high build quality, cutting-edge features, and advanced technology. Apple’s value-based pricing strategy capitalizes on these attributes. While iPhones are priced at a premium compared to other smartphones, customers are willing to pay due to the perceived superior quality and innovative features. The brand’s reputation for delivering high-quality products justifies the premium pricing strategy.
The link between product quality, features, and pricing is a fundamental consideration in crafting effective pricing strategies. Understanding how these elements interact allows businesses to position their products effectively in the market, ensuring that the pricing strategy aligns with the product’s perceived value and customer expectations.
Value-Based Pricing vs. Cost-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing and cost-based pricing are two distinct approaches that businesses use to determine the price of their products. Each approach has its advantages and considerations:
1. Value-Based Pricing:
- Focus: This approach revolves around the value perceived by the customer. It sets the price based on how much customers are willing to pay for the benefits and value they receive from the product.
- Advantages: Value-based pricing allows businesses to capture higher profits by aligning prices with the perceived value of the product. It is particularly effective when the product offers unique features or solutions.
- Considerations: Accurately assessing customer perceptions and willingness to pay can be challenging. Additionally, value-based pricing may not work well for commoditized products with many substitutes.
2. Cost-Based Pricing:
- Focus: Cost-based pricing involves setting prices by adding a predetermined profit margin to the production cost. It’s based on the internal cost structure of the business.
- Advantages: This approach provides a clear understanding of the minimum price needed to cover costs and generate a profit. It’s straightforward and can work well for standardized products.
- Considerations: Cost-based pricing may not take into account customer preferences or the perceived value of the product. It can lead to underpricing if the value offered is higher than the cost-based price.
Balancing Product Positioning with Pricing to Maximize Value Perception
Balancing product positioning with pricing is crucial to create a strong value perception among customers. Here’s how businesses can achieve this balance:
1. Align Pricing with Value:
- Value Communication: Clearly communicate the unique features, benefits, and solutions that the product offers. Highlight how these features meet customer needs and justify the price.
- Premium Positioning: For products positioned as premium or luxury, pricing should reflect the exclusivity, quality, and unique attributes.
2. Conduct Market Research:
- Customer Insights: Gather insights into customer preferences, needs, and willingness to pay. This information helps in setting the right price for the value provided.
- Competitor Analysis: Understand how competitors are pricing similar products and what value they are offering. This helps in positioning and pricing decisions.
3. Test Different Price Points:
- Price Testing: Experiment with different price points and observe customer reactions. A/B testing can help identify the optimal price that maximizes perceived value while ensuring profitability.
4. Bundle Value-Added Services:
- Bundling: Offer value-added services or complementary products along with the main product. This enhances the perceived value and justifies a higher price.
5. Monitor and Adjust:
- Dynamic Pricing: Monitor market trends, customer feedback, and competitor movements. Adjust prices accordingly to maintain a competitive edge and perceived value.
Example: Starbucks’ Pricing Strategy
Starbucks employs a value-based pricing strategy. It positions itself as offering premium coffee and a unique coffeehouse experience. Customers are willing to pay a premium for the quality of coffee, ambiance, and personalized service. Starbucks communicates this value through its branding and consistently high prices, enhancing its value perception.
Balancing product positioning with pricing involves understanding customer perceptions, aligning value with price, and continuously monitoring market dynamics. A well-executed pricing strategy can maximize the perceived value of the product, leading to higher customer satisfaction and profitability.
Adapting Products for Cultural and Regional Markets
The globalization of commerce has opened up vast opportunities for companies to expand into new regions and tap into diverse consumer bases. However, success in international markets requires more than simply exporting products; it demands a deep understanding of cultural nuances, local preferences, and regional idiosyncrasies. Adapting products for cultural and regional markets is a strategic imperative for companies seeking to thrive in a globalized business environment.
Importance of Cultural Sensitivity in Product Development
Cultural sensitivity in product development is crucial for successfully adapting products to diverse cultural and regional markets. Here’s why it matters:
1. Cultural Relevance:
- Different cultures have unique preferences, values, and traditions. Adapting products to align with these cultural nuances enhances their relevance and appeal in specific markets.
2. Avoiding Cultural Insensitivity:
- Failure to consider cultural differences can lead to misunderstandings or offense, damaging the brand’s reputation. Cultural insensitivity may arise from inappropriate symbols, colors, or messaging.
3. Building Trust and Connection:
- When products resonate with the local culture, consumers feel understood and valued. This builds trust and fosters a deeper emotional connection with the brand.
4. Addressing Local Needs:
- Cultural insights help identify specific needs and challenges within a region. Adapting products to address these needs enhances their usefulness and positions the brand as attentive.
5. Language and Communication:
- Language is a key cultural element. Ensuring accurate translation and communication helps prevent misinterpretations or unintended messages.
6. Successful Product Adoption:
- Cultural sensitivity improves the likelihood of successful product adoption. Products that align with local preferences are more likely to gain acceptance and popularity.
Example: McDonald’s in India
McDonald’s is an example of a global brand that has successfully adapted its products to local cultural preferences. In India, where the majority of the population follows Hindu dietary practices, McDonald’s offers a range of vegetarian options to cater to local tastes. The menu includes items like the McAloo Tikki burger made from a spiced potato patty, as well as vegetarian wraps and desserts. This cultural adaptation has played a significant role in McDonald’s success in the Indian market.
Strategies for Achieving Cultural Sensitivity:
1. Market Research:
- Conduct thorough market research to understand cultural norms, values, and consumer behaviors in the target region.
2. Collaborate with Local Experts:
- Work with local experts or consultants who have a deep understanding of the culture to guide product adaptations.
3. Test and Feedback:
- Test products with focus groups from the target culture to gather feedback and make necessary adjustments.
4. Customization vs. Standardization:
- Decide whether product adaptations should be subtle modifications or complete customizations based on cultural preferences.
5. Maintain Brand Identity:
- While adapting, ensure that the core brand identity is preserved to maintain brand consistency.
6. Communication and Marketing:
- Tailor marketing messages to resonate with local values and use appropriate language.
In conclusion, cultural sensitivity is a critical factor in adapting products for different cultural and regional markets. Brands that recognize and respect cultural differences can create products that truly resonate with consumers, building stronger relationships and driving business success.
Tailoring Products to Match Regional Preferences and Norms
Adapting products to align with regional preferences and norms is a key strategy for global brands seeking success in diverse markets. Here’s how tailoring products can lead to higher market acceptance:
- Localized Flavor Profiles: Food and beverage brands often adjust ingredients and flavors to suit local tastes. For instance, Lay’s potato chips offer unique flavors in different countries, such as “Masala” in India or “Prawn Cocktail” in the UK.
- Cultural Symbolism: Incorporating cultural symbols and references into product design or packaging can create a sense of familiarity and relevance. McDonald’s “McLobster” sandwich in Canada is an example of a product tailored to the region’s love for seafood.
- Sizing and Portioning: Different cultures have varying preferences for portion sizes. Brands like Starbucks offer larger sizes of beverages in the U.S. compared to some European countries where smaller sizes are more common.
- Climate and Environment: Products may need to be adapted based on the local climate or environmental conditions. Clothing brands may offer different collections for tropical and cold climates.
- Packaging and Design: Colors, imagery, and packaging style should resonate with local aesthetics and cultural preferences. Tide, for instance, changed its packaging in the Middle East to reflect regional fashion trends.
- Language and Communication: Product labeling, instructions, and marketing messages should be accurately translated to the local language to ensure clarity and understanding.
Examples of Global Brands Customizing Products for Different Markets
1. Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign involved printing popular names on their cans and bottles to encourage personalization and sharing. In some markets, cultural variations included using local names and phrases, making the campaign more relatable.
2. McDonald’s: McDonald’s adapts its menu to local tastes. In Japan, the “Teriyaki Burger” caters to the preference for teriyaki flavors. In India, the “McAloo Tikki” burger is a vegetarian option suited to the local diet.
3. IKEA: IKEA’s product names are often inspired by Scandinavian languages, but the brand customizes these names for other markets. For example, in China, some product names are modified to be easier to pronounce and remember.
4. Kit Kat: Kit Kat, owned by Nestlé, offers a wide range of unique flavors in different countries. In Japan, Kit Kat offers flavors like matcha (green tea) and sake, catering to local tastes and preferences.
5. KFC: KFC adapts its menu to fit regional preferences. In China, the brand introduced a “Dragon Twister” wrap with ingredients reminiscent of Chinese cuisine, blending local and international flavors.
6. Unilever’s Dove: Unilever’s Dove brand showcases its sensitivity to cultural norms. In the Middle East, Dove introduced a range of skincare products designed for Muslim women, considering their needs and values.
In conclusion, global brands recognize the importance of tailoring products to suit regional preferences and norms. These adaptations show respect for local cultures and enhance the likelihood of success in diverse markets.
Product Innovation and Future Strategy

The ability to create new, groundbreaking products or enhance existing ones is not just a competitive advantage; it’s a strategic imperative for companies looking to secure their future in an increasingly dynamic and disruptive market.
Necessity of Continuous Product Innovation
Continuous product innovation is a crucial component of a successful business strategy. Stagnation in product development can lead to reduced market relevance and a loss of competitive advantage. Here’s why continuous product innovation is necessary:
- Meeting Changing Customer Needs: Consumer preferences evolve over time. Continuous innovation ensures that products remain aligned with these changing needs, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Market Differentiation: Innovative products set a business apart from competitors. A unique and compelling product can capture consumer attention and establish a distinctive market position.
- Maintaining Relevance: As technology advances and industries evolve, outdated products can become obsolete. Regular innovation ensures a business remains relevant in a fast-paced market.
- Adapting to Trends: Market trends and industry dynamics can shift quickly. Innovative businesses can capitalize on emerging trends to create products that resonate with current consumer behaviors.
- Driving Growth: New products can open doors to untapped markets and revenue streams. Innovation is often a driver of business growth, allowing expansion into new segments.
- Responding to Competition: Rivals introducing innovative products can pose a threat. Continuous innovation helps a business stay ahead of competitors and retain market share.
- Attracting Talent: Businesses known for innovation often attract top talent. Creative minds are drawn to companies that value and invest in innovation.
- Sustainable Business: Long-term success requires a forward-thinking approach. Continuous product innovation contributes to a business’s sustainability and longevity.
Strategies for Continuous Product Innovation
- Market Research: Understand customer needs and pain points through surveys, feedback, and data analysis to identify areas for innovation.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Collaborate across departments to bring diverse perspectives into product development, fostering creative solutions.
- Rapid Prototyping: Build and test prototypes quickly to gather feedback and refine ideas before full-scale production.
- Open Innovation: Partner with external entities, like startups or research institutions, to tap into external expertise and fresh ideas.
- Incremental and Radical Innovation: Pursue both small, incremental improvements and bold, transformative changes in product design.
- Customer Co-Creation: Involve customers in the innovation process, allowing them to contribute ideas and provide feedback.
- Trend Monitoring: Keep an eye on emerging technologies, consumer behaviors, and market trends to stay ahead of the curve.
- Risk-Taking Culture: Encourage a culture where calculated risks and failures are embraced as opportunities for learning and growth.
In conclusion, continuous product innovation is vital for business success in today’s dynamic markets. By staying attuned to customer needs, fostering creativity, and adapting to industry changes, businesses can secure their relevance and competitiveness for the future.
Incorporating Technology Trends into Product Offerings
Incorporating technology trends into product offerings is essential to staying competitive in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape. Technology not only enhances the functionality of products but also provides opportunities for differentiation and innovation. Here’s how businesses can effectively integrate technology trends into their products:
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of emerging technology trends relevant to your industry. Follow tech publications, attend conferences, and engage with industry experts to stay informed.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Understand how technology can address customer pain points or enhance their experience. Develop products that align with customer needs and preferences.
- R&D Investment: Allocate resources to research and development to explore how new technologies can be applied to your products. Experimentation can lead to breakthrough innovations.
- Partnerships and Collaboration: Collaborate with technology providers, startups, or research institutions to access cutting-edge solutions and expertise.
- User Experience (UX): Focus on creating intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. Technology should enhance the product’s usability and convenience.
- Adaptability: Design products with flexibility to accommodate future technology updates. Modular designs can make it easier to integrate new features.
- Data Utilization: Leverage data analytics and insights to refine product offerings and identify areas for improvement.
- Sustainability: Consider how technology can contribute to sustainable practices, whether through energy efficiency, reduced waste, or eco-friendly materials.
Anticipating Customer Needs and Staying Ahead of Competitors
Anticipating customer needs and staying ahead of competitors is a core strategy for sustained business success. By proactively understanding and addressing customer preferences, businesses can maintain their competitive edge:
- Market Research: Regularly conduct market research to understand changing customer preferences, pain points, and emerging trends.
- Customer Feedback: Actively seek feedback from customers to identify areas for improvement and innovation.
- Predictive Analytics: Utilize data-driven insights to predict future customer needs based on historical behavior and market trends.
- Competitor Analysis: Monitor competitors to understand their product offerings, strategies, and areas where you can differentiate.
- Agile Development: Adopt agile methodologies to quickly respond to changing customer needs and market dynamics.
- Customer-Centric Culture: Foster a culture that prioritizes customer-centricity, encouraging employees to think from the customer’s perspective.
- Innovation Culture: Cultivate an environment that encourages creative thinking and rewards innovative ideas from employees.
- Prototyping and Testing: Develop prototypes and conduct testing to gather early feedback from potential users.
By incorporating technology trends, understanding customer needs, and continuously innovating, businesses can create products that resonate with customers and maintain a competitive advantage in the ever-evolving market.
Case Studies
A. Apple Inc.: How Product Innovation Drives Marketing Strategy
Apple Inc. is a prime example of how product innovation can drive a successful marketing strategy. The company’s focus on developing cutting-edge technology products has shaped its marketing approach:
- Innovative Products: Apple is known for launching groundbreaking products like the iPhone, iPad, and MacBook. These innovations not only captivate consumers but also set new industry standards.
- User Experience: Apple places a strong emphasis on user experience, ensuring that products are intuitive, user-friendly, and aesthetically appealing. This has led to a loyal customer base that eagerly anticipates new releases.
- Design Excellence: Apple products are characterized by sleek, minimalist designs. This design philosophy has become a core part of its brand identity, differentiating it from competitors.
- Ecosystem: Apple has created an ecosystem where its devices and services seamlessly integrate. This encourages customers to remain within the Apple ecosystem, boosting customer retention and cross-selling opportunities.
- Marketing Communication: Apple’s marketing campaigns focus on product features, design, and benefits rather than technical specifications. This approach resonates with consumers who value simplicity and elegance.
B. Coca-Cola: Adapting Products to Diverse Cultural Contexts
Coca-Cola is a global brand that has successfully adapted its products to diverse cultural contexts around the world:
- Localized Flavors: Coca-Cola offers regional flavors in different markets to cater to local tastes. For example, in Japan, they offer unique flavors like Sakura Cherry Blossom.
- Packaging and Labeling: Coca-Cola modifies its packaging and labeling to align with cultural events and traditions. Special edition bottles for festivals and holidays are common.
- Cultural Campaigns: The brand runs culturally relevant marketing campaigns that connect with local values and traditions. These campaigns create an emotional connection with consumers.
- Community Engagement: Coca-Cola engages with local communities by supporting local causes and events, strengthening its ties with the culture.
C. Tesla: Using Product Features to Redefine an Industry
Tesla is renowned for using product features to redefine the electric vehicle (EV) industry and establish itself as a leader:
- Electric Performance: Tesla’s electric vehicles offer impressive acceleration and performance, challenging the perception that EVs are slow and lack power.
- Autonomous Driving: Tesla’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving features have pushed the boundaries of autonomous driving technology, capturing consumers’ interest and setting industry standards.
- Long Range: Tesla’s focus on battery technology has allowed them to offer EVs with longer ranges, alleviating range anxiety and increasing the appeal of electric vehicles.
- Sustainability: Tesla’s commitment to sustainability and environmental consciousness resonates with consumers who value eco-friendly products.
- Direct-to-Consumer Sales: Tesla’s direct-to-consumer sales model disrupts the traditional dealership model, giving the company more control over the customer experience.
These case studies illustrate how product innovation, cultural adaptation, and leveraging unique features can drive successful marketing strategies and contribute to the success of businesses in various industries.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the crucial role that products play in the marketing mix. We’ve discussed how the product is one of the key components that connects businesses with consumers and drives sales. We’ve highlighted the significance of product functionality, customer satisfaction, and the influence of product features and design. Additionally, we’ve examined how ancillary services, packaging, and post-sale support contribute to the overall marketing strategy.
In conclusion, the role of the product in the marketing mix cannot be understated. It’s the driving force behind consumer engagement, sales generation, and brand reputation. By delivering high-quality products that resonate with customers, businesses can build strong foundations for their marketing strategies and achieve long-term success.

