Role Of Marketing Mix In Advertising
Are you ready to unravel the secrets behind successful advertising campaigns? Look no further than the powerful marketing mix. In this article, we delve into the crucial role of the marketing mix in advertising and how it influences the perfect blend of strategies to captivate your audience. Join us as we explore the dynamic interplay of product, price, place, and promotion to unlock the true potential of advertising success. Let’s dive in!
What is the Marketing Mix?
The marketing mix is a fundamental concept in the field of marketing that refers to the set of tactical tools and strategies that a company uses to promote its products or services and achieve its marketing objectives. It encompasses a combination of controllable factors that can be adjusted by a company to influence consumer purchasing decisions.
Definition and Concept of Marketing Mix
The marketing mix, often referred to as the “4 Ps,” was first introduced by Neil Borden in 1964 and later popularized by E. Jerome McCarthy in his book “Basic Marketing: A Managerial Approach.” The 4 Ps stand for Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Let’s briefly explore each component:
- Product: This element involves defining the characteristics, features, and benefits of the product or service being offered. It includes decisions related to product design, quality, branding, and packaging. A well-defined product meets the needs and wants of the target market.
- Price: Price refers to the amount of money customers are willing to pay for the product. Setting the right price is crucial, as it directly affects sales revenue and profitability. Pricing strategies may vary based on market conditions, competition, and customer perception of value.
- Place: Also known as distribution, this element focuses on making the product available to the target customers at the right place and time. Distribution channels, such as wholesalers, retailers, or direct sales, are essential considerations in the marketing mix.
- Promotion: Promotion involves the communication and promotion of the product to the target audience. It includes various promotional tools such as advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and personal selling. Effective promotion creates awareness, interest, desire, and action among potential customers.
Importance of Marketing Mix in Business Strategy
The marketing mix plays a critical role in shaping a company’s overall marketing strategy. Here’s why it is essential:
- Strategic Decision Making: The marketing mix provides a structured framework that helps marketers make informed decisions. By analyzing each element, companies can align their marketing efforts with their overall business goals.
- Market Differentiation: A well-crafted marketing mix allows businesses to differentiate their products from competitors in the market. It helps create a unique selling proposition (USP) that sets the brand apart.
- Customer-Centric Approach: By understanding and addressing customer needs through the marketing mix, companies can tailor their products and services to meet customer demands effectively.
- Resource Allocation: The marketing mix helps allocate resources efficiently by focusing on the most critical elements that influence customer behavior and drive sales.
- Adaptability to Market Changes: As market conditions change, companies can adjust their marketing mix to accommodate new trends and customer preferences.
The marketing mix is a foundational concept that underpins effective marketing strategies. It allows businesses to craft a holistic approach that optimizes product offerings, pricing, distribution, and promotional efforts to resonate with their target market and achieve marketing success.
Understanding Advertising in the Marketing Mix
In the previous section, we explored the concept of the marketing mix and its four crucial variables, known as the 4 Ps – Product, Price, Promotion, and Place. While all four components play a significant role in a company’s marketing strategy, this section will focus on the specific part of advertising within the promotion element of the marketing mix.
Role of Advertising in the Promotion Element
Advertising is a vital element of the promotional mix, which also includes publicity, personal selling, and sales promotion techniques. Its primary purpose is to communicate with the target audience and create awareness, interest, desire, and action toward the products or services being offered by the company.
- Informing and Educating Customers: One of the fundamental roles of advertising in the promotion mix is to inform and educate potential customers about the various aspects of a product. Whether it’s the features, benefits, usage, or other relevant details, advertising serves as a medium to disseminate this information effectively.
- Building Brand Image and Loyalty: Through consistent and strategic advertising campaigns, companies can establish and reinforce their brand image in the minds of consumers. A strong brand image enhances customer trust, loyalty, and perceived value of the products or services.
- Countering Competitor Claims: In a competitive market, companies often face challenges from rival brands making claims about their products. Advertising can be used to counter such claims and highlight the unique selling points of the company’s offerings.
- Influencing Buying Decisions: Effective advertising can influence consumer buying decisions. By creating compelling and persuasive advertisements, companies can sway customers to choose their products over alternatives.
Integration of Advertising with other Marketing Mix Components
While advertising plays a crucial role in the promotion element, it is essential to understand how it integrates with the other components of the marketing mix:
- Product: Advertising contributes to the success of a product by showcasing its features and benefits, creating demand, and building a brand reputation.
- Price: Through advertising, companies can communicate the value proposition of their products, justifying their price points to customers.
- Place: Advertising can help in expanding the market reach by promoting the availability of products at different physical locations or through online channels.
- Promotion: As a part of the promotion mix, advertising works in synergy with other promotional tools to create a cohesive and effective marketing campaign.
Advertising plays a vital role in the marketing mix, especially within the promotion element. It serves as a powerful tool for communicating with customers, building brand image, and influencing buying decisions. When integrated effectively with other marketing mix components, advertising can contribute significantly to the overall success of a company’s marketing efforts.
The Significance of a Balanced Marketing Mix
In the previous sections, we delved into the concept of the marketing mix and its crucial variables, the 4 Ps – Product, Price, Promotion, and Place. Now, let’s explore the importance of achieving a balanced marketing mix and the impact it can have on a company’s overall business success.
Achieving Synergy Among the Four P’s
The marketing mix is like a puzzle, and each element – Product, Price, Promotion, and Place – represents a vital piece that contributes to the overall picture of a successful marketing strategy. The significance lies in harmonizing these elements to create synergy and enhance the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
- Consistency and Clarity: A balanced marketing mix ensures that all elements work cohesively, sending a consistent and clear message to the target audience. This consistency builds trust and reliability, enhancing the overall brand perception.
- Comprehensive Approach: By considering all aspects of the marketing mix, companies can address different customer needs and preferences comprehensively. This comprehensive approach broadens the market appeal and attracts a diverse customer base.
- Maximizing Resources: A balanced marketing mix helps allocate resources optimally across different elements. By understanding which elements have the most significant impact on target customers, companies can invest their resources strategically.
- Adaptability to Market Changes: The marketing landscape is dynamic, with changing consumer behaviors and market trends. A balanced marketing mix allows companies to adapt quickly to these changes and stay competitive.
Impact of an Effective Marketing Mix on Business Success
A well-crafted and balanced marketing mix can significantly influence a company’s success in the following ways:
- Increased Market Share: An effective marketing mix that resonates with the target audience can lead to increased market share, as customers are more likely to choose the company’s offerings over competitors.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: Consistency in marketing efforts and delivering value through the marketing mix can build a strong brand reputation, making the company a preferred choice among consumers.
- Customer Loyalty and Retention: A balanced marketing mix that meets customer expectations and needs fosters loyalty among existing customers, leading to repeat business and long-term customer relationships.
- Improved ROI: By strategically allocating resources and focusing on the most impactful marketing mix elements, companies can improve their return on investment (ROI) and achieve better cost-effectiveness.
- Effective Market Penetration: An optimized marketing mix allows companies to penetrate new markets effectively and expand their customer base.
- Innovation and Competitive Advantage: A balanced marketing mix encourages companies to innovate in their products, pricing, promotions, and distribution, giving them a competitive edge in the market.
A balanced marketing mix is a cornerstone of successful marketing strategies. By achieving synergy among the four P’s and leveraging their strengths, companies can enhance their brand image, attract and retain customers, and ultimately achieve business success in the competitive marketplace.
The Four P’s of Marketing Mix
The Four P’s of Marketing Mix is a foundational framework that outlines the essential elements that businesses need to consider when developing their marketing strategies. The concept was introduced by E. Jerome McCarthy in the 1960s and has since become a fundamental model in marketing management. The Four P’s represent the key marketing variables that businesses can control to influence consumer purchasing behavior. They are as follows:
1. Product: Positioning and Branding
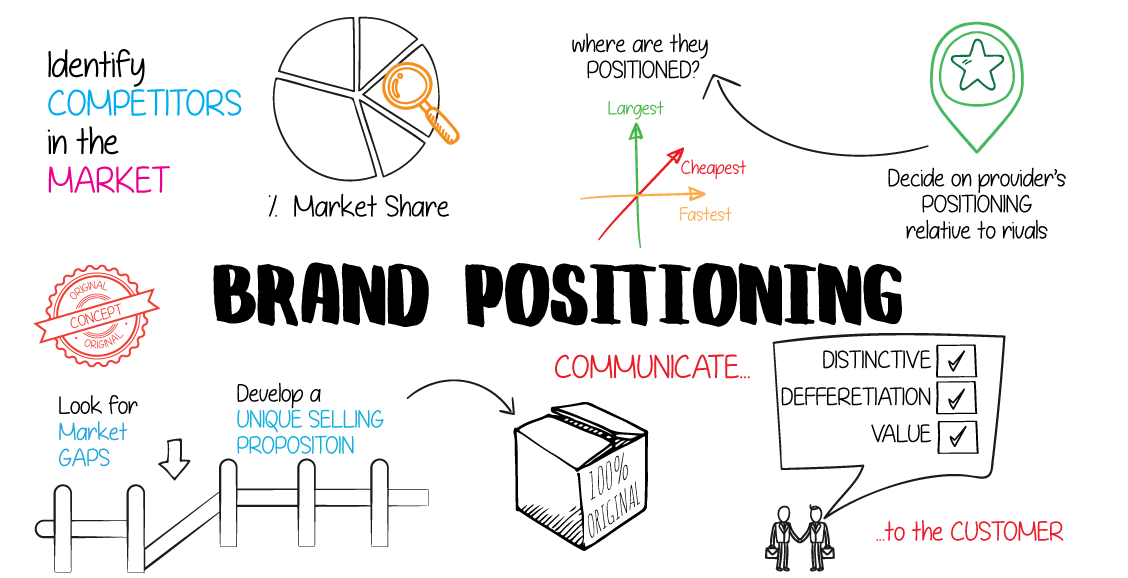
Product positioning and branding are essential components of the marketing mix, along with price, place, and promotion. They play a crucial role in shaping how customers perceive and connect with a product or service.
Defining the Product in Advertising Terms
- Product Attributes and Features: Advertising plays a vital role in highlighting the various attributes and features of a product. From its physical characteristics to its unique functionalities, advertising communicates the specific aspects that set the product apart from others in the market.
- Product Benefits and Value Proposition: Advertising goes beyond describing the product’s features; it focuses on communicating the benefits and value it brings to the customers’ lives. By presenting the product’s value proposition, advertising persuades potential customers to consider the product as a solution to their needs or desires.
- Emotional Appeal and Brand Storytelling: Effective advertising connects with consumers emotionally by using compelling storytelling. By portraying the product in real-life scenarios or by appealing to customers’ emotions, advertising creates a strong emotional bond between the brand and its target audience.
Creating a Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
- Identifying the Competitive Edge: A USP is a distinctive factor that sets a product apart from its competitors. Advertising plays a pivotal role in identifying this competitive edge and crafting a message around it.
- Highlighting the Differentiators: Advertising effectively highlights the unique features, benefits, or qualities of the product that competitors may lack. By focusing on these differentiators, advertising reinforces the product’s USP.
- Consistency and Reinforcement: Advertising ensures that the USP is consistently communicated across different marketing channels and campaigns. The repetitive nature of advertising helps reinforce the USP in the minds of consumers.
Branding Strategies and Their Influence on Advertising
- Brand Identity and Recognition: Advertising contributes to establishing a brand’s identity in the market. By consistently using brand elements such as logos, taglines, and colors, advertising helps in brand recognition and recall.
- Building Brand Equity: Strategic advertising campaigns can enhance a brand’s equity by creating positive associations and perceptions in the minds of consumers. Brand equity translates into customer loyalty and willingness to pay a premium for the brand.
- Brand Positioning: Advertising plays a pivotal role in positioning the brand in the minds of the target audience. By aligning the brand’s values and image with the customers’ preferences, advertising helps position the brand as the desired choice in the market.
- Brand Story and Emotional Connection: Advertising is an excellent medium for conveying the brand’s story and values. By establishing an emotional connection with consumers, advertising fosters brand loyalty and advocacy.
The Product element of the marketing mix is closely tied to advertising as it enables companies to showcase their offerings to the target audience effectively. By defining the product in advertising terms, creating a compelling USP, and leveraging branding strategies, companies can elevate their advertising efforts and create a strong market presence for their products and brands.
2. Price: Pricing Strategies and Communication
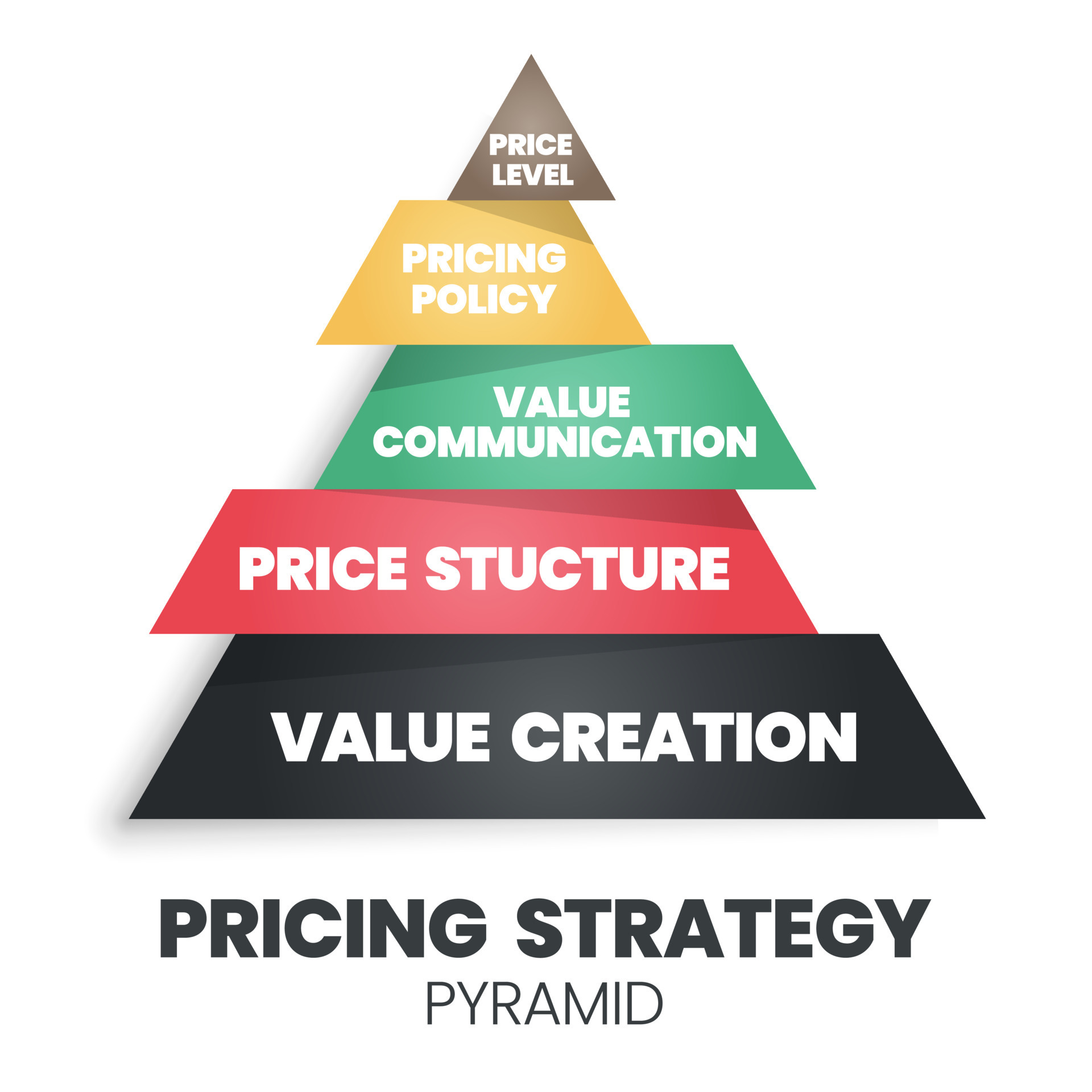
Price is a crucial element of the marketing mix, as it directly influences customer perceptions, purchase decisions, and overall profitability. Pricing strategies and effective communication are essential aspects of the price component. Let’s explore this in detail:
Pricing Tactics and Their Role in Advertising
- Cost-Based Pricing: One of the common pricing tactics is cost-based pricing, where the price is determined by adding a markup to the production cost. Advertising can play a role in justifying the price by highlighting the quality and value the product offers.
- Competitive Pricing: In competitive pricing, the price is set based on the prices charged by competitors. Advertising can emphasize the unique selling points of the product to justify any premium over competitors’ prices.
- Penetration Pricing: Penetration pricing involves setting a low initial price to gain market share quickly. Advertising can communicate this strategy by promoting limited-time offers, special discounts, or introductory prices.
- Price Skimming: Price skimming is setting a high initial price for a new product and gradually lowering it over time. Advertising can create a sense of exclusivity and value for early adopters who are willing to pay a higher price.
Communicating Value through Price in Advertising
- Value Proposition: Advertising plays a crucial role in communicating the value proposition of the product. It shows how the product’s features and benefits justify the price and provide a superior value compared to alternatives.
- Positioning and Perception: Effective advertising positions the product in a way that consumers perceive it as worth the price. By highlighting the unique aspects and superior qualities, advertising shapes consumers’ perception of the product’s value.
- Emphasizing Quality and Premium: Advertising can emphasize the high-quality materials, craftsmanship, or technology that justifies a premium price. This can create a perception of exclusivity and luxury among consumers.
Price Promotion and Its Impact on Consumer Behavior
- Discounts and Offers: Advertising plays a significant role in promoting price discounts, special offers, and promotions. These tactics can create a sense of urgency and encourage consumers to make a purchase.
- Influencing Purchase Decisions: Price promotions, such as limited-time offers or buy-one-get-one-free deals, can influence consumer behavior by triggering impulsive buying decisions.
- Brand Loyalty and Price Sensitivity: Advertising can reinforce brand loyalty by offering loyalty discounts or rewards programs. It can also communicate the long-term benefits of sticking with the brand, which reduces price sensitivity among loyal customers.
- Perceived Value and Sale Events: Advertising can create perceived value by promoting sales events, clearance sales, or end-of-season discounts. These events generate excitement and attract customers looking for good deals.
The Price element of the marketing mix is a crucial factor in consumer decision-making. Through advertising, companies can effectively communicate pricing strategies, justify the price based on product value, and influence consumer behavior through price promotions. Strategic use of advertising can enhance a product’s perceived value and create a positive impact on overall marketing efforts.
3. Place: Distribution and Advertising
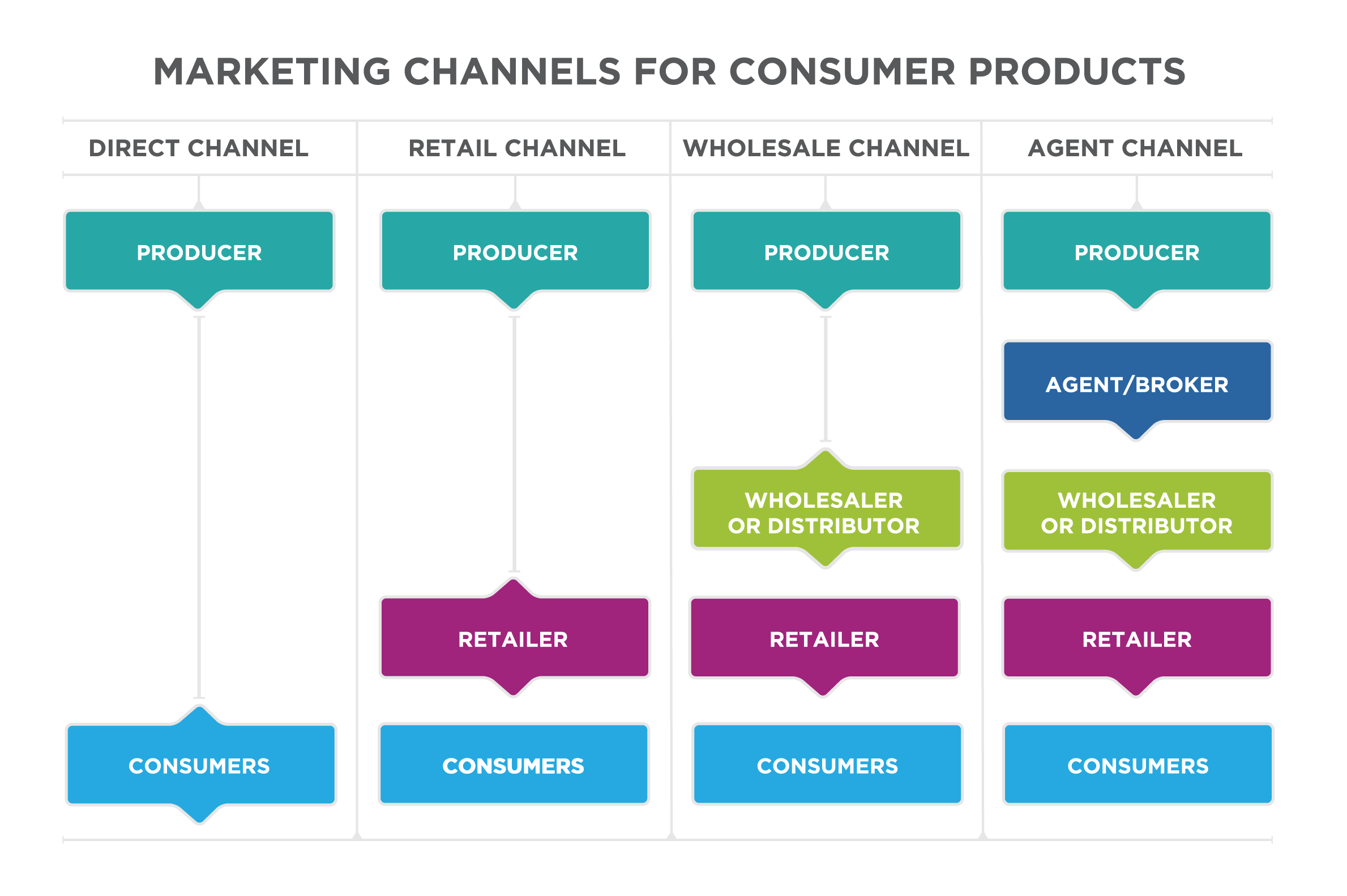
Price, Place, Distribution, and Advertising are essential components of the marketing mix that collectively contribute to a successful marketing strategy. Let’s explore each of them in detail:
Understanding Place in the Marketing Mix
Place, also known as Distribution, refers to the process of making the product available to consumers at the right time and in the right location. It involves the physical distribution of the product and the channels through which it reaches the end consumers. The key aspects of Place include:
- Physical Distribution: This involves the logistics and transportation of the product from the manufacturer to the retailer and finally to the consumer. Efficient physical distribution ensures timely availability of the product in the market.
- Distribution Channels: These are the intermediaries involved in the distribution process, such as wholesalers, retailers, and distributors. The choice of distribution channels can significantly impact the reach and accessibility of the product.
- Market Coverage: Decisions related to market coverage determine the extent of the product’s availability in different geographical areas. Market coverage can be selective, intensive, or exclusive, depending on the product and target market.
Leveraging Distribution Channels in Advertising
Advertising plays a vital role in leveraging distribution channels and maximizing the product’s visibility and accessibility to consumers. Here’s how advertising can achieve this:
- Brand Awareness: Advertising creates brand awareness among consumers, making them familiar with the product and its availability in the market. This increased visibility helps in attracting the attention of potential buyers.
- Channel Promotion: Advertising can promote the distribution channels themselves, highlighting the convenience of buying from specific retailers or online platforms. This encourages consumers to choose these channels for purchasing the product.
- Cooperative Advertising: Cooperative advertising involves collaborating with retailers and distributors to promote the product. By sharing advertising costs, manufacturers can increase the product’s visibility in various channels.
Geographical Targeting and its Relevance in Advertising
Geographical targeting in advertising refers to tailoring marketing messages and promotions based on specific locations or regions. This strategy is relevant in several ways:
- Local Marketing: Advertising can be customized to cater to the preferences and needs of consumers in different geographical areas. Localized campaigns can better resonate with the target audience and improve sales.
- Seasonal Advertising: Geographical targeting allows advertisers to adjust their messages based on regional seasons, events, or holidays. This makes the advertising more relevant and timely for consumers in specific locations.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Advertisers can be sensitive to cultural differences in different regions, ensuring that their messages do not offend or alienate specific communities.
- Market Expansion: Geographical targeting can be used strategically to expand the product’s market presence by entering new regions and attracting a diverse customer base.
Place or Distribution is a critical component of the marketing mix, and advertising plays a pivotal role in maximizing the product’s visibility and accessibility to consumers. By leveraging distribution channels and employing geographical targeting, advertisers can enhance brand awareness, promote specific channels, and cater to the preferences of diverse markets.
4. Promotion: Role of Advertising in Promotional Mix
Promotion is a vital element of the marketing mix that focuses on communicating the value of a product or service to the target audience. It encompasses various marketing activities aimed at creating awareness, generating interest, and encouraging customer engagement. Advertising plays a significant role in the promotional mix, as it allows businesses to reach a large audience, convey their brand messages, and promote their offerings effectively. Let’s explore the role of advertising in the promotional mix:
Components of the Promotional Mix
The promotional mix consists of various tools and techniques used to communicate with the target audience and promote the product or service. The key components of the promotional mix include:
- Advertising: Advertising is a paid form of communication, typically delivered through various media channels such as television, radio, print, digital, and social media. It aims to create awareness, inform, persuade, and remind the target audience about the product or brand.
- Sales Promotion: Sales promotion involves short-term incentives or offers to stimulate immediate purchasing behavior. Examples include discounts, coupons, free samples, contests, and loyalty programs.
- Public Relations (PR): Public relations focus on building and maintaining a positive image and relationship with the public, media, customers, and other stakeholders. PR activities may include press releases, media coverage, events, and sponsorships.
- Personal Selling: Personal selling involves direct communication between sales representatives and potential buyers. It allows for personalized product demonstrations, explanations, and addressing customer queries.
- Direct Marketing: Direct marketing refers to direct communication with individual consumers, often through email marketing, telemarketing, direct mail, and other personalized approaches.
Utilizing Advertising to Create Awareness and Demand
Advertising is a powerful tool in the promotional mix, especially for creating awareness and generating demand for the product or service. Here’s how advertising can achieve these objectives:
- Creating Awareness: Through advertising, companies can introduce their products to a wide audience and make them aware of the product’s features, benefits, and availability. It helps in building brand recognition and familiarity.
- Informing and Educating: Advertising provides an opportunity to educate consumers about the product’s unique selling points, its advantages over competitors, and how it fulfills their needs and desires.
- Building Desire: Effective advertising can create desire and aspiration for the product, appealing to consumers’ emotions and desires. It can showcase the product’s value proposition and how it can enhance the consumer’s lifestyle.
- Generating Demand: By showcasing the product’s benefits and appealing to consumer wants, advertising can stimulate demand for the product, leading to increased sales.
Coordinating Advertising with Other Promotional Tools
To achieve the best results, companies often coordinate advertising with other components of the promotional mix. Here’s how coordination can be beneficial:
- Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC): IMC involves aligning all promotional activities to create a seamless and consistent brand message. Coordinating advertising with other tools ensures a unified approach and reinforces the brand message across all channels.
- Synergy: Each component of the promotional mix has its strengths and weaknesses. By integrating advertising with other tools, companies can leverage the strengths of each tool to enhance the overall promotional impact.
- Reinforcement: Advertising can reinforce the messages communicated through other promotional tools. For example, an advertising campaign can reinforce a sales promotion or event, increasing its effectiveness.
In conclusion, advertising is a vital component of the promotional mix and plays a significant role in creating awareness, educating consumers, building desire, and generating demand for the product or service. By coordinating advertising with other promotional tools, companies can create a cohesive and effective marketing strategy to reach their target audience and achieve their marketing objectives.
Targeting the Right Audience
Targeting the right audience is a critical aspect of effective marketing. Identifying and reaching the most relevant audience ensures that marketing efforts are focused, cost-efficient, and yield higher conversion rates. Here are essential steps to target the right audience successfully:
1. Identifying Target Market Segments
Identifying target market segments is a critical step in developing an effective marketing strategy. It involves dividing the broader market into distinct groups of customers who share similar characteristics, needs, preferences, and behaviors. By understanding these segments, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to meet the specific needs of each group, leading to better customer engagement, higher conversion rates, and increased customer satisfaction.
Importance of Market Segmentation for Advertising
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a larger market into smaller, distinct groups of consumers who have similar characteristics, needs, preferences, and behaviors. It is a crucial step in developing an effective advertising strategy. Here’s why market segmentation is important for advertising:
- Efficient Resource Allocation: By identifying specific target segments, advertisers can focus their resources and efforts on reaching the most relevant and receptive audience. This helps in maximizing the return on investment (ROI) and minimizing wastage of resources.
- Message Relevance: Different segments have varying needs and preferences. Through market segmentation, advertisers can create tailored messages that resonate with each segment, increasing the chances of capturing their attention and interest.
- Better Understanding of Customers: Market segmentation provides valuable insights into the characteristics and behaviors of different customer groups. Advertisers can use this information to understand their customers better and address their pain points effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: By catering to specific market segments, advertisers can differentiate their products or services from competitors and create a unique selling proposition (USP).
Targeting Based on Demographics, Psychographics, and Behavior
When identifying target market segments for advertising, advertisers often consider three key criteria: demographics, psychographics, and behavior.
- Demographics: Demographic segmentation involves categorizing consumers based on objective, measurable characteristics such as age, gender, income, education, occupation, marital status, and geographic location. For example, a company may target young adults (18-24 years old) living in urban areas with higher education and disposable income for a premium product.
- Psychographics: Psychographic segmentation focuses on consumers’ lifestyles, values, interests, attitudes, and personality traits. Advertisers use psychographic information to understand what motivates their target audience and craft messages that align with their beliefs and aspirations.
- Behavior: Behavioral segmentation is based on consumers’ purchasing behavior, usage patterns, brand loyalty, and response to marketing stimuli. For instance, advertisers may target frequent buyers, first-time buyers, or brand switchers differently.
Tailoring Advertisements to Specific Audience Segments
Once market segments have been identified, advertisers can customize their advertisements to appeal to each segment effectively. Here are some strategies for tailoring advertisements to specific audience segments:
- Message and Content: Craft messages that address the unique needs, desires, and pain points of each segment. Use language, visuals, and examples that resonate with the segment’s preferences and lifestyle.
- Media Selection: Choose advertising channels that align with the media consumption habits of the target segment. For example, younger audiences may be more reachable through digital and social media, while older audiences may respond better to traditional print and television ads.
- Personalization: Leverage data-driven marketing to personalize advertisements for individual consumers within each segment. Personalization can enhance the relevance and impact of the message.
- Call-to-Action (CTA): Include specific and relevant CTAs in advertisements to encourage the target audience to take the desired action, whether it’s making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or visiting a store.
Market segmentation is essential for effective advertising. By identifying target market segments based on demographics, psychographics, and behavior, advertisers can create tailored advertisements that resonate with specific audience groups. This approach leads to more efficient resource allocation, better message relevance, and a competitive advantage in the market.
2. Consumer Behavior and Advertising
Consumer behavior and advertising are interconnected aspects of marketing that influence how customers make decisions and respond to promotional efforts. Understanding consumer behavior is crucial for advertisers to create effective campaigns that resonate with the target audience and drive desired actions.
Understanding Consumer Decision-Making Process
The consumer decision-making process refers to the series of steps that consumers go through when making a purchase or choosing a product or service. This process can be divided into several stages:
- Recognition of Need: The process begins when a consumer recognizes a need or a problem that requires a solution. This could be triggered by internal factors like hunger or external factors like advertisements.
- Information Search: After recognizing the need, consumers actively seek information about different products or services that could satisfy that need. They may use various sources such as online research, word-of-mouth, or advertisements to gather information.
- Evaluation of Alternatives: Once consumers have gathered information, they evaluate different alternatives to make an informed decision. They compare the features, benefits, prices, and other attributes of each option.
- Purchase Decision: After evaluating alternatives, the consumer makes the purchase decision. Factors like brand perception, price, and personal preferences influence this decision.
- Post-Purchase Evaluation: After the purchase, consumers assess their satisfaction with the product or service. Positive experiences may lead to brand loyalty, while negative experiences may result in dissatisfaction or switching to a different brand.
Psychological Factors Affecting Consumer Response to Advertising
Advertisers must understand the psychological factors that influence consumer responses to advertising. Some of the key factors include:
- Perception: Consumers’ perception of an advertisement depends on how they interpret and make sense of the information presented. Advertisers use various techniques to capture attention, create positive associations, and enhance memorability.
- Attitudes and Beliefs: Consumer attitudes and beliefs about a product or brand can significantly impact their response to advertising. Advertisers aim to shape positive attitudes and beliefs through persuasive messaging and emotional appeals.
- Motivation: Understanding consumer motivation is crucial for effective advertising. Motivation drives consumers to take action, and advertisers can use incentives, rewards, and appeals to motivate consumers to make a purchase.
- Learning and Memory: Consumers learn from advertisements and retain information in memory. Advertisers use repetition, storytelling, and visual cues to enhance learning and improve brand recall.
- Emotions: Emotional responses play a significant role in consumer decision-making. Advertisers often use emotional appeals to create connections with consumers and influence their buying behavior.
Incorporating Consumer Insights in Advertising Strategies
To create effective advertising campaigns, it is essential to incorporate consumer insights into the strategies. Here’s how advertisers can do this:
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand consumers’ needs, preferences, and pain points. Use surveys, focus groups, and data analysis to gain valuable insights.
- Segmentation: Use market segmentation to divide the target audience into distinct groups based on common characteristics and behaviors. This allows for personalized and targeted messaging.
- Message Tailoring: Customize advertisements to resonate with each segment by addressing their unique needs and aspirations.
- A/B Testing: Test different advertising strategies to identify the most effective approaches. A/B testing can help determine which messages, visuals, or platforms yield the best results.
- Engagement and Interaction: Encourage consumer engagement and interaction with the brand through social media, contests, or user-generated content. This fosters brand loyalty and builds a community of brand advocates.
By understanding the consumer decision-making process and the psychological factors that influence consumer behavior, advertisers can create more impactful and successful advertising campaigns. Incorporating consumer insights into advertising strategies helps build brand loyalty, drive sales, and achieve marketing objectives.
Crafting Compelling Advertising Campaigns
Crafting compelling advertising campaigns requires a thoughtful and strategic approach to engage the target audience, communicate the brand’s value proposition, and drive desired actions. Here are essential steps and best practices to create impactful and compelling advertising campaigns:
1. The Art of Storytelling in Advertising
The art of storytelling in advertising is a powerful technique used to captivate audiences, create emotional connections, and convey brand messages in a compelling and memorable way. Through storytelling, advertisers can transform ordinary advertisements into captivating narratives that resonate with consumers and leave a lasting impression.
Using Narratives to Engage Audiences
Storytelling is a powerful tool in advertising that captivates and engages audiences on a deeper level. Instead of simply presenting product features or benefits, advertisers weave narratives that resonate with consumers’ emotions and experiences. By creating relatable and compelling stories, brands can establish a meaningful connection with their target audience.
Successful advertising campaigns often feature relatable characters, compelling plots, and relatable situations that evoke emotions and provoke thought. These stories can be humorous, heartwarming, inspiring, or even thought-provoking. The goal is to leave a lasting impression and make the brand memorable in the minds of consumers.
Emotional Appeal and Story Arcs in Ads
Emotional appeal is a critical aspect of storytelling in advertising. By evoking emotions such as joy, nostalgia, empathy, or excitement, advertisers can create a strong bond between the audience and the brand. Emotions drive consumer behavior, and ads that trigger an emotional response are more likely to be remembered and shared.
A well-crafted story arc is another essential element of effective advertising. A story arc follows a narrative structure that includes an introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. This structure creates tension and keeps the audience engaged until the end of the ad. It also helps in delivering the brand’s message effectively.
Showcasing the Brand’s Values and Identity
Storytelling in advertising provides an opportunity for brands to showcase their values, mission, and identity. By aligning the brand’s story with its core values, advertisers can establish authenticity and build trust with consumers. When the audience identifies with the brand’s values, they are more likely to become loyal customers.
The brand’s identity should be reflected in the characters, settings, and themes of the ad. Consistency in storytelling helps in reinforcing the brand’s image and positioning in the market.
Advertisers can also use storytelling to highlight the brand’s impact on people’s lives, communities, or the environment. This social responsibility aspect can create a positive perception of the brand and attract socially-conscious consumers.
The art of storytelling in advertising goes beyond product promotion; it is about creating a connection with the audience and leaving a lasting impression. Through emotional appeal, well-crafted story arcs, and alignment with the brand’s values, advertisers can create compelling and memorable advertising campaigns that resonate with consumers on a deeper level. By understanding the power of storytelling, brands can craft ads that not only sell products but also build relationships and loyalty with their customers.
2. Creative Elements in Advertising
Creative elements in advertising are the artistic and visual components that make an advertisement visually appealing, memorable, and impactful. These elements play a crucial role in capturing the attention of the audience, conveying the brand’s message, and evoking emotions that resonate with consumers.
Importance of Visuals in Grabbing Attention
Visual elements play a crucial role in advertising as they are often the first thing that catches the audience’s attention. Human beings are naturally drawn to visuals, and incorporating eye-catching images or videos can instantly engage the audience.
Advertisers use visuals to create a strong association between the brand and its message. The use of colors, typography, and graphics can evoke emotions and convey the brand’s personality. A well-designed visual can communicate the brand’s essence and values, even without the need for extensive text.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, attention spans are limited, and advertisers have only a few seconds to make an impact. By using visually appealing elements, brands can stand out amidst the clutter and make a lasting impression on the audience.
Writing Persuasive Ad Copy
While visuals are essential, ad copy is equally vital in persuading the audience to take action. Ad copywriting involves crafting compelling and concise text that communicates the brand’s message effectively.
The key to writing persuasive ad copy lies in understanding the target audience and addressing their needs and desires. By focusing on the benefits of the product or service, advertisers can convince consumers that their lives will be better with the product in question.
Furthermore, the use of persuasive language, call-to-action phrases, and a sense of urgency can prompt immediate action from the audience. Effective ad copy should be clear, concise, and aligned with the brand’s tone and positioning.
Designing Memorable and Impactful Advertisements
To create impactful advertisements, a harmonious blend of visuals and ad copy is essential. The design should complement the copy and vice versa, creating a cohesive and memorable message.
Memorable advertisements often have a unique and distinctive visual style that sets them apart from competitors. Consistency in visual branding across various platforms reinforces brand recognition and builds trust with consumers.
Advertisers can also use storytelling techniques in visuals and ad copy to create a narrative that resonates with the audience. When consumers connect emotionally with an ad, they are more likely to remember the brand and develop a positive perception.
The impact of an advertisement is measured by its ability to influence consumer behavior positively. By crafting compelling visuals, persuasive ad copy, and a memorable overall design, advertisers can achieve their campaign objectives and drive desired actions from the audience.
The creative elements in advertising, such as visuals, ad copy, and overall design, are powerful tools for capturing the audience’s attention and driving engagement. By combining visually appealing elements with persuasive and compelling ad copy, brands can create impactful and memorable advertisements that resonate with the target audience. A well-executed advertising campaign can leave a lasting impression on consumers and reinforce brand loyalty.
3. Selecting the Right Advertising Channels
Selecting the right advertising channels is a critical aspect of creating a successful advertising campaign. Each advertising channel offers different advantages and reaches a distinct audience. By strategically choosing the appropriate channels, advertisers can effectively target their desired audience, maximize their reach, and achieve their marketing objectives.
Evaluating Different Media Options
When planning an advertising campaign, it’s essential to consider the various media options available. Each medium has its strengths and target audience, and choosing the right one depends on the campaign’s objectives and budget.
- Television: TV advertising remains a powerful tool for reaching a broad audience, particularly for products with mass appeal. It allows advertisers to use visuals and sound to create impactful messages.
- Radio: Radio advertising is effective for targeting specific demographics and local markets. It is often more cost-effective than television and can be used to reach commuters and listeners who prefer audio content.
- Print: Print advertising, including newspapers and magazines, can be beneficial for reaching specific niche audiences and engaging readers who prefer physical media.
- Outdoor: Billboards and outdoor advertising are ideal for creating brand awareness and reaching a wide audience in high-traffic areas.
- Digital: Digital advertising includes various channels such as online banners, social media ads, and search engine marketing. It allows for precise targeting and real-time data analysis.
- Social Media: Social media platforms offer unique opportunities for targeting specific demographics and engaging with consumers through interactive content.
- Influencer Marketing: Collaborating with influencers can enhance brand credibility and reach niche audiences that trust the influencer’s recommendations.
Combining Traditional and Digital Advertising
The modern advertising landscape calls for a strategic combination of traditional and digital advertising. While traditional media can still reach broad audiences, digital channels offer more granular targeting options and data-driven insights.
The key is to integrate both approaches seamlessly, ensuring a consistent brand message across all platforms. For instance, using a TV commercial to create brand awareness and supplementing it with social media ads to drive online engagement can be a powerful combination.
By integrating traditional and digital advertising, brands can effectively reach various segments of their target audience and maximize the campaign’s impact.
Leveraging Social Media and Influencer Marketing
Social media has transformed the way brands interact with consumers. It provides a direct line of communication and allows for real-time feedback and engagement. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn offer diverse opportunities to engage with users through organic posts and paid advertising.
Influencer marketing takes advantage of social media’s influence on consumer behavior. Partnering with influencers who align with the brand’s values can lead to authentic and persuasive content that resonates with their followers.
By leveraging social media and influencer marketing, brands can create a community around their products and services, fostering brand loyalty and driving word-of-mouth referrals.
Selecting the right advertising channels is a critical aspect of crafting a successful advertising campaign. By evaluating different media options, combining traditional and digital advertising, and leveraging social media and influencer marketing, brands can effectively engage with their target audience and achieve their campaign goals. The key is to develop a well-rounded strategy that aligns with the brand’s objectives and resonates with the consumers.
Measuring Advertising Effectiveness
Measuring advertising effectiveness is crucial for determining the success of an advertising campaign and optimizing future marketing efforts. It involves analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the impact of the ads on brand awareness, audience engagement, and conversion rates.
1. Key Metrics for Assessing Advertising Performance
Assessing advertising performance requires the analysis of key metrics that provide insights into how well the ads are achieving their intended objectives. These metrics help advertisers understand the impact of their campaigns, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions. Here are the key metrics for assessing advertising performance:
Reach and Frequency: Measuring Audience Exposure
Reach: refers to the total number of unique individuals or households exposed to an advertisement during a specific period. It provides an estimate of the size of the audience reached by the campaign.
Frequency: represents the average number of times an individual or household is exposed to the advertisement within the same time frame. It measures the repetition of the ad’s exposure to the same audience.
Evaluating the reach and frequency helps advertisers understand the extent of their ad’s visibility and the potential impact it can have on the target audience. It is essential to strike a balance between reaching a broad audience and maintaining an optimal frequency to avoid overexposure.
Click-Through Rates (CTR) and Conversion Rates
Click-Through Rate (CTR) measures the percentage of people who click on an ad after viewing it. It is commonly used in digital advertising, particularly for display ads and paid search campaigns.
CTR provides insights into how engaging and relevant the ad is to the audience. A higher CTR generally indicates that the ad is resonating well with the viewers and compelling them to take action, such as clicking on the ad to learn more.
Conversion Rate, on the other hand, measures the percentage of users who complete a desired action after clicking on the ad. This action could be making a purchase, filling out a form, signing up for a newsletter, etc.
While CTR indicates the ad’s ability to attract clicks, the conversion rate assesses its effectiveness in driving actual conversions. A high CTR may not necessarily lead to a high conversion rate if the landing page or user experience is not optimized.
Return on Advertising Investment (ROAI)
Return on Advertising Investment (ROAI) is a critical metric that calculates the revenue generated as a result of the advertising campaign compared to the total cost of the campaign.
ROAI helps advertisers understand the overall effectiveness and profitability of their advertising efforts. It considers both the revenue generated directly from the ad campaign and any other associated benefits, such as increased brand awareness and customer loyalty.
To calculate ROAI, the total revenue generated from the campaign is divided by the total advertising cost, and the result is expressed as a percentage. A positive ROAI indicates that the campaign is generating more revenue than it costs, making it a successful investment.
Measuring advertising effectiveness is essential to determine the impact of advertising campaigns and optimize future strategies. Key metrics such as reach, frequency, CTR, conversion rate, and ROAI provide valuable insights into how well the ads are performing and whether they are delivering the desired outcomes. By analyzing these metrics, advertisers can make informed decisions, refine their campaigns, and achieve better results.
2. Analyzing and Interpreting Advertising Data
Analyzing and interpreting advertising data is a crucial step in assessing the effectiveness of an advertising campaign. The data collected from various advertising channels and platforms provide valuable insights into the campaign’s performance, audience engagement, and return on investment.
Tools and Techniques for Data Analysis
Advertisers use various tools and techniques to analyze advertising data. These may include web analytics platforms, social media analytics tools, and data visualization software. These tools help advertisers track and measure the performance of their ads across different channels.
Making Data-Driven Decisions for Campaign Optimization
Data-driven decisions involve using the insights obtained from data analysis to optimize advertising campaigns. By understanding which ads perform best, advertisers can allocate their budget more effectively and make necessary adjustments to improve results.
Understanding Attribution Models in Advertising
Attribution models help advertisers understand which touchpoints or interactions lead to conversions. Different models, such as first-click, last-click, and multi-touch attribution, provide insights into the customer journey and the effectiveness of various marketing channels in driving conversions.
Understanding these attribution models allows advertisers to allocate credit and budget more accurately, ensuring that each marketing channel receives the appropriate recognition for its contribution to conversions.
Measuring advertising effectiveness through key metrics like reach, frequency, CTR, conversion rate, and ROAI is essential for advertisers. It provides valuable insights into the success of ad campaigns and helps advertisers make data-driven decisions for campaign optimization. Analyzing advertising data using appropriate tools and understanding attribution models enables advertisers to refine their strategies and achieve better results.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Advertising
Legal and ethical considerations in advertising are critical to ensuring that marketing campaigns comply with laws, regulations, and ethical standards while maintaining trust and credibility with consumers. Advertisers must be aware of various legal requirements and ethical principles to avoid potential legal issues and reputational damage.
1. Advertisements and Consumer Protection Laws
Advertisements are subject to consumer protection laws to ensure that consumers are not misled or deceived by false or unfair advertising practices. These laws are designed to safeguard consumers’ rights, promote fair competition, and maintain trust between businesses and their customers. Various regulations govern advertising practices, and they can vary by country or region.
Regulatory Framework for Advertising
Advertising is subject to various consumer protection laws and regulations that aim to safeguard the interests of consumers and promote fair competition. These regulations may vary from country to country, but they generally cover aspects such as false advertising, deceptive practices, and unfair competition.
False Advertising: Advertisers must avoid making false claims about their products or services. They should not provide misleading information that could deceive consumers.
Deceptive Practices: Advertisers should refrain from using tactics that mislead consumers or manipulate their understanding of the product’s features, pricing, or benefits.
Unfair Competition: Advertisers should not engage in practices that unfairly undermine their competitors’ businesses.
Ensuring Truthfulness and Avoiding Deception in Ads
To ensure truthfulness and transparency in advertising, advertisers should follow these guidelines:
1. Substantiation of Claims: Advertisers should have evidence to back up their claims about products or services. They should be able to provide proof that supports any statements made in the ads.
2. Clear and Unambiguous Language: Advertisements should use language that is clear and easily understandable by the target audience. Ambiguous or confusing language should be avoided.
3. Disclosure of Material Information: If there are any material conditions, limitations, or disclaimers related to the product or offer, they should be disclosed clearly and prominently in the advertisement.
4. Avoiding False Comparisons: Advertisers should refrain from making false or misleading comparisons with competitors’ products or services.
5. Honest Testimonials: Testimonials and endorsements should reflect the genuine opinions or experiences of the individuals involved.
Compliance with Advertising Standards and Guidelines
To ensure compliance with advertising standards and guidelines, advertisers can consider the following:
1. Self-Regulatory Bodies: Many industries have self-regulatory bodies that establish guidelines and standards for advertising within their sector. Advertisers can adhere to these industry-specific guidelines.
2. Government Regulatory Agencies: Advertisers should be aware of the regulatory agencies that oversee advertising practices in their region. They should comply with the rules and regulations set forth by these agencies.
3. Ethical Considerations: Advertisers should consider the ethical implications of their advertising. They should avoid tactics that may harm consumers or exploit vulnerable groups.
Adhering to consumer protection laws and ethical standards is essential for advertisers. By ensuring truthfulness, avoiding deception, and complying with advertising regulations, advertisers can build trust with consumers and maintain a positive reputation. Advertisers should stay updated with the evolving advertising landscape and adapt their practices accordingly to remain compliant and ethical in their advertising efforts.
2. Ethical Advertising Practices
Ethical advertising practices involve promoting products and services in a manner that upholds honesty, transparency, and respect for consumers’ rights and values. Ethical advertising not only ensures legal compliance but also fosters trust, credibility, and a positive brand reputation.
Responsibility towards Consumers and Society
Ethical advertising practices prioritize the well-being of consumers and society as a whole. Advertisers should take the following responsibilities seriously:
1. Truthfulness and Accuracy: Advertisements should provide accurate information about products and services. Claims made in ads should be substantiated with evidence to avoid misleading consumers.
2. Protection of Vulnerable Groups: Advertisers should be cautious not to exploit or deceive vulnerable groups, such as children, the elderly, or individuals with specific needs.
3. Privacy and Data Protection: Advertisers should respect consumer privacy and adhere to data protection laws when collecting and using personal information for advertising purposes.
4. Honesty in Testimonials: Testimonials and endorsements should reflect the genuine experiences and opinions of individuals and not be fabricated or misleading.
5. Avoiding Harmful Content: Advertisements should not promote harmful products or behaviors, such as tobacco, drugs, or unsafe practices.
6. Social and Environmental Responsibility: Ethical advertisers consider the social and environmental impact of their products and avoid promoting items that could harm individuals or the planet.
Diversity and Inclusivity in Advertising
Ethical advertising practices embrace diversity and inclusivity to reflect the varied experiences and identities of consumers. Advertisers should consider the following:
1. Representation: Advertisements should feature diverse representations of race, ethnicity, gender, age, and other identities to avoid stereotypes and promote inclusivity.
2. Cultural Sensitivity: Advertisers should be culturally sensitive and avoid appropriating or misrepresenting cultures in their ads.
3. Accessibility: Advertisements should be accessible to individuals with disabilities, considering visual and auditory impairments, and provide appropriate accommodations.
4. Language: Advertisers should use clear and inclusive language that appeals to diverse audiences and avoids offensive or discriminatory terms.
Avoiding Controversial and Offensive Content
Ethical advertisers should steer clear of content that may cause harm, controversy, or offense. Considerations include:
1. Respectful Messaging: Advertisements should avoid offensive, violent, or explicit content that could upset or harm audiences.
2. Sensitivity to Social Issues: Advertisers should be cautious when addressing sensitive social or political issues, ensuring their messaging is responsible and respectful.
3. Brand Safety: Advertisers should ensure their ads do not appear alongside harmful or inappropriate content online.
Ethical advertising practices are essential for building trust with consumers and promoting a positive impact on society. Advertisers should prioritize truthfulness, consumer well-being, and inclusivity in their advertising efforts. By taking social responsibility seriously and avoiding controversial or harmful content, advertisers can contribute to a more ethical and socially conscious advertising landscape.
Conclusion
Mastering the 4Ps of the marketing mix is the key to powerful advertising. From showcasing products to setting the right price, crafting compelling promotions, and selecting strategic placements, each element plays a vital role in captivating your audience. By achieving synergy and integration, advertisers can create a cohesive and impactful message that resonates with their target customers. Embracing future trends and staying agile in the dynamic advertising landscape will ensure continued success. Remember, with the right mix, your advertising game will be unstoppable!
