What Are Marketing Pricing Strategies
What are marketing pricing strategies, and how can they impact your business’s success? In the competitive world of commerce, pricing plays a pivotal role in influencing consumer behavior and determining a company’s profitability. From premium pricing to penetration pricing and everything in between, understanding the various pricing strategies empowers businesses to make strategic decisions that resonate with their target audience. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating realm of marketing pricing strategies and uncover the secrets to optimizing your pricing approach for maximum results. Get ready to unlock the potential of pricing strategies and gain a competitive edge in the market!
Overview of Marketing Pricing Strategies
Marketing pricing strategies encompass a range of approaches that businesses adopt to determine the most effective pricing for their offerings. These strategies take into account various factors, including costs, customer behavior, competition, and market dynamics. By understanding and employing these strategies, businesses can enhance their competitive edge and achieve their financial objectives.
Thesis Statement
This article explores the key marketing pricing strategies and examines how they influence consumer behavior and contribute to the overall success of businesses. By analyzing these strategies and their real-world applications, readers will gain valuable insights into the art and science of pricing and learn to make informed decisions that drive business growth.
What Are Marketing Pricing Strategies
Marketing pricing strategies are techniques that businesses use to set the prices of their products or services to achieve specific marketing objectives. Pricing plays a crucial role in the overall marketing mix, as it directly affects sales, profitability, and brand perception. There are several pricing strategies that businesses can adopt based on their target market, competition, and product positioning. Here are some common marketing pricing strategies:
4 Common Marketing Pricing Strategies
I. Cost-Based Pricing Strategies

Cost-based pricing strategies are based on determining the price of a product or service by considering the costs incurred in producing or providing it. These strategies provide a straightforward approach to pricing and ensure that costs are covered while generating a desired profit margin. Here is a breakdown of the key cost-based pricing strategies:
Definition and Rationale Behind Cost-Based Pricing
Cost-based pricing involves setting prices by adding a markup or profit margin to the cost of producing or acquiring a product. The rationale behind this strategy is to ensure that the selling price adequately covers the costs incurred and allows for a reasonable profit.
1. Markup Pricing
Markup pricing is a common cost-based strategy where a predetermined percentage is added to the cost of a product to determine its selling price. The markup percentage is usually based on industry norms or desired profit margins. This strategy simplifies pricing decisions by focusing on a consistent margin across products.
2. Cost-Plus Pricing
Cost-plus pricing involves calculating the total cost of producing a product and then adding a predetermined markup percentage to cover both costs and desired profit. This approach provides a more comprehensive view of costs and allows for more precise pricing decisions based on individual products.
3. Target Return Pricing
Target return pricing aims to achieve a specific return on investment (ROI) or target profit margin. This strategy considers the desired level of profitability and sets prices accordingly. By focusing on achieving a specific financial goal, businesses can align their pricing with their profitability objectives.
4. Break-Even Pricing
Break-even pricing involves determining the price at which total revenue equals total costs, resulting in zero profit or loss. This strategy is particularly useful for new products or businesses aiming to recover costs and establish a market presence. It helps determine the minimum price required to cover expenses.
Pros and Cons of Cost-Based Pricing Strategies
Pros:
- Provides a straightforward and easy-to-understand pricing approach.
- Ensures that costs are covered and allows for desired profit margins.
- Simplifies pricing decisions by focusing on costs and profitability.
Cons:
- Ignores customer demand and value perceptions, potentially leading to misalignment with the market.
- Does not consider external factors such as competition or consumer preferences.
- May not fully capture the value or uniqueness of a product, limiting pricing flexibility.
Real-World Examples of Companies Utilizing Cost-Based Pricing Strategies
- Supermarket Chains: Many supermarket chains apply cost-based pricing strategies for their private-label products. The pricing is determined by calculating the production costs, adding a desired profit margin, and adjusting for industry standards.
- Construction Companies: Construction companies often use cost-based pricing to determine the pricing for their services. Costs, such as labor, materials, equipment, and overhead expenses, are considered along with a predetermined markup to calculate the selling price.
- Manufacturing Companies: Manufacturers frequently adopt cost-based pricing strategies, especially for standardized products. By factoring in production costs and desired profit margins, they set prices that ensure profitability while remaining competitive within the market.
- Professional Service Providers: Many professional service providers, such as consultants, lawyers, or accountants, employ cost-based pricing. They calculate their hourly rates based on their expenses, overhead costs, and desired profitability.
These examples illustrate how businesses across various industries utilize cost-based pricing strategies to determine their prices and achieve profitability. However, it’s important to note that cost-based pricing is just one approach and should be considered alongside other factors to create a comprehensive pricing strategy.
II. Value-Based Pricing Strategies
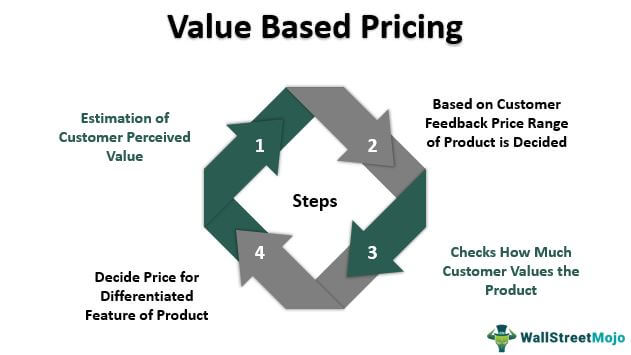
Value-based pricing strategies focus on setting prices based on the perceived value of a product or service to the customer. Rather than solely considering costs or competition, value-based pricing emphasizes the customer’s willingness to pay for the benefits and value they receive. Here is an exploration of key value-based pricing strategies:
Definition and Rationale Behind Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing involves setting prices based on the perceived value that a product or service delivers to customers. The rationale behind this strategy is that customers are willing to pay more for offerings that they perceive as valuable, unique, and aligned with their needs and preferences. Value-based pricing allows businesses to capture the maximum value they provide to customers and can lead to higher profitability.
1. Premium Pricing
Premium pricing is a strategy where products or services are priced higher than competitors’ offerings to create the perception of superior quality, exclusivity, or luxury. This approach is commonly used for products with unique features, exceptional craftsmanship, or prestigious branding. By positioning the product as high-value and charging a premium, businesses can attract customers who associate price with quality and are willing to pay more for perceived superiority.
2. Skimming Pricing
Skimming pricing involves setting initially high prices for new or innovative products to capitalize on the early adopters or customers willing to pay a premium. This strategy is suitable when a product offers significant advantages or is considered highly desirable. Over time, as the market becomes more competitive or customer demand evolves, the price may be gradually lowered to target broader customer segments.
3. Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing aims to set the initial price of a product or service relatively low to gain rapid market share and attract price-sensitive customers. This strategy is effective when businesses aim to quickly establish a customer base, create brand awareness, or disrupt existing markets. By offering competitive prices, businesses can generate demand, drive sales volume, and potentially benefit from economies of scale, leading to long-term profitability.
4. Bundle Pricing
Bundle pricing involves offering multiple products or services together as a package at a discounted price compared to purchasing each item separately. This strategy creates value by providing customers with convenience, cost savings, or additional features. Bundling can increase the overall perceived value of the offering and incentivize customers to choose the bundled package over individual items.
Pros and Cons of Value-Based Pricing Strategies
Pros:
- Aligns pricing with customer value perception, maximizing the willingness to pay.
- Allows businesses to capture the value they provide and increase profitability.
- Supports differentiation and premium positioning in the market.
Cons:
- Requires a deep understanding of customer preferences, needs, and willingness to pay.
- May be challenging to quantify and communicate the value proposition effectively.
- Can be less suitable for products or services with commoditized or price-sensitive markets.
Real-World Examples of Companies Utilizing Value-Based Pricing Strategies
- Apple: Apple is known for implementing premium pricing strategies for its products, such as iPhones and MacBooks. By offering high-quality, innovative devices with a sleek design and a user-friendly experience, Apple has successfully created a perception of exclusivity and luxury, allowing them to charge premium prices.
- Tesla: Tesla, an electric vehicle manufacturer, applies a combination of skimming and value-based pricing strategies. Initially, Tesla introduced its electric cars at premium prices to target early adopters and showcase their cutting-edge technology. As the market expanded and competition increased, Tesla introduced more affordable models to reach a broader customer base.
- Netflix: Netflix uses a bundle pricing strategy by offering different subscription plans that include access to its streaming service. By providing various options based on the number of screens or video quality, Netflix caters to different customer needs and price points, increasing the perceived value and attracting a wide range of subscribers.
- Luxury Fashion Brands: Companies like Louis Vuitton, Gucci, and Chanel employ premium pricing strategies in the luxury fashion industry. By positioning themselves as exclusive and offering high-quality materials, craftsmanship, and unique designs, these brands can command premium prices and maintain a sense of luxury and prestige.
These examples highlight how companies leverage value-based pricing strategies to differentiate themselves, communicate value to customers, and capture a premium for their offerings. Successful implementation of value-based pricing requires a deep understanding of the target market, effective communication of value propositions, and continuous monitoring of customer preferences and market dynamics.
III. Competition-Based Pricing Strategies

Competition-based pricing strategies involve setting prices based on the prices charged by competitors. This approach takes into account the pricing decisions of other businesses operating in the same market. Here is an examination of key competition-based pricing strategies:
Definition and Rationale Behind Competition-Based Pricing
Competition-based pricing is a strategy that considers the prices set by competitors as a benchmark for determining the prices of products or services. The rationale behind this approach is to stay competitive in the market by aligning prices with what customers are willing to pay in relation to similar offerings. By monitoring and responding to competitor pricing, businesses aim to attract customers, maintain market share, and mitigate the risk of losing sales to rivals.
1. Price Matching
Price matching involves setting prices at the same level as competitors for identical or similar products or services. This strategy ensures that customers perceive the offering as competitively priced and reduces the likelihood of losing customers due to higher prices. Price matching can be an effective way to maintain market share and prevent customers from switching to competitors offering lower prices.
2. Discount Pricing
Discount pricing entails setting prices below the regular or original price to attract price-sensitive customers. This strategy aims to increase sales volume by leveraging lower prices as a competitive advantage. Discounts can be offered through various means, such as limited-time promotions, seasonal sales, or bulk purchase discounts. Discount pricing can help businesses stimulate demand, clear excess inventory, and attract price-conscious customers.
3. Loss Leader Pricing
Loss leader pricing involves offering a product or service at a price lower than the cost incurred by the business. The purpose of this strategy is to attract customers to the low-priced item with the expectation that they will also purchase additional higher-margin products or services. While the initial item may be sold at a loss, the goal is to generate revenue and profit through complementary or follow-up purchases. Loss leader pricing can be particularly effective in retail settings or industries where customer loyalty and repeat purchases are essential.
4. Price Leadership
Price leadership refers to a situation where one dominant company in a market sets the price, and other competitors follow suit. This strategy typically occurs when a market leader, with a significant market share and influence, establishes price levels that competitors find difficult to deviate from. Price leadership can lead to price stability in the market, reduce intense price competition, and create an environment where competitors adjust their prices in response to the market leader’s pricing decisions.
Pros and Cons of Competition-Based Pricing Strategies
Pros:
- Enables businesses to respond to competitive dynamics and stay relevant in the market.
- Helps attract price-sensitive customers by offering competitive prices.
- Reduces the risk of losing customers to competitors with lower prices.
- Can contribute to market stability when price leadership is established.
Cons:
- Focuses primarily on price as a competitive factor, potentially neglecting other value propositions.
- This may lead to price wars and diminishing profit margins if competitors continuously undercut each other.
- Limits pricing decisions to the actions of competitors rather than independent market analysis.
- This can result in a race to the bottom, eroding profitability for all businesses in the market.
Real-World Examples of Companies Utilizing Competition-Based Pricing Strategies
- Walmart: Walmart is known for its discount pricing strategy, offering a wide range of products at low prices. By leveraging its purchasing power and operational efficiencies, Walmart aims to offer competitive prices that attract customers looking for affordability. Its “Everyday Low Prices” approach has made Walmart a price leader in the retail industry.
- Amazon: Amazon utilizes price matching as part of its pricing strategy. The company continually monitors competitor prices and adjusts its own prices to match or beat them. Through its algorithmic pricing system, Amazon ensures that customers perceive its prices as competitive and compelling, helping it capture a significant share of the e-commerce market.
- Airlines: Airlines often employ competition-based pricing strategies by closely monitoring competitors’ prices and adjusting their own fares accordingly. Dynamic pricing models and fare-matching initiatives are used to attract customers and remain competitive in a price-sensitive industry. This approach allows airlines to respond to changes in demand, market conditions, and competitor actions.
- Fast-Food Chains: Fast-food chains frequently use discount pricing to drive sales and attract customers. Through limited-time promotions, value menus, and combo deals, they offer discounted prices to entice customers to visit their establishments. By providing affordable options, fast-food chains aim to maintain customer loyalty and compete with other players in the highly competitive fast-food industry.
These examples demonstrate how competition-based pricing strategies are employed across various industries. By closely monitoring competitors’ pricing decisions and implementing appropriate pricing tactics, businesses can respond to market dynamics, attract customers, and gain a competitive edge. However, it is important for businesses to carefully assess the long-term implications of intense price competition and consider other value drivers to maintain profitability and sustainable growth.
IV. Psychological Pricing Strategies

Psychological pricing strategies involve setting prices based on psychological factors that influence consumer perception and behavior. These strategies take advantage of customers’ cognitive biases and emotions to shape their perception of price and encourage purchasing decisions. Here is an exploration of key psychological pricing strategies:
Definition and Rationale Behind Psychological Pricing
Psychological pricing is a strategy that leverages the psychological and emotional responses of consumers to certain price points. It aims to create a perception of value, affordability, or prestige by strategically setting prices. The rationale behind psychological pricing is that consumers are not purely rational when making purchasing decisions; instead, they are influenced by subconscious psychological cues and biases.
1. Odd-Even Pricing
Odd-even pricing is a strategy that involves setting prices ending in odd numbers (e.g., $9.99) or even numbers (e.g., $10.00) instead of rounded figures. This strategy capitalizes on the left-digit effect, where consumers tend to focus more on the leftmost digit of a price. Prices ending in 9, such as $9.99, create the perception of a significantly lower price compared to a rounded figure like $10.00. This strategy exploits consumers’ tendency to perceive a psychological difference between prices that differ by just a few cents.
2. Prestige Pricing
Prestige pricing, also known as premium pricing or image pricing, involves setting higher prices for products or services to create a perception of exclusivity, luxury, or superior quality. This strategy taps into the association between higher prices and superior value, leading consumers to believe that higher-priced items are of higher quality. Prestige pricing is commonly employed by luxury brands, high-end retailers, and businesses targeting affluent customers who equate price with desirability or status.
3. Charm Pricing
Charm pricing is a strategy that involves setting prices slightly below a whole number (e.g., $9.95 instead of $10). This strategy takes advantage of consumers’ tendency to focus on the leftmost digit while perceiving the rightmost digits as insignificant. The price difference between $9.95 and $10 seems relatively small, yet the presence of the number 9 makes the price feel significantly lower. Charm pricing exploits consumers’ cognitive bias and their inclination to perceive prices as more appealing when they are slightly below the next whole number.
4. Bundle Pricing
Bundle pricing is a strategy where multiple products or services are offered together as a package at a lower combined price than if each item were purchased separately. This strategy creates the perception of a better deal or value for the customer. By bundling products, businesses can increase sales volume and encourage customers to trade up to a higher-priced bundle, even if they may not have initially considered purchasing all the items individually. Bundle pricing leverages the principle of perceived value and taps into consumers’ desire for cost savings.
Pros and Cons of Psychological Pricing Strategies
Pros:
- Influences consumer perception and behavior through psychological cues.
- Can create a perception of value, affordability, or prestige.
- May increase sales volume and encourage purchasing decisions.
- Allows businesses to differentiate their offerings and stand out in the market.
Cons:
- May be perceived as manipulative or deceptive if not used ethically.
- Not suitable for all product categories or target markets.
- Requires a deep understanding of consumer psychology and market dynamics.
- Effectiveness may vary depending on cultural, regional, or demographic factors.
Real-World Examples of Companies Utilizing Psychological Pricing Strategies
- Apple: Apple Inc. employs prestige pricing for its products, positioning them as premium and high-end. By setting higher prices compared to competitors, Apple creates a perception of superior quality, cutting-edge technology, and exclusivity. The higher price points contribute to the brand’s image as a luxury and aspirational choice for consumers.
- Amazon: Amazon utilizes bundle pricing as part of its strategy. The company often offers product bundles, such as “Frequently Bought Together” or “Customers Who Bought This Also Bought,” which present complementary items at a discounted price when purchased together. By bundling products, Amazon encourages customers to spend more and enjoy the perceived value of a bundled deal.
- Walmart: Walmart utilizes odd-even pricing extensively throughout its stores. By setting prices that end in 9 (e.g., $9.99), Walmart creates the perception of lower prices and affordability. The practice of ending prices with 9 has become a common strategy in the retail industry, with many businesses using it to appeal to price-conscious customers.
- McDonald’s: McDonald’s utilizes charm pricing in its menu pricing. The company often sets prices for its value menu items just below whole numbers (e.g., $0.99 instead of $1.00). This approach creates the perception of lower prices, encouraging customers to perceive the items as highly affordable options.
These examples illustrate how psychological pricing strategies are implemented by well-known companies. By leveraging consumers’ psychological biases and emotions, businesses can shape perceptions of value, affordability, and quality, influencing purchasing decisions in their favor. However, it is crucial for businesses to use these strategies ethically and consider the overall value proposition of their products or services to ensure long-term customer satisfaction and trust.
Conclusion
Discover the power of pricing strategies! In this article, we explored five key approaches: cost-plus, competitive, price skimming, penetration, and value-based pricing. Each method offers unique advantages and considerations for your business. From maximizing early profits to captivating customers with value-driven offers, the right pricing strategy can make or break your success. So, which one will you choose? Select wisely and watch your business thrive in the ever-changing market landscape. Remember, pricing decisions hold the key to profitability, customer perception, and market positioning. Stay informed, stay agile, and let your pricing strategy be the catalyst for sustainable growth and triumph!


