Unleashing the Power of Generic Marketing Strategies
Are you ready to unlock the secrets of effective marketing strategies that transcend industries and stand the test of time? Look no further! In this article, we will dive into the world of generic marketing strategies and discover how they can unleash the true potential of your business. Whether you’re a startup founder, a seasoned entrepreneur, or a marketing enthusiast, these powerful strategies have the potential to revolutionize your approach and drive remarkable results.
Join us on this captivating journey as we delve into the core principles of generic marketing strategies and explore how they can pave the way for success in any competitive landscape. Let’s dive in and harness the true power of these time-tested marketing approaches!
Understanding Generic Marketing Strategies
Generic marketing strategies refer to a set of broad, overarching approaches that businesses adopt to achieve a competitive advantage in the marketplace. These strategies can be applied to products or services across various industries and are not limited by the size or type of organization.
What are Generic Marketing Strategies?
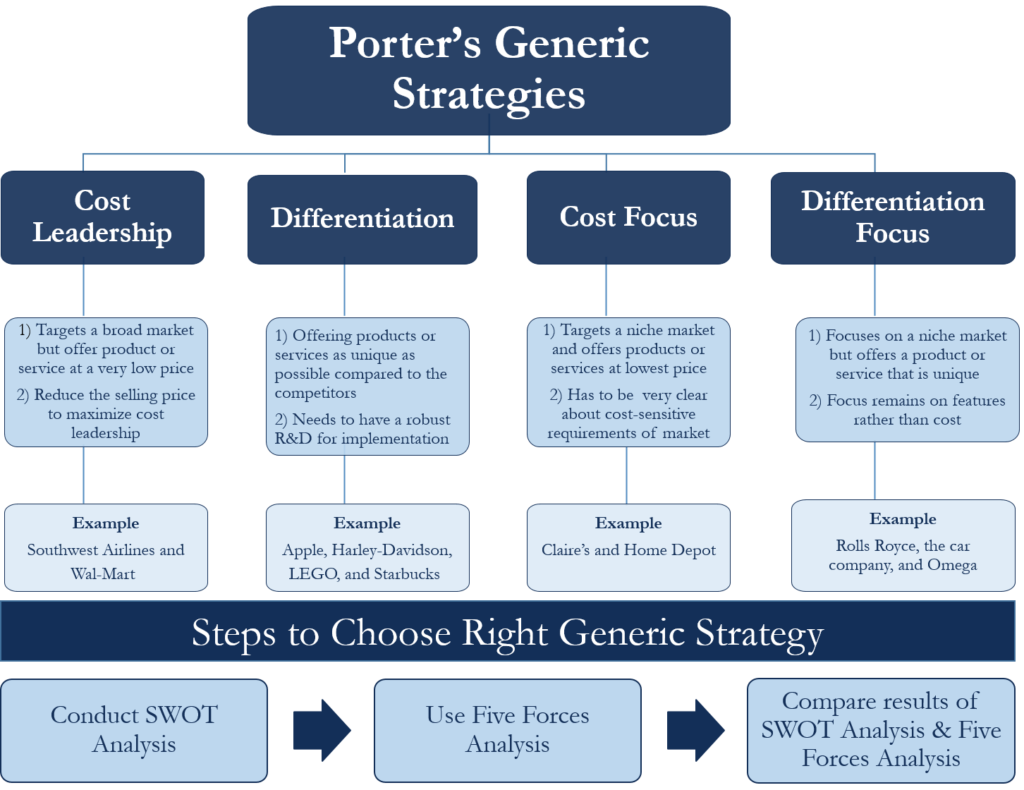
Generic marketing strategies were first introduced by Michael Porter in 1985 in his book, “Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance.” Porter identified three primary generic strategies: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. Cost leadership involves achieving a competitive edge by minimizing costs and offering products or services at lower prices. Differentiation focuses on creating unique and desirable offerings that stand out from competitors. Focus strategy targets a specific niche market by tailoring products or services to meet the unique needs of that segment.
Importance of Generic Marketing Strategies for Businesses
Having a well-defined generic marketing strategy is crucial for businesses for several reasons. Firstly, it provides a clear direction and framework for decision-making, ensuring that all efforts align with the overall strategic objectives. A well-executed generic marketing strategy helps businesses differentiate themselves from competitors, attract target customers, and build a sustainable competitive advantage. It allows organizations to position themselves effectively in the market and communicate their value proposition to customers.
Generic marketing strategies also enable businesses to optimize resource allocation and enhance operational efficiency. By focusing on specific strategies, companies can streamline their processes, allocate resources efficiently, and deliver products or services that meet customer expectations. Additionally, generic marketing strategies help businesses adapt to market changes and remain agile in the face of evolving consumer preferences and competitive dynamics.
Common Misconceptions About Generic Marketing Strategies
Despite the benefits of generic marketing strategies, there are some common misconceptions that need to be addressed. One misconception is that these strategies are one-size-fits-all approaches that guarantee success. In reality, the effectiveness of a generic marketing strategy depends on various factors, such as the industry, target market, and competitive landscape. It is essential for businesses to tailor and customize these strategies to suit their specific contexts.
Another misconception is that generic marketing strategies are static and unchanging. In fact, successful organizations continually evaluate and adapt their strategies to remain relevant and competitive. The market is dynamic, and customer preferences evolve over time. Businesses need to stay vigilant, monitor market trends, and be willing to make adjustments to their strategies to meet changing demands.
Lastly, some may believe that generic marketing strategies are only applicable to large corporations. However, these strategies can be implemented by businesses of all sizes, including small and medium-sized enterprises. The key is to understand the unique strengths and capabilities of the organization and align the strategy accordingly.
By understanding the true essence of generic marketing strategies and dispelling these misconceptions, businesses can harness their power to drive growth, outperform competitors, and achieve sustainable success in the marketplace.
The Four Pillars of Generic Marketing Strategies
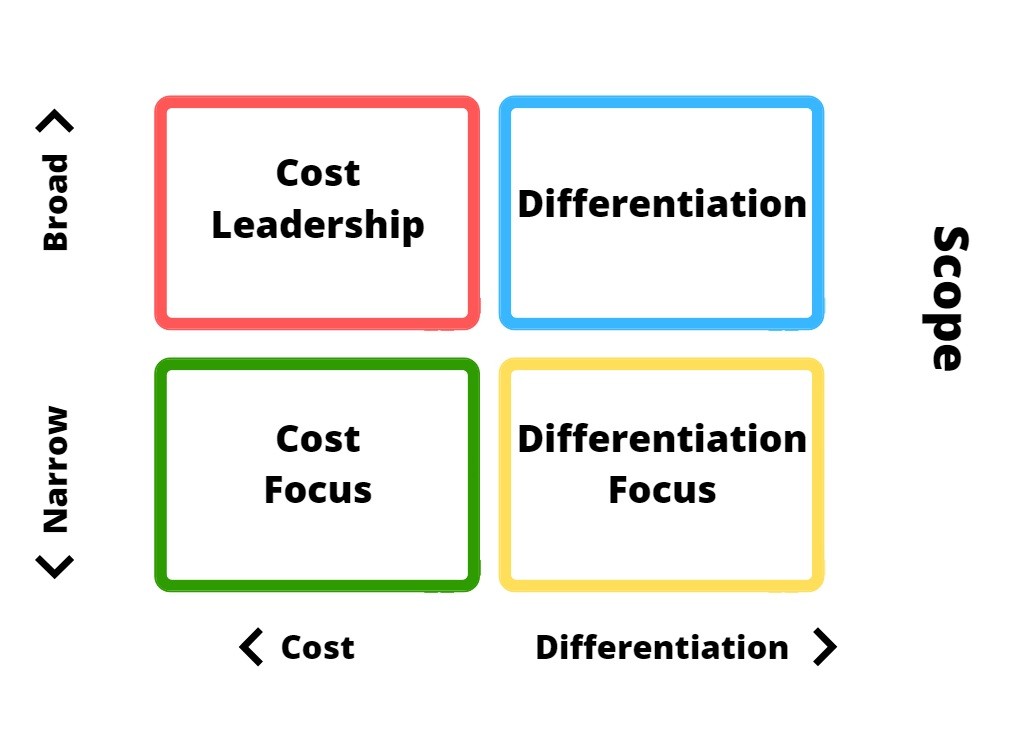
In the realm of generic marketing strategies, there are four key pillars that organizations can leverage to gain a competitive advantage. Each strategy offers a unique approach to positioning and differentiating a business in the market. Let’s explore each strategy in detail:
A. Cost Leadership Strategy
The cost leadership strategy aims to become the industry’s low-cost producer or provider while maintaining profitability. Organizations following this strategy focus on minimizing costs across their value chain, allowing them to offer products or services at lower prices than their competitors. By achieving cost leadership, companies can gain market share and potentially drive competitors out of the market.
Examples of companies successfully implementing cost leadership:
- Walmart: Walmart has achieved cost leadership by employing efficient supply chain management practices, negotiating favorable deals with suppliers, and leveraging economies of scale. These cost-saving measures enable Walmart to offer everyday low prices and attract price-sensitive customers.
Key considerations for implementing a cost leadership strategy:
- Invest in technologies and processes that help streamline operations, reduce production costs, and improve efficiency.
- Develop strategic partnerships with suppliers to negotiate lower prices for raw materials or components.
- Continuously monitor and analyze costs to identify areas for improvement and implement cost-reduction measures.
- Establish stringent cost control measures to ensure ongoing cost efficiency throughout the organization.
Potential challenges and risks associated with cost leadership:
- Increased competition from new entrants or existing competitors that can replicate cost-saving strategies.
- Difficulty in differentiating the brand solely based on price, leading to the perception of low quality.
- Volatile market conditions or fluctuating costs could affect profitability.
- Limited ability to pass cost savings onto customers in highly price-sensitive markets.
B. Differentiation Strategy
The differentiation strategy focuses on creating unique and desirable products or services that stand out in the market. Organizations adopting this strategy seek to provide added value to customers through features, quality, innovation, customer service, or brand image. By differentiating themselves, companies can command higher prices and build customer loyalty.
Examples of companies successfully implementing differentiation:
- Apple: Apple has differentiated itself through its innovative design, user-friendly interfaces, and seamless integration of hardware and software. Their products, such as iPhones and MacBooks, offer a unique and premium experience, setting them apart from competitors.
Key considerations for implementing a differentiation strategy:
- Conduct market research to understand customer needs, preferences, and pain points.
- Invest in research and development to innovate and create products or services that address customer demands.
- Build a strong brand image and communicate the unique value proposition effectively to target customers.
- Continuously monitor the competitive landscape to ensure sustained differentiation.
Potential challenges and risks associated with differentiation:
- High costs associated with research, development, and innovation.
- The risk of imitation by competitors, diluting the uniqueness of the differentiation.
- Difficulty in maintaining consistent differentiation across different product lines or geographic markets.
- Limited market segments or niche markets that appreciate differentiated features.
C. Focus Strategy
The focus strategy involves concentrating efforts on serving a specific niche market or a particular customer segment. By understanding the unique needs, preferences, and dynamics of the target market, organizations can develop tailored products or services that cater specifically to those customers. Focus strategies can be based on either cost focus or differentiation focus.
Examples of companies successfully implementing focus strategy:
- Rolex: Rolex has successfully implemented a focus strategy by targeting the luxury watch market. They have positioned themselves as a symbol of prestige, craftsmanship, and exclusivity, catering to high-end customers who value luxury timepieces.
Key considerations for implementing a focus strategy:
- Thoroughly research and understand the targeted niche market, including customer preferences, behavior, and unmet needs.
- Tailor products, services, and marketing efforts to cater to the specific demands of the chosen market segment.
- Build strong relationships with customers in the niche market to foster loyalty and brand advocacy.
- Continuously monitor changes in the market and adapt the focus strategy accordingly.
Potential challenges and risks associated with focus strategy:
- Limited market size and potential revenue compared to broader market strategies.
- The risk of market changes or shifts that may render the niche market less attractive.
- Dependence on the specific niche market makes the organization vulnerable to changes in customer preferences or economic conditions.
- Intense competition from other focused competitors targeting the same market segment.
D. Combination Strategy
The combination strategy, as the name suggests, involves combining elements of two or more generic strategies to create a unique approach. This strategy allows organizations to tailor their offerings to specific market segments while achieving either cost leadership or differentiation. It can involve targeting multiple market segments with different strategies or offering a hybrid product that provides both value and differentiation.
Examples of companies successfully implementing combination strategy:
- Toyota: Toyota has implemented a combination strategy by offering a range of vehicles that cater to different market segments. They provide cost-effective and fuel-efficient models, such as the Corolla, targeting price-sensitive customers. Simultaneously, they offer higher-end vehicles, like the Lexus, focusing on luxury and differentiation.
Key considerations for implementing a combination strategy:
- Identify the specific market segments to target and determine the appropriate combination of generic strategies to meet their needs.
- Develop a clear value proposition for each target segment that highlights the unique features or cost advantages.
- Ensure alignment across different elements of the organization, including operations, marketing, and customer service, to deliver the desired combination strategy.
Potential challenges and risks associated with combination strategy:
- The complexity of managing multiple strategies simultaneously.
- Potential conflicts or trade-offs between cost leadership and differentiation elements within the organization.
- The need for sufficient resources and capabilities to effectively execute the combination strategy.
- Continuous monitoring and adaptation to changes in market dynamics and customer preferences.
By understanding and carefully implementing these four pillars of generic marketing strategies, organizations can position themselves strategically, gain a competitive advantage, and drive business success in their respective markets.
Selecting the Right Generic Marketing Strategy
Choosing the appropriate generic marketing strategy requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some key points to consider when selecting a generic marketing strategy:
Factors to consider when choosing a generic marketing strategy:
- Market analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of the target market, including customer preferences, needs, and behavior. Identify market trends, growth potential, and competitive dynamics. This analysis will help determine which strategy aligns best with the market conditions.
- Internal capabilities: Assess your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, resources, and capabilities. Consider factors such as financial resources, technology, operational efficiency, and talent. Choose a strategy that leverages and aligns with your organization’s core competencies and resources.
- Customer segmentation: Identify and understand your target customer segments. Analyze their specific needs, preferences, and pain points. Different strategies may be more suitable for different customer segments. Select a strategy that resonates with the targeted customers and provides them with unique value.
- Competitive advantage: Evaluate your competitive landscape and identify your organization’s unique value proposition. Determine how your chosen strategy will give you a competitive edge over rivals. Consider how your strategy will differentiate you from competitors and create barriers to entry or substitution.
Assessing the competitive landscape and market conditions:
- Analyze the competitive intensity in the market, including the number and strength of competitors. Evaluate their strategies, strengths, and weaknesses.
- Consider the industry life cycle and market growth rate. Different strategies may be more suitable for mature, stable markets versus rapidly evolving or emerging markets.
- Evaluate the potential for market disruption or technological advancements that could impact the chosen strategy.
- Anticipate potential changes in customer preferences, regulatory environments, or economic conditions that may affect the viability of the selected strategy.
Aligning the strategy with business goals and capabilities:
- Ensure that the chosen strategy aligns with your organization’s overall business goals, vision, and mission.
- Consider the compatibility of the strategy with your organization’s culture and values.
- Evaluate the feasibility of implementing and sustaining the chosen strategy based on available resources, expertise, and capabilities.
- Determine the impact of the strategy on key stakeholders, such as customers, employees, suppliers, and shareholders.
Flexibility and adaptability in strategy selection:
- Recognize that market conditions and customer preferences can change over time. Choose a strategy that allows for flexibility and adaptation to evolving circumstances.
- Develop mechanisms for continuous monitoring and assessment of market trends, customer feedback, and competitive actions. Be prepared to adjust the strategy accordingly.
- Foster a culture of innovation and learning within the organization to support strategic agility and the ability to pivot when needed.
- Build strategic alliances or partnerships that can enhance the organization’s adaptability and responsiveness to market changes.
By carefully considering these factors and conducting a thorough analysis, organizations can select the most appropriate generic marketing strategy that aligns with their goals, capabilities, and the dynamics of the market they operate in.
Implementing and Executing Generic Marketing Strategies
Implementing and executing generic marketing strategies requires careful planning, resource allocation, performance measurement, and continuous monitoring. Here are the key aspects to consider:
Planning and organizing for strategy execution:
- Develop an implementation plan: Create a detailed plan that outlines the specific actions, timelines, responsibilities, and milestones for executing the chosen generic marketing strategy. Ensure clear communication of the plan throughout the organization to align everyone’s efforts.
- Organizational alignment: Ensure that the entire organization, from top management to frontline employees, understands the strategy and their roles in its execution. Foster a culture that supports the chosen strategy and encourages cross-functional collaboration.
- Change management: Recognize that implementing a new strategy may require changes in processes, systems, and behaviors. Develop a change management plan to address potential resistance, provide training and support, and facilitate a smooth transition.
Allocating resources and managing budgets:
- Allocate resources, such as finances, personnel, technology, and equipment, based on the requirements of the chosen strategy. Ensure that resources are aligned with the critical activities and initiatives needed to execute the strategy effectively.
- Develop a comprehensive budget that accounts for both the initial implementation phase and ongoing execution. Monitor and manage the budget closely to ensure resources are utilized efficiently and effectively.
- Consider the need for additional investments in areas such as research and development, marketing and advertising, talent acquisition and development, technology infrastructure, and customer service, based on the requirements of the chosen strategy.
Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics:
- Define clear and measurable KPIs and metrics that align with the goals and objectives of the chosen generic marketing strategy. These metrics should be specific, relevant, attainable, and time-bound.
- KPIs may include market share, customer acquisition and retention rates, revenue growth, profitability, customer satisfaction, brand perception, and other relevant performance indicators.
- Establish a system for tracking and reporting on the identified KPIs and metrics regularly. Use technology tools and dashboards to provide real-time visibility into the progress and performance of the strategy.
Monitoring and adjusting the strategy based on feedback and results:
- Regularly monitor the performance of the strategy using the established KPIs and metrics. Analyze the data and feedback collected to assess the effectiveness of the strategy in achieving the desired outcomes.
- Identify areas of success and areas needing improvement. Use insights gained from monitoring and analysis to make informed decisions about adjusting and optimizing the strategy.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement and learning. Encourage feedback and suggestions from employees, customers, and stakeholders to identify potential opportunities and challenges.
- Be agile and adaptable in responding to changes in the market, customer preferences, or competitive dynamics. Adjust the strategy as needed to ensure its relevance and effectiveness over time.
By effectively planning, organizing, allocating resources, establishing KPIs, and continuously monitoring and adjusting the strategy, organizations can execute their chosen generic marketing strategies with greater success and drive competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Overcoming Challenges and Pitfalls

Implementing generic marketing strategies can be challenging, but by recognizing common pitfalls and employing effective strategies, organizations can overcome these challenges and stay competitive. Here are the key aspects to consider:
Common challenges in implementing generic marketing strategies:
- Resistance to change: Implementing a new strategy may face resistance from employees who are accustomed to existing processes and ways of doing things. Overcoming this challenge requires effective change management, clear communication, and involvement of employees in the strategy development process.
- Resource constraints: Organizations may face limitations in terms of financial resources, talent, technology, or time. Adequate resource allocation and prioritization are essential to ensure the successful implementation of the chosen strategy.
- Competitive dynamics: The marketplace is dynamic and competitive, and competitors may respond to or counteract the implemented strategy. Organizations need to continuously monitor and analyze the market landscape to proactively address competitive challenges.
- Lack of alignment and coordination: Successful strategy implementation requires alignment and coordination across different departments and functions within the organization. Lack of alignment can lead to inefficiencies, confusion, and conflicting priorities.
Strategies to overcome implementation challenges:
- Leadership support and commitment: Strong leadership support and commitment are crucial for overcoming implementation challenges. Leaders need to clearly articulate the strategy, provide resources, address concerns, and actively champion the strategy throughout the organization.
- Effective communication: Clear and frequent communication is essential to ensure that employees understand the rationale, objectives, and benefits of the chosen strategy. Communication should be two-way, allowing employees to provide feedback, ask questions, and share ideas.
- Training and skill development: Equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to implement the strategy effectively. Provide training programs, workshops, and resources to enhance their capabilities and ensure their readiness for the new strategy.
- Collaboration and cross-functional teamwork: Foster collaboration and teamwork across departments and functions to ensure a holistic and integrated approach to strategy implementation. Encourage open communication, knowledge sharing, and joint problem-solving.
Avoiding pitfalls and staying competitive:
- Continuous monitoring and adaptation: Stay vigilant and monitor the effectiveness of the implemented strategy. Regularly review performance metrics, analyze market trends, and gather feedback from customers and stakeholders. Use this information to make necessary adjustments and adaptations to stay competitive.
- Innovation and differentiation: Continuously innovate and differentiate your products, services, or customer experiences to maintain a competitive edge. Stay ahead of customer needs, embrace emerging trends, and invest in research and development to offer unique value propositions.
- Customer focus: Place a strong emphasis on understanding and meeting customer needs and preferences. Continuously gather customer feedback, conduct market research, and engage with customers to tailor your strategy and offerings to their evolving demands.
- Agility and flexibility: Adaptability is key in a rapidly changing market. Embrace a culture of agility and flexibility, allowing your organization to respond quickly to new opportunities or challenges. Encourage experimentation, embrace new technologies, and foster a learning mindset.
By proactively addressing common implementation challenges, employing effective strategies, and staying agile and customer-focused, organizations can avoid pitfalls and maintain their competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Conclusion
Embracing generic marketing strategies can unlock a competitive advantage in today’s dynamic marketplace. Whether it’s Cost Leadership, Differentiation, or Focus, these powerful frameworks provide a path to success based on your strengths and customer needs.
Yet, it doesn’t end there. In a rapidly evolving landscape, these strategies require continuous evaluation and adaptation. Flexibility, agility, and a culture of innovation are essential to stay ahead.
Regularly evaluate your strategy’s effectiveness, monitor market trends, and seize emerging opportunities. Foster a culture of experimentation and improvement to maintain your competitive edge.
Selecting the right strategy is just the beginning. Analyze your competencies, perform SWOT and Five Forces analyses, and explore additional tools for insights.
By aligning efforts, embracing change, and fostering strategic thinking, organizations can achieve sustainable success. Embrace generic marketing strategies as a dynamic journey towards differentiation, customer attraction, and long-term growth.

