Maximizing Success: Effective Marketing Strategies Based on the Product Life Cycle
The product life cycle (PLC) is a crucial concept in marketing that outlines the various stages a product goes through from its introduction to its eventual decline in the market. Understanding the PLC is essential for marketers to develop effective strategies and maximize their marketing success. In this article, we will delve into the details of the product life cycle and explore how marketers can leverage it to drive their marketing efforts.
Overview of the Article’s Structure
This article will provide an in-depth exploration of marketing strategies based on the product life cycle. It will be structured as follows:
- Introduction: An overview of the article’s content and the importance of understanding the product life cycle for marketing success.
- Definition of the Product Life Cycle (PLC): A detailed explanation of the different stages of the PLC, including introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
- Strategies for Each Stage: A comprehensive analysis of effective marketing strategies for each stage of the PLC, including examples, case studies, and practical tips.
- Cross-Stage Strategies: Exploration of strategies that can be applied across multiple stages of the PLC to maximize marketing success.
- Conclusion: A summary of key takeaways and the importance of adapting marketing strategies as a product moves through the different stages of the PLC.
By following this structure, we will gain a deep understanding of marketing strategies based on the product life cycle and equip ourselves with the knowledge to excel in our marketing endeavors.
What is Product Life Cycle (PLC)?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Product-Life-Cycle-a8eb8c754345415db3d837dec4a14276.png)
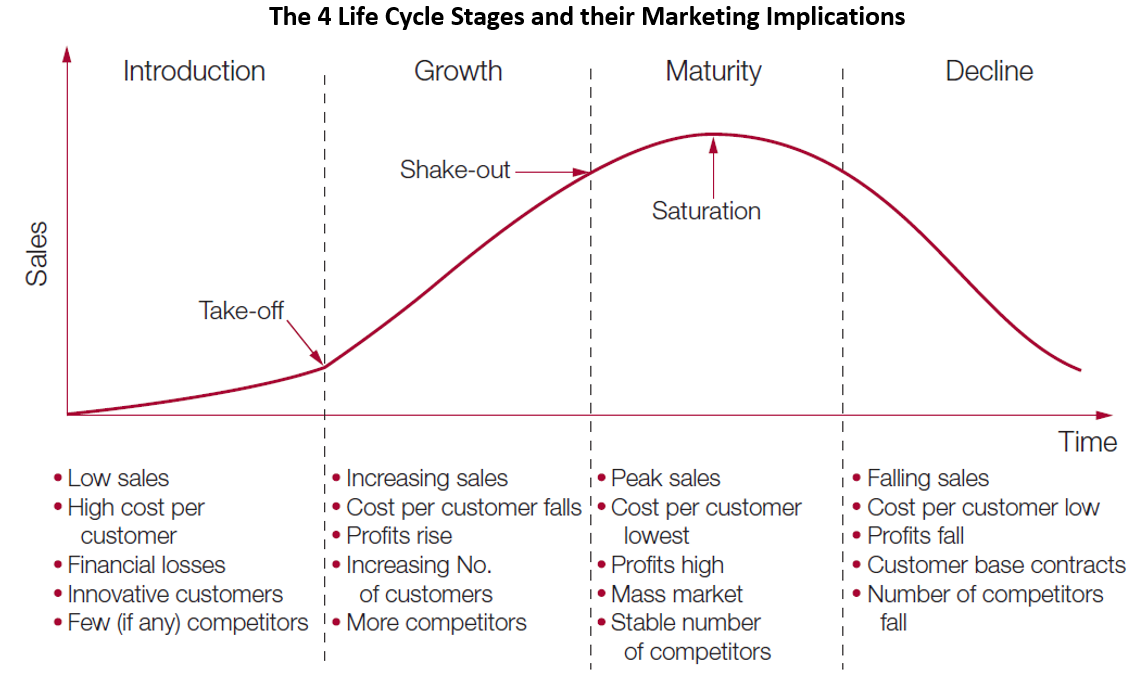
The Product Life Cycle (PLC) is a concept that describes the stages through which a product passes from its introduction to its eventual decline in the market. It is a valuable marketing tool that helps businesses understand and manage the evolution of a product over time. The PLC model provides insights into the product’s performance, sales trends, and customer demand, enabling businesses to make informed marketing and strategic decisions. The four main stages of the product life cycle are:
- Introduction: This is the stage where a product is first introduced to the market. It involves building awareness and generating interest among consumers. Marketing efforts at this stage focus on creating a strong product identity, establishing a market presence, and gaining early adopters.
- Growth: In the growth stage, the product experiences a rapid increase in sales and market acceptance. Consumers become more aware of the product, and competitors enter the market. Marketing strategies during this phase aim to expand market share, build brand loyalty, and differentiate the product from competitors.
- Maturity: The maturity stage is characterized by a high level of market saturation and intense competition. Sales growth stabilizes, and the focus shifts towards retaining existing customers and finding new market segments. Marketing efforts in this stage revolve around brand reinforcement, product differentiation, and customer retention strategies.
- Decline: In the decline stage, sales and market share decrease due to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, or the emergence of new products. Companies may choose to discontinue the product or make minor modifications to extend its life. Marketing strategies during this phase involve managing the product’s decline, minimizing costs, and exploring exit strategies.
Importance of Understanding the PLC for Marketing Success
A solid understanding of the product life cycle is crucial for marketing success. Here’s why:
- Strategic Planning: By recognizing the current stage of a product’s life cycle, marketers can develop effective marketing strategies tailored to each stage. This enables them to allocate resources appropriately and focus on activities that maximize results.
- Resource Allocation: The PLC helps marketers allocate resources effectively by identifying which stages require more investment and attention. For example, during the introduction stage, marketers may allocate resources towards creating awareness, while in the maturity stage, the focus may shift towards customer retention and loyalty programs.
- Competitive Advantage: Understanding the PLC allows marketers to anticipate and respond to competitors’ actions at each stage. By being proactive and adaptive, marketers can gain a competitive advantage by offering unique value propositions and differentiating their products from competitors.
- Product Innovation: Recognizing the decline stage of a product enables marketers to plan for innovation and introduce new products or modifications to extend the product’s life. This can help companies maintain their market presence and continue serving existing customers.
Product Life Cycle: Stages, Strategies, and Examples

Stage 1: Introduction
In the product life cycle (PLC), the introduction stage is the first phase a product goes through. During this stage, the product is launched into the market, and the primary goal is to build awareness and generate interest among consumers. Let’s explore the key characteristics, marketing objectives, strategies, and examples of successful introduction stage marketing.
Explanation of the Introduction Stage of the PLC
During the introduction stage, the product is new to the market, and consumers may have limited awareness or knowledge about it. The key features of this stage include:
- Limited Sales: Sales volume is typically low during the introduction stage as the product is being introduced to the market.
- Slow Growth: The growth rate of sales is relatively slow during this stage as the product is still gaining traction.
- High Marketing Expenses: Companies invest heavily in marketing activities such as advertising, promotion, and product launch events to create awareness and generate interest.
- Price Instability: Pricing strategies may vary during the introduction stage. Some companies may set higher prices to recoup their initial investments, while others may adopt lower prices to attract early adopters.
Marketing Objectives for the Introduction Stage
The marketing objectives during the introduction stage focus on creating a strong foundation for the product’s success. They include:
- Building Awareness: The primary objective is to create awareness among the target market about the product’s existence, features, and benefits.
- Generating Trial: Encouraging potential customers to try the product for the first time is crucial. This helps create initial customer experiences and build positive word-of-mouth.
- Securing Distribution Channels: Establishing effective distribution channels to ensure the product is readily available to consumers who show interest.
Marketing Strategies for the Introduction Stage
To effectively navigate the introduction stage, marketers employ specific strategies tailored to the product’s unique characteristics and target market. Some key strategies include:
- Extensive Advertising and Promotion: Utilize various advertising channels, such as television, radio, print media, and digital platforms, to create widespread awareness. Promotional activities like free samples, product demonstrations, and influencer collaborations can also be effective.
- Target Early Adopters: Identify and target early adopters who are more open to trying new products. These individuals are crucial in creating initial traction and generating positive word-of-mouth.
- Focus on Product Differentiation: Clearly communicate the unique features, benefits, and value proposition of the product to distinguish it from competitors.
- Limited Product Line Extensions: Rather than offering an extensive range of products initially, focus on launching a core product with a clear value proposition. This allows for better resource allocation and targeted marketing efforts.
Case Studies/Examples of Successful Introduction Stage Marketing Strategies
- Apple iPhone: When the first iPhone was introduced, Apple focused on generating buzz and anticipation through a series of well-executed marketing campaigns. They strategically positioned the iPhone as a revolutionary device, emphasizing its sleek design, intuitive user interface, and advanced capabilities.
- Tesla Model S: Tesla’s introduction of the Model S electric vehicle involved extensive marketing efforts, including showcasing the car’s long-range capabilities, superior performance, and environmental benefits. Tesla targeted tech enthusiasts and environmentally conscious consumers, creating a sense of exclusivity and innovation.
- Airbnb: In its introduction stage, Airbnb employed a unique marketing strategy to build trust and gain traction. They offered professional photographs of hosts’ properties, implemented a secure payment system, and provided detailed reviews and ratings to establish credibility and overcome the initial hesitation of travelers.
These case studies demonstrate successful introduction stage marketing strategies that focused on differentiation, awareness building, and targeting the right audience to drive initial adoption and positive brand perception.
Remember, the introduction stage is crucial for setting the foundation of a product’s success. By implementing effective marketing strategies, companies can maximize their chances of capturing market share and positioning their product for future growth.
Stage 2: Growth
In the product life cycle (PLC), the growth stage follows the introduction stage. During this stage, the product experiences rapid market acceptance and sales growth. Let’s explore the key characteristics, marketing objectives, strategies, and examples of successful growth stage marketing.
Explanation of the Growth Stage of the PLC
The growth stage is characterized by a significant increase in sales, expanding market acceptance, and growing competition. The key features of this stage include:
- Rapid Sales Growth: The product experiences a substantial increase in sales as consumer awareness and demand grows.
- Growing Market Acceptance: More consumers become aware of the product, leading to a broader customer base and higher market penetration.
- Entry of Competitors: As the market potential becomes evident, competitors enter the market, leading to increased competition.
- Improved Profitability: With increased sales and economies of scale, the product becomes more profitable.
Marketing Objectives for the Growth Stage
During the growth stage, the marketing objectives focus on sustaining market growth, expanding market share, and solidifying the product’s position. They include:
- Market Expansion: Identify and enter new market segments to broaden the product’s customer base.
- Increase Market Share: Capture a larger share of the market by attracting new customers and convincing existing customers to continue purchasing the product.
- Build Brand Loyalty: Establish strong brand loyalty and customer preference through excellent customer service, product quality, and positive customer experiences.
Marketing Strategies for the Growth Stage
To capitalize on the growth stage’s opportunities and navigate the challenges, marketers employ specific strategies. Some key strategies include:
- Product Improvement and Innovation: Continuously enhance product features, quality, and performance to meet evolving customer needs and stay ahead of competitors.
- Expand Distribution Channels: Strengthen the distribution network by adding new retail outlets, expanding online presence, or partnering with distributors to ensure easy access to the product.
- Target New Market Segments: Identify and enter new market segments that show potential for growth and align with the product’s value proposition.
- Increase Promotional Efforts: Shift promotional efforts from creating awareness to building product conviction and emphasizing the product’s unique selling points.
- Pricing Strategies: Assess the market dynamics and adjust pricing strategies accordingly. This may involve reducing prices to attract price-sensitive consumers or maintaining premium pricing to emphasize the product’s value.
- Monitor and Respond to Competition: Stay vigilant about competitors’ actions and adjust marketing strategies to maintain a competitive edge. This may include offering incentives, launching counter-campaigns, or highlighting unique product features.
Case Studies/Examples of Successful Growth Stage Marketing Strategies
- Netflix: During the growth stage, Netflix capitalized on the increasing demand for online streaming by continuously enhancing its content library, expanding its user base, and investing in original programming. By providing a convenient and cost-effective alternative to traditional cable TV, Netflix experienced rapid growth and solidified its position in the streaming market.
- Fitbit: Fitbit, a pioneer in wearable fitness trackers, successfully leveraged the growth stage by continuously improving its products, introducing new models with advanced features, and targeting health-conscious consumers. Their marketing strategies emphasized the product’s health benefits, ease of use, and integration with mobile apps, resulting in significant market growth and increased market share.
- Starbucks: Starbucks utilized the growth stage to expand its market presence globally by entering new markets, opening new stores, and diversifying its product offerings. Their marketing strategies focused on creating a unique and premium coffee experience, establishing a strong brand identity, and fostering customer loyalty through personalized customer service.
These case studies demonstrate successful growth-stage marketing strategies that revolved around product innovation, market expansion, strong brand positioning, and customer-centric approaches. By adopting these strategies, companies can capitalize on the growth stage’s opportunities and solidify their market position.
The growth stage is a crucial phase in the product life cycle, and by implementing effective marketing strategies, companies can maximize their market share, customer base, and profitability.
Stage 3: Maturity
In the product life cycle (PLC), the maturity stage follows the growth stage. During this stage, the product experiences a peak in sales and market saturation. Let’s explore the key characteristics, marketing objectives, strategies, and examples of successful maturity-stage marketing.
Explanation of the Maturity Stage of the PLC
The maturity stage is characterized by a stable sales volume and market saturation. The key features of this stage include:
- Peak Sales: The product reaches its highest sales volume during this stage, but the growth rate starts to decline.
- Market Saturation: The market becomes saturated with competitors and similar products, making it challenging to attract new customers.
- Intense Competition: Competitors strive to gain a larger market share, resulting in aggressive marketing and pricing strategies.
- Price Sensitivity: Consumers become more price-sensitive, seeking value for their money and comparing prices among competing products.
Marketing Objectives for the Maturity Stage
During the maturity stage, the marketing objectives focus on maintaining market share, maximizing profitability, and extending the product’s life cycle. They include:
- Sustain Market Share: Retain the current market share by defending against competitors’ strategies and retaining loyal customers.
- Maximize Profitability: Optimize profitability by managing costs, improving operational efficiency, and streamlining marketing efforts.
- Extend Product Life Cycle: Introduce strategies to extend the product’s life cycle by attracting new customer segments or finding new uses for the product.
Marketing Strategies for the Maturity Stage
To navigate the challenges of the maturity stage and prolong the product’s life cycle, marketers employ specific strategies. Some key strategies include:
- Market Segmentation and Targeting: Identify and target specific customer segments that have not yet been fully reached or penetrated by the product.
- Product Line Extension: Introduce variations of the product or expand the product line to cater to different customer preferences and needs.
- Competitive Pricing: Adjust pricing strategies to remain competitive in the market while maintaining profitability. This may involve offering discounts, bundles, or loyalty programs.
- Marketing Communications: Focus on building brand loyalty, reinforcing product benefits, and differentiating the product from competitors through effective marketing communications and advertising.
- Distribution Channel Optimization: Review and optimize the distribution channels to ensure the product is easily accessible to consumers and reaches untapped markets.
- Customer Retention: Implement strategies to retain existing customers by providing excellent customer service, loyalty programs, and personalized experiences.
Case Studies/Examples of Successful Maturity Stage Marketing Strategies
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola has successfully navigated the maturity stage by constantly innovating and introducing new product variants, such as Diet Coke, Coca-Cola Zero, and Coca-Cola Cherry. These variations cater to different consumer preferences while leveraging the strong brand equity of the original Coca-Cola product.
- Apple iPhone: Apple has sustained the maturity stage of the iPhone by regularly introducing new models with improved features and performance. They have also focused on creating a unique brand experience and fostering customer loyalty through their ecosystem of products and services.
- McDonald’s: McDonald’s has extended the maturity stage of their core products, such as the Big Mac and Chicken McNuggets, by continuously adapting to changing consumer tastes. They have introduced limited-time promotions, expanded their menu to include healthier options, and localized their offerings to cater to regional preferences.
These case studies demonstrate successful maturity-stage marketing strategies that revolve around product innovation, diversification, brand loyalty, and market adaptation. By adopting these strategies, companies can maintain market share, sustain profitability, and extend the life cycle of their products.
The maturity stage presents both challenges and opportunities for marketers. By implementing effective marketing strategies, companies can retain their competitive edge, attract new customers, and prolong the product’s profitability and relevance in the market.
Stage 4: Decline
In the product life cycle (PLC), the decline stage is the final stage that occurs when a product’s sales and profitability start to decline. During this stage, the market becomes saturated, and consumer interest decreases. Let’s explore the key characteristics, marketing objectives, strategies, and examples of successful decline-stage marketing.
Explanation of the Decline Stage of the PLC
The decline stage is characterized by a decline in sales and profitability. It occurs when the product becomes outdated, faces intense competition, or is replaced by newer and more innovative alternatives. The key features of this stage include:
- Sales Decline: The product experiences a significant decline in sales due to decreased consumer demand and market saturation.
- Obsolescence: The product may become technologically outdated or lose its relevance in the market as newer products or technologies emerge.
- Increased Competition: Intense competition from substitutes and alternative products further accelerates the decline.
- Profit Erosion: The declining sales and increased competition lead to a reduction in profitability.
Marketing Objectives for the Decline Stage
During the decline stage, the marketing objectives focus on managing the product’s decline while maximizing profits. The objectives include:
- Profit Maximization: Extract the maximum profit from the declining product by reducing costs, streamlining operations, and optimizing pricing strategies.
- Market Exit Strategy: Develop an exit strategy for the product, considering factors such as product discontinuation, resource reallocation, or sale to another company.
- Brand Preservation: Preserve the brand’s reputation and image throughout the decline to avoid negative impacts on other products or the company’s overall brand equity.
Marketing Strategies for the Decline Stage
To navigate the challenges of the decline stage and minimize the negative impact, marketers employ specific strategies. Some key strategies include:
- Cost Reduction: Streamline production processes, reduce overhead costs, and negotiate better terms with suppliers to maximize profitability during the declining phase.
- Harvesting: Gradually reduce marketing investments and other resources allocated to the declining product, focusing on maximizing short-term profits rather than long-term growth.
- Product Differentiation: Differentiate the product from competitors by highlighting unique features, benefits, or target markets that may still find value in the product.
- Niche Market Focus: Identify niche or specialized markets where the product can still find a small but profitable customer base.
- Product Line Consolidation: Consolidate product variations or models to focus on the most profitable or in-demand versions, reducing production and marketing complexities.
- End-of-Life Strategies: Determine the best course of action for the product’s end-of-life, such as selling production and sales rights to other companies or gradually discontinuing the product while transitioning resources to other products.
Case Studies/Examples of Successful Decline Stage Marketing Strategies
- Kodak: Kodak, a renowned photography company, faced the decline stage as digital photography emerged. While Kodak struggled to adapt to the digital era, it successfully transitioned its business to focus on commercial printing and imaging technologies, preserving its brand value and avoiding a complete market exit.
- Blockbuster: Blockbuster, a video rental company, faced a decline with the rise of online streaming services. Despite eventually filing for bankruptcy, Blockbuster could have adopted a strategy to shift towards digital streaming or invest in new technologies to adapt to changing consumer preferences.
These case studies demonstrate both successful and unsuccessful approaches to managing the decline stage. Successful strategies involve adapting to emerging trends, exploring new markets, diversifying product offerings, and optimizing resources. Failing to respond to market changes or clinging to outdated business models can lead to market exit or significant decline.
During the decline stage, it is crucial for companies to evaluate the viability of the product and make strategic decisions to minimize losses and explore new opportunities. Managing the decline effectively can protect the company’s brand reputation and create a smooth transition to new products or business ventures.
Strategies Across the Product Life Cycle

While each stage of the product life cycle (PLC) requires unique strategies, there are cross-stage strategies that can be applied throughout the entire cycle. These strategies help maintain competitiveness, maximize profits, and adapt to changing market conditions. Let’s explore some strategies that can be effective at multiple stages and the importance of adapting and evolving strategies as the product moves through the PLC.
1. Continuous Product Innovation: Innovation is crucial at all stages of the PLC. By continuously improving and enhancing the product, companies can meet evolving customer needs, differentiate themselves from competitors, and extend the product’s life cycle. This strategy involves investing in research and development, staying updated with market trends, and incorporating customer feedback into product improvements.
2. Market Research and Customer Insights: Market research and gathering customer insights are essential at every stage of the PLC. Understanding customer preferences, behaviors, and emerging trends helps companies make informed decisions, develop targeted marketing campaigns, and identify new market opportunities. Regularly conducting market research and obtaining customer feedback provide valuable information for adapting strategies to changing market dynamics.
3. Brand Building and Customer Loyalty: Building a strong brand and fostering customer loyalty are long-term strategies that have a positive impact at various stages of the PLC. A strong brand image helps create customer trust, enhances brand recognition, and differentiates the product from competitors. By delivering consistent quality, excellent customer service, and engaging marketing communications, companies can build customer loyalty and increase customer retention throughout the product’s life cycle.
4. Effective Communication and Promotion: Effective communication and promotion are vital strategies that apply across the PLC. Clear and targeted messaging helps create awareness, generate interest, and drive sales. Companies should employ a mix of advertising, public relations, social media marketing, and other promotional tactics to reach their target audience at each stage of the PLC. The specific focus of communication and promotion may shift as the product progresses through different stages, adapting to changing market conditions and consumer preferences.
5. Strategic Pricing: Pricing is a critical element throughout the PLC. Companies need to determine appropriate pricing strategies based on market demand, competition, and product positioning. In the introduction stage, companies may use skimming or penetration pricing to gain market share or recover costs. As the product moves through subsequent stages, pricing strategies may evolve to maximize profitability or maintain competitiveness. Pricing adjustments should align with market conditions, customer value perceptions, and the product’s life cycle stage.
Importance of Adapting and Evolving Strategies
Adapting and evolving strategies as the product moves through the PLC is essential for maintaining competitiveness and maximizing results. Here’s why it’s important:
- Market Dynamics Change: Market conditions, customer preferences, and competitive landscapes evolve over time. Adapting strategies ensures that the product remains relevant, meets changing customer needs, and stays ahead of competitors.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: By analyzing the product’s performance at each stage, companies can allocate resources effectively. Shifting investments, adjusting marketing budgets, and focusing on high-potential market segments maximize returns on investment.
- Maximize Profitability: Adapting strategies help companies identify opportunities to optimize pricing, reduce costs, and maximize profits. It allows businesses to capitalize on high-growth stages, sustain profitability during maturity, and minimize losses during decline.
- Stay Customer-Centric: Adapting strategies based on customer insights and feedback ensures that the product continues to provide value and meet customer expectations. It helps maintain customer satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term relationships.
- Competitive Advantage: Evolving strategies enable companies to differentiate themselves from competitors, respond to competitive threats, and capitalize on emerging market trends. Staying proactive and agile in strategy formulation and implementation enhances competitive advantage.
In summary, cross-stage strategies such as continuous innovation, market research, brand building, effective communication, and strategic pricing provide a foundation for success throughout the product life cycle. Adapting and evolving these strategies as the product progresses through different stages is crucial for maintaining competitiveness, maximizing profits, and meeting changing market dynamics.
Conclusion
The product life cycle (PLC) is a dynamic journey that presents marketers with unique challenges and opportunities. By adapting strategies to suit each stage – introduction, growth, maturity, and decline – marketers can effectively navigate the PLC and drive product success. From creating awareness in the introduction stage to sustaining growth, maintaining market share, and managing decline, strategic decision-making is key. By monitoring market trends and customer preferences, and by continuously evolving strategies, companies can make the most of the PLC and achieve long-term success.
FAQs
1. What is the Product Life Cycle, and why is it important for marketing? The Product Life Cycle (PLC) is a concept that describes the various stages a product goes through from its introduction to its eventual decline in the market. The stages include introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Understanding the PLC is crucial for marketers as it helps them develop appropriate strategies and make informed decisions at each stage. It guides marketers in allocating resources, planning promotions, pricing the product, identifying market opportunities, and managing the product’s overall life cycle.
2. How can a company effectively market a product in the introduction stage? During the introduction stage, a company should focus on creating product awareness and generating trials among early adopters. Effective marketing strategies for this stage include:
- Conducting extensive market research to understand target customers and their needs.
- Designing a compelling product launch campaign to generate curiosity and interest.
- Using selective distribution channels to reach early adopters.
- Employing persuasive advertising and public relations to educate the market about the product’s unique features and benefits.
- Offering introductory pricing or promotions to encourage trial and adoption.
- Establishing partnerships or endorsements with influential individuals or organizations to enhance credibility.
3. What marketing strategies are effective during the growth stage of the PLC? During the growth stage, the focus shifts from creating awareness to sustaining and accelerating market growth. Effective marketing strategies for this stage include:
- Expanding distribution channels to reach a broader customer base.
- Enhancing product quality, features, and design to differentiate from competitors.
- Introducing product variations or extensions to cater to different customer segments.
- Increasing marketing efforts to build brand preference and loyalty.
- Shifting advertising and promotion towards product conviction and differentiation.
- Adjusting pricing strategies to maximize profitability while remaining competitive.
- Monitoring competitors and proactively defending market share.
4. How can a company sustain success during the maturity stage of the PLC? In the maturity stage, intense competition and market saturation require companies to adopt strategies that sustain success. Effective marketing strategies for this stage include:
- Differentiating the product through superior customer service, warranties, or bundling options.
- Identifying and entering new market segments or international markets.
- Investing in product modifications or innovations to meet changing customer preferences.
- Optimizing the marketing mix (product, price, promotion, distribution) to maintain market share.
- Implementing customer loyalty programs to retain existing customers.
- Exploring cost-saving measures in production and distribution to maximize profitability.
- Monitoring market trends and competitors to anticipate shifts in customer preferences.
5. What are some signs that a product is entering the decline stage, and how should marketing strategies be adjusted accordingly? Signs that a product is entering the decline stage include declining sales, reduced market share, and an increase in customers switching to alternative products. In this stage, marketing strategies should be adjusted as follows:
- Focus on profitable market segments and discontinue unprofitable segments.
- Reduce marketing expenses and allocate resources to more promising products.
- Consider product diversification or repositioning to extend the product’s life.
- Offer discounts, promotions, or incentives to maintain sales volume.
- Explore partnerships or collaborations to generate renewed interest.
- Consider discontinuing the product gradually or replacing it with a new offering.
6. Are there any strategies that can be applied throughout the entire PLC? Yes, there are cross-stage strategies that can be applied throughout the entire PLC. These include:
- Continuous product innovation to meet evolving customer needs and stay ahead of competitors.
- Market research and customer insights to understand customer preferences and market trends.
- Building a strong brand and fostering customer loyalty through consistent quality and excellent customer service.
- Effective communication and promotion to create awareness, generate interest, and maintain customer engagement.
- Strategic pricing to optimize profitability and remain competitive.
7. Can you provide examples of successful marketing strategies for each stage of the PLC? Certainly! Here are some examples:
- Introduction Stage: Apple’s marketing strategy for the iPhone involved high product differentiation, a sleek design, and an extensive advertising campaign to create buzz and generate curiosity among tech enthusiasts.
- Growth Stage: Nike’s marketing strategy during the growth stage focused on expanding its product line to include apparel and accessories, entering new market segments, and leveraging endorsements from athletes to build brand loyalty.
- Maturity Stage: Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy in the maturity stage involved maintaining a strong brand presence through nostalgic advertising campaigns, introducing limited-edition flavors, and expanding distribution channels globally.
- Decline Stage: Kodak, while facing declines in its traditional film photography business, adjusted its marketing strategy by shifting its focus to digital cameras, investing in new technologies, and entering different market segments to sustain relevance.
These examples demonstrate how companies adapt their marketing strategies to each stage of the PLC to maximize their product’s success.

