Decoding Marketing Research: What It Is, Types and Examples
Marketing research plays a pivotal role in helping businesses make informed decisions by uncovering valuable insights about their target market. By conducting thorough research, businesses gain a deeper understanding of consumer behavior, preferences, and market trends. This article aims to shed light on the definition, significance, and role of marketing research in shaping successful business strategies.
What is Marketing Research?
Marketing research refers to the systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to gain insights into consumer behavior, market dynamics, and competitive landscape. It involves the use of various research methodologies, tools, and techniques to gather relevant information, identify opportunities, and mitigate risks.
Here are some key aspects of marketing research:
- Objective-driven: Marketing research is conducted with a specific objective in mind. Whether it’s understanding customer preferences, evaluating the effectiveness of a marketing campaign, or exploring market opportunities, research is designed to answer specific questions and provide actionable insights.
- Data Collection: Marketing research involves gathering data from primary and secondary sources. Primary data is collected directly from the target audience or market through surveys, interviews, focus groups, observations, or experiments. Secondary data refers to existing information gathered from published sources, industry reports, government data, or competitor analysis.
- Quantitative and Qualitative: Marketing research can be quantitative or qualitative, or a combination of both. Quantitative research involves numerical data, such as surveys with close-ended questions or data analysis using statistical methods. Qualitative research focuses on exploring opinions, attitudes, and perceptions through open-ended questions, interviews, or observations.
- Market Segmentation: Research helps in identifying and segmenting the target market based on demographic, psychographic, geographic, or behavioral factors. This segmentation helps businesses tailor their marketing strategies and messages to specific customer groups.
- Competitive Analysis: Marketing research helps businesses understand their competitors, their strengths, weaknesses, market share, and strategies. This knowledge enables businesses to identify their competitive advantage and develop strategies to differentiate themselves in the market.
- Market Trends and Analysis: Research provides insights into market trends, changes in consumer behavior, technological advancements, regulatory factors, and other environmental influences. By staying abreast of these trends, businesses can adapt their marketing strategies and stay ahead of the competition.
- Marketing Decision-making: Marketing research plays a crucial role in making informed decisions. It provides data-driven insights that reduce uncertainty and guide marketing strategy development, product development, pricing decisions, promotional activities, and distribution strategies.
- Risk Mitigation: Marketing research helps businesses mitigate risks associated with marketing initiatives. By understanding customer needs, preferences, and market dynamics, businesses can avoid costly mistakes and minimize the risk of launching unsuccessful products or campaigns.
- Evaluation and Measurement: Research allows businesses to evaluate the effectiveness of their marketing efforts. By setting benchmarks, tracking key metrics, and measuring the impact of marketing activities, businesses can assess their performance, identify areas for improvement, and optimize their strategies for better results.
Overall, marketing research is a crucial tool for businesses to make informed decisions, understand their customers and competitors, identify market opportunities, and evaluate their marketing efforts. It enables businesses to develop effective marketing strategies, stay competitive, and drive business growth.
Importance and Role of Marketing Research in Business Decision-Making

Marketing research plays a vital role in business decision-making by providing valuable insights and data-driven information to support strategic planning, marketing activities, and overall business growth. Here are some key reasons why marketing research is important in business decision-making:
I. Understanding Customer Needs
Marketing research helps businesses understand the needs, preferences, and expectations of their target audience. By identifying consumer pain points and desires, companies can tailor their products, services, and marketing campaigns to effectively meet customer demands.
II. Assessing Market Potential
Through comprehensive research, businesses can evaluate the size, growth potential, and profitability of target markets. This information enables them to make strategic decisions regarding market entry, expansion, and diversification.
III. Competitor Analysis
Marketing research allows companies to monitor and analyze their competitors’ strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. This insight empowers businesses to develop competitive advantages and differentiate themselves in the marketplace.
IV. Testing and Refining Marketing Strategies
Research provides a platform for testing marketing concepts, advertisements, pricing strategies, and product features before full-scale implementation. It helps businesses optimize their marketing mix and minimize the risk of costly failures.
V. Tracking Market Trends
By monitoring market trends, emerging technologies, and shifts in consumer behavior, businesses can proactively adapt their strategies to stay ahead of the curve. Marketing research acts as a compass, guiding companies toward the most promising opportunities.
VI. Mitigating Risks
Research enables businesses to identify potential risks and challenges in their target markets. By understanding consumer preferences, market dynamics, and regulatory environments, companies can mitigate risks and make more informed decisions.
In conclusion, marketing research serves as a vital tool for businesses seeking success in a competitive marketplace. It empowers companies to uncover consumer insights, assess market potential, refine strategies, and make data-driven decisions. By investing in effective marketing research, businesses can gain a competitive edge, enhance customer satisfaction, and achieve long-term growth.
Purpose and Objectives of Marketing Research
Marketing research serves specific purposes in helping businesses make informed decisions and achieve their goals. By understanding the purpose of conducting marketing research, defining research objectives, and aligning them with business goals, companies can effectively leverage research to drive success. This section delves into the significance of marketing research, the importance of defining research objectives, and explores different types of research objectives.
Understanding the Purpose of Conducting Marketing Research
Marketing research serves as a crucial tool for businesses to gather data and insights that aid in decision-making processes. The key purposes of conducting marketing research include:
I. Gaining Consumer Insights
Marketing research helps businesses understand consumer behavior, preferences, and needs. It provides valuable insights into consumer demographics, buying patterns, motivations, and perceptions, enabling companies to develop targeted marketing strategies and tailor their offerings to meet customer demands effectively.
II. Evaluating Market Opportunities
By conducting research, businesses can identify market trends, assess market potential, and uncover new opportunities. Research helps companies understand market dynamics, competitive landscape, and customer needs, allowing them to make informed decisions regarding product development, market-entry, and expansion strategies.
III. Improving Business Performance
Marketing research helps companies evaluate and measure the effectiveness of their marketing efforts. It provides feedback on marketing campaigns, product features, pricing strategies, and customer satisfaction levels, enabling businesses to make data-driven improvements and enhance overall performance.
Defining Research Objectives and Their Alignment with Business Goals
To derive meaningful insights, it is crucial to define clear research objectives that align with the broader goals of the business. Research objectives serve as guiding principles and help focus data collection efforts. Some key considerations when defining research objectives include:
- Specificity: Research objectives should be specific and well-defined. They should outline the precise information or insights required to address the research problem or support business decision-making.
- Measurability: Research objectives should be measurable, allowing for the collection of data that can be quantified or analyzed. This ensures that the research outcomes can be assessed objectively and contribute to evidence-based decision-making.
- Relevance: Research objectives should be relevant to the business goals and align with the specific challenges or opportunities the company is facing. They should directly contribute to addressing key issues or supporting strategic initiatives.
Types of Market Research
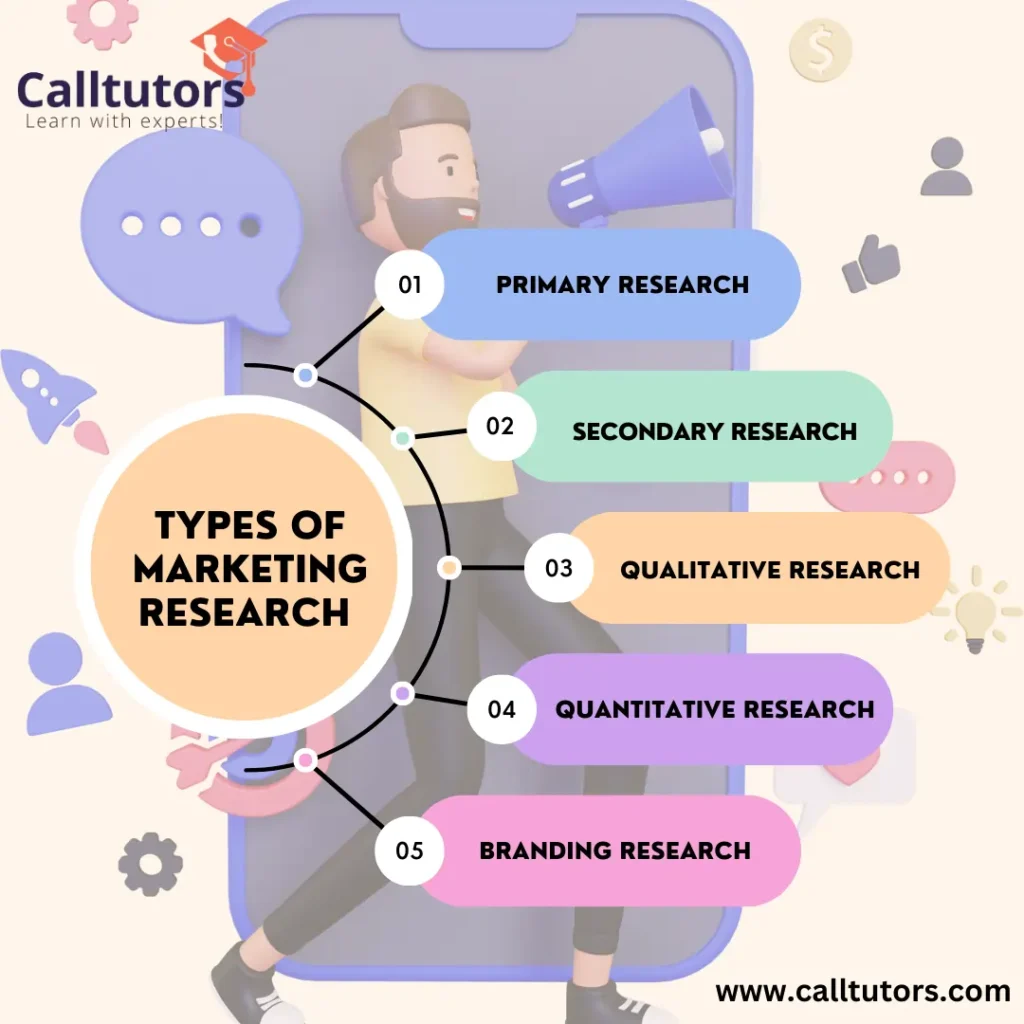
Market research encompasses various methods and approaches to gather data and insights about markets, customers, competitors, and the overall business environment. Here are some common types of market research:
1. Primary Market Research
This type of market research involves collecting data directly from the target audience or customers. It is conducted to gather specific and customized information for a particular research objective. Primary market research can be further classified into two methods:
a). Qualitative Research: This method focuses on gathering non-numerical data and insights to understand consumer behavior, attitudes, motivations, and opinions. Qualitative research methods include techniques such as focus groups, interviews, observations, and case studies.
b). Quantitative Research: This method involves collecting numerical data and conducting statistical analysis to quantify and measure consumer preferences, opinions, and behaviors. Quantitative research methods include surveys, questionnaires, experiments, and statistical modeling.
2. Secondary Market Research
Secondary research involves utilizing existing data and information that has been previously collected by other sources. This type of research is often conducted to gain a broader understanding of the market, industry trends, competitor analysis, and other relevant factors. Secondary market research sources can include published reports, government publications, industry studies, market databases, and online resources.
3. Exploratory Research
Exploratory research is conducted in the early stages of a project or when there is limited existing knowledge about a particular topic. Its purpose is to gain insights, identify trends, generate hypotheses, and explore potential opportunities. Exploratory research methods include literature reviews, focus groups, interviews, and pilot studies.
4. Descriptive Research
Descriptive research aims to describe and quantify characteristics, behaviors, and trends within a specific market or target audience. It focuses on providing a clear picture of the current situation or status. Surveys, observational studies, and correlational studies are commonly used in descriptive research.
5. Causal Research
Causal research investigates cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It seeks to understand how changes in one variable affect another variable. Causal research often involves experiments, where variables are manipulated and controlled to determine their impact on the outcome.
6. Behavioral Research
Behavioral research focuses on studying and understanding consumer behavior, including purchasing habits, decision-making processes, and responses to marketing stimuli. This research helps businesses tailor their strategies to meet customer needs and preferences.
7. Market Segmentation Research
Market segmentation research involves dividing the target market into distinct segments based on common characteristics, such as demographics, psychographics, behavior, or needs. This research helps businesses identify and target specific customer segments effectively.
8. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis research aims to evaluate and understand the strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market positions of competitors. It helps businesses identify opportunities, differentiate themselves, and make informed decisions to gain a competitive edge.
9. Brand Research
Brand research focuses on studying the perceptions, attitudes, and associations consumers have with a brand. It helps businesses measure brand awareness, brand image, brand loyalty, and customer satisfaction, providing insights to enhance brand positioning and marketing strategies.
10. Product Research
Product research is conducted to assess and gather feedback on new or existing products. It involves understanding customer needs, preferences, and satisfaction levels, as well as testing product features, usability, and performance.
Key Steps in Conducting Marketing Research

Step 1: Defining the Research Problem
Importance of clearly defining the research problem: Clearly defining the research problem is crucial because it sets the direction and scope of the entire marketing research project. It helps researchers focus their efforts on specific objectives and ensures that the research outcomes are relevant and useful. Without a well-defined problem, the research may lack clarity and fail to provide meaningful insights.
Techniques for defining the research problem effectively:
- Conduct preliminary research: Before defining the problem, researchers should gather background information and conduct a preliminary analysis to gain a deeper understanding of the subject. This helps in identifying gaps in knowledge and formulating relevant research questions.
- Consult stakeholders: Engaging with relevant stakeholders, such as clients, managers, or subject matter experts, can provide valuable insights and perspectives on the problem. Their input can help refine the research objectives and ensure alignment with business goals.
- Use SMART criteria: The research problem should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). This framework ensures that the problem is well-defined, realistic, and can be effectively addressed within the available resources and timeline.
- Consider multiple perspectives: It is important to consider various angles and viewpoints related to the research problem. This helps in capturing a comprehensive understanding of the issue and exploring different potential solutions or insights.
- Refine and iterate: The process of defining the research problem may involve multiple iterations and refinements. Researchers should be open to feedback and be willing to revise and clarify the problem statement as necessary.
Step 2: Developing the Research Plan
Overview of the research plan and its components: The research plan outlines the overall approach and methodology for conducting the marketing research. It includes several components, such as:
- Research objectives: Clear and specific goals that the research aims to achieve.
- Research design: The overall framework and structure for data collection and analysis, which can be experimental, observational, or descriptive.
- Sampling strategy: Determining the sample size and selection process to ensure representative and statistically valid data.
- Data collection methods: Choosing appropriate techniques for gathering data, such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments.
- Data analysis techniques: Select the appropriate methods to analyze the collected data, such as statistical analysis, qualitative coding, or thematic analysis.
- Timeline and budget: Planning the schedule and allocating resources to ensure the research is completed within the defined timeframe and budget.
Designing the research methodology: The research methodology involves making decisions about the overall approach to collecting and analyzing data. It includes selecting the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques. The choice of methodology depends on the research objectives, available resources, and the nature of the research problem. Common methodologies include surveys, interviews, focus groups, experiments, observations, and case studies. Researchers should carefully consider the strengths and limitations of each method and choose the most appropriate one to gather the required insights effectively.
Determining the sample size and selection process: Determining the sample size involves deciding the number of participants or observations needed for the research. It is essential to ensure that the sample size is statistically significant and representative of the target population. The selection process can involve probability sampling, where participants are chosen randomly, or non-probability sampling, where specific criteria are used to select participants. Researchers should consider factors such as diversity, sample representativeness, and the desired level of statistical confidence when determining the sample size and selection process.
Step 3: Collecting Data
Overview of data collection methods: Data collection methods involve the techniques used to gather information for market research. Common methods include surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, and the analysis of existing data. Each method has its strengths and limitations, and the choice depends on the research objectives, target population, resources, and timeframe.
Pros and cons of primary and secondary data sources: Primary data refers to original data collected specifically for the research project, while secondary data refers to existing data collected by others for different purposes.
Pros of primary data:
- Provides firsthand and tailored information to address specific research objectives.
- Enables control over the data collection process, ensuring relevance and accuracy.
- Can generate unique insights and support original research.
Cons of primary data:
- Requires more time, effort, and resources to collect and analyze.
- May be influenced by biases or errors introduced during data collection.
- Can be costly, especially when targeting large and diverse populations.
Pros of secondary data:
- Saves time and resources by utilizing existing data.
- Provides historical or industry-wide information for benchmarking and trend analysis.
- Can cover a larger population or longer time span than primary data.
Cons of secondary data:
- May lack relevance or specificity to the research objectives.
- Quality and accuracy may vary across different sources.
- Potential limitations in access to comprehensive or up-to-date data.
Step 4: Analyzing and Interpreting Data
Techniques for analyzing data: Data analysis involves transforming raw data into meaningful insights. Common techniques include statistical analysis, qualitative coding, thematic analysis, regression analysis, and data visualization. The choice of technique depends on the research objectives, data type (quantitative or qualitative), and available resources.
Importance of data interpretation in generating insights: Data interpretation is crucial for extracting meaningful insights from the analyzed data. It involves making sense of the findings, identifying patterns, relationships, and trends, and drawing conclusions based on the research objectives. Effective data interpretation helps researchers understand the implications of the findings, make informed decisions, and generate actionable recommendations.
Step 5: Reporting and Presenting Findings
Creating a comprehensive research report: A comprehensive research report includes an executive summary, introduction, methodology, findings, analysis, conclusions, and recommendations. It provides a clear and concise overview of the research objectives, methodology, key findings, and actionable insights. The report should be structured, well-organized, and visually appealing, incorporating relevant charts, graphs, and tables to support the findings.
Effective ways to present research findings: To effectively present research findings, consider the audience and their needs. Some effective ways include:
- Summarizing key findings in a visually appealing and concise manner.
- Using charts, graphs, and infographics to convey information.
- Providing context and explaining the implications of the findings.
- Tailoring the presentation style and format to the audience (e.g., executive summary for management, detailed analysis for researchers).
- Using storytelling techniques to engage the audience and make the findings relatable.
Common Research Techniques and Approaches
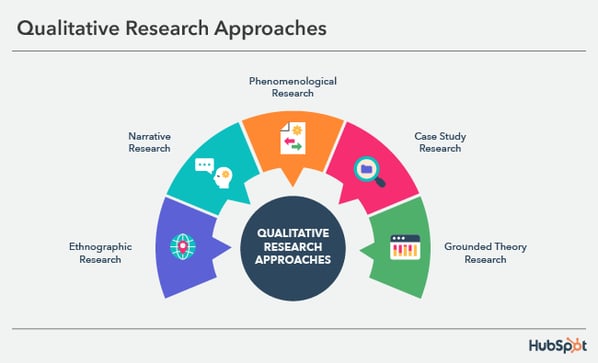
A. Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a method used to gather in-depth insights and understanding of people’s experiences, opinions, and behaviors. Its purpose is to explore and interpret complex phenomena, allowing researchers to uncover underlying motivations, attitudes, and beliefs.
Common qualitative research techniques:
Some common qualitative research techniques include interviews, focus groups, observations, case studies, and content analysis. These methods involve open-ended questions, probing, and capturing rich, descriptive data.
Benefits and limitations of qualitative research:
Qualitative research provides detailed and contextual information, allowing for a deep understanding of individuals’ perspectives. It can generate new hypotheses and ideas, and it is flexible in adapting to the research context. However, qualitative research is time-consuming, subjective in interpretation, and may have a smaller sample size, limiting generalizability.
B. Quantitative Research
Quantitative research involves the systematic collection and analysis of numerical data to quantify trends, patterns, and relationships. Its purpose is to measure variables, test hypotheses, and provide statistical evidence to support or refute research questions.
Common quantitative research techniques:
Some common quantitative research techniques include surveys, experiments, statistical analysis, and data mining. These methods use structured questionnaires, standardized measures, and statistical tools to collect and analyze data.
Benefits and limitations of quantitative research:
Quantitative research allows for statistical analysis and generalizability of findings to larger populations. It provides precise measurements, facilitates comparisons, and supports statistical inference. However, it may oversimplify complex phenomena, limit participants’ responses, and overlook contextual factors.
C. Mixed Methods Research:
Mixed methods research involves combining qualitative and quantitative approaches within a single study. It integrates the strengths of both methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of a research problem. Qualitative data helps explore and understand complex phenomena, while quantitative data provides statistical validation and generalizability.
Ethical Considerations in Marketing Research
Importance of ethics in marketing research: Ethics play a crucial role in marketing research as they ensure the responsible and ethical treatment of participants and the integrity of the research process. Ethical practices in marketing research foster trust, protect participant rights and maintain the reputation of the research industry.
Key ethical considerations in conducting research:
- Informed Consent: Researchers must obtain informed consent from participants, ensuring they understand the purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits of the research before voluntarily participating.
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Researchers should protect participants’ privacy by safeguarding their personal information and ensuring the confidentiality of their responses.
- Anonymity: Participants should have the option to remain anonymous, and their identities should be protected to prevent any negative consequences or potential harm.
- Voluntary Participation: Participation in research should be voluntary, and participants should have the freedom to withdraw at any time without facing any negative consequences.
- Avoiding Harm: Researchers should take precautions to minimize any potential physical, psychological, or emotional harm to participants during the research process.
Ensuring participant confidentiality and data privacy: To ensure participant confidentiality and data privacy, researchers should implement measures such as:
- Secure Data Storage: Safely storing research data using secure systems and encryption methods to protect participants’ personal information.
- Anonymization: Removing any identifiable information from research data to ensure participant anonymity.
- Data Access Control: Limiting access to research data to authorized personnel only and implementing strict protocols for data handling and sharing.
- Compliance with Data Protection Laws: Adhering to relevant data protection regulations, such as obtaining necessary consent, notifying participants about data usage, and ensuring compliance with data privacy laws like GDPR or CCPA.
- Confidentiality Agreements: Have participants sign confidentiality agreements to protect their information and ensure researchers uphold their commitment to confidentiality.
Examples of Market Research
Market research involves gathering information and data about the market, consumers, and competitors to make informed business decisions. Here are some examples of market research:
I. Surveys
Conducting surveys is a common method of market research. Surveys can be administered through various channels, such as online questionnaires, phone interviews, or in-person interviews. The collected data can provide insights into customer preferences, satisfaction levels, purchasing habits, and demographic information.
II. Focus Groups
Focus groups involve bringing together a small group of individuals to discuss a product, service, or concept. A moderator facilitates the discussion and gathers qualitative data on participants’ opinions, perceptions, and feedback. Focus groups can provide in-depth insights into consumer attitudes, preferences, and motivations.
III. Interviews
In-depth interviews are conducted with individuals to gather detailed information about their experiences, opinions, and preferences. Interviews can be structured (with predetermined questions) or unstructured (allowing for open-ended discussions). Interviews can be conducted face-to-face, over the phone, or via video calls.
IV. Observational Research
Observational research involves observing and recording consumer behavior in real-life situations. Researchers may observe consumers in stores, public spaces, or during product usage. This method can provide valuable insights into consumer interactions, purchasing decisions, and usage patterns.
V. Online Data Analysis
With the growth of the internet and social media, researchers can analyze online data to understand consumer sentiment, trends, and behavior. This includes analyzing social media conversations, online reviews, website analytics, and online surveys. Online data analysis can provide real-time and large-scale insights.
VI. Competitive Analysis
The market research also involves analyzing and studying competitors. This includes researching competitors’ products, pricing strategies, marketing campaigns, and target markets. Understanding the competitive landscape helps businesses identify opportunities and develop effective strategies.
VII. Secondary Research
Secondary research involves gathering information from existing sources, such as industry reports, market studies, government publications, and academic papers. It provides valuable data and insights without conducting primary research. Secondary research helps in understanding market trends, industry benchmarks, and customer demographics.
These are just a few examples of market research methods. The choice of methods depends on the research objectives, target audience, available resources, and the specific information needed to make informed business decisions.
Conclusion
Market research is a crucial process for businesses to collect data systematically and make informed decisions. It involves various methods such as surveys, focus groups, interviews, and qualitative research to gather insights from consumers. The data collected is then analyzed and interpreted to uncover patterns, trends, and consumer preferences. Market research helps businesses understand their target customers, recognize competition, identify opportunities, and forecast market trends. By conducting market research, organizations can make well-informed decisions, tailor their products and services to customer needs, and gain a competitive edge in the market.

