What Is The Role Of Marketing In Business?
Marketing plays a fundamental role in the success and growth of businesses across industries. It serves as the driving force behind attracting customers, building brand awareness, and ultimately generating revenue. In today’s competitive business landscape, understanding the role of marketing is crucial for organizations aiming to thrive and stay ahead of the curve.
This article delves into the multifaceted role of marketing in business and explores its significance in achieving strategic objectives. From creating customer demand to fostering customer loyalty, marketing encompasses a wide range of activities that contribute to the overall success of an organization.
What is Marketing?
Marketing is a dynamic and essential function within businesses that encompasses a wide range of activities aimed at promoting products or services and satisfying customer needs. It involves strategic planning, research, communication, and implementation of various techniques to attract and retain customers. By effectively understanding and responding to market demands, marketing plays a pivotal role in driving business growth and success.
Importance of Marketing in Business
Marketing holds immense importance in the realm of business for several reasons. Here are some key points highlighting its significance:
- Creating Awareness and Building Brand Equity: Marketing helps businesses establish and enhance their brand image in the market. Through strategic messaging and communication, companies can create awareness and familiarity among potential customers, building brand equity that sets them apart from competitors.
- Targeting and Reaching the Right Customers: With the help of market research and segmentation, marketing enables businesses to identify and target specific customer segments. By tailoring marketing efforts to reach these target audiences, companies can optimize their resources and maximize the impact of their promotional activities.
- Driving Sales and Revenue: Effective marketing campaigns can generate leads, attract customers, and drive sales. By highlighting the unique value proposition of products or services, marketing efforts can create a desire and demand, resulting in increased revenue for the business.
- Building Customer Relationships: Marketing plays a crucial role in building and nurturing relationships with customers. Through personalized communication, providing valuable information, and offering exceptional customer service, businesses can cultivate loyalty and long-term relationships with their customer base.
- Adapting to Market Changes: The market landscape is constantly evolving, with new competitors, emerging trends, and changing consumer preferences. Marketing helps businesses stay agile by monitoring market dynamics, identifying opportunities, and adapting strategies to stay relevant and competitive.
- Influencing Purchase Decisions: Well-executed marketing initiatives have the power to influence consumers’ purchase decisions. By effectively communicating the unique benefits and value of products or services, marketing can sway consumer perceptions, build trust, and ultimately drive conversion.
Marketing is the driving force behind business growth, enabling companies to reach and engage their target audience, build brand equity, and generate revenue. Understanding the importance of marketing and leveraging its strategies and tactics is vital for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s competitive landscape.
Role Of Marketing In Business
The role of marketing in business is essential as it plays a vital part in driving the success and growth of a company. Marketing encompasses a wide range of activities aimed at understanding customer needs, creating value, building brand awareness, attracting and retaining customers, and ultimately driving revenue. Here are the key roles that marketing plays in a business:
I. Building Brand Awareness

Building brand awareness is a fundamental role of marketing in business. Brand awareness refers to the level of familiarity and recognition that a brand has among its target audience. It involves creating and maintaining a strong presence in the minds of consumers, making the brand easily recognizable and memorable. Here are key aspects of building brand awareness:
A. Creating a Strong Brand Identity: Building brand awareness starts with establishing a strong brand identity. This includes developing a unique brand name, logo, tagline, and visual elements that represent the essence of the brand. A strong brand identity helps differentiate the brand from competitors and makes it easily identifiable to consumers.
B. Consistent Brand Messaging: Consistency in brand messaging is crucial for building brand awareness. All marketing communications, including advertising, social media posts, website content, and packaging, should convey a consistent message that aligns with the brand’s values, personality, and positioning. Consistency helps reinforce the brand’s identity and build familiarity among consumers.
C. Multi-Channel Marketing: To build brand awareness, businesses need to utilize multiple marketing channels to reach their target audience effectively. This may include traditional channels like print advertising, television, and radio, as well as digital channels such as social media, content marketing, email marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO). A multi-channel approach ensures that the brand is visible to consumers across various touchpoints, increasing the chances of brand recognition and recall.
D. Engaging Content Marketing: Content marketing plays a significant role in building brand awareness. By creating and sharing valuable, relevant, and engaging content, businesses can establish themselves as thought leaders and trusted sources of information within their industry. This helps to build credibility, attract and retain customers, and increase brand visibility and awareness.
E. Influencer Partnerships: Collaborating with influencers and industry experts can significantly enhance brand awareness. Influencers have established credibility and a loyal following, making them effective in spreading brand messages to their audience. By partnering with influencers who align with the brand’s values and target market, businesses can reach a larger audience and build brand awareness through authentic endorsements and recommendations.
F. Public Relations and Media Coverage: Securing media coverage and engaging in public relations activities can boost brand awareness. This includes press releases, media interviews, guest articles, and participation in industry events. Positive media coverage helps increase brand visibility and credibility, reaching a wider audience and generating brand awareness.
G. Brand Activation and Experiential Marketing: Engaging consumers through brand activation and experiential marketing initiatives can create memorable experiences that contribute to brand awareness. This may involve organizing events, sponsorships, pop-up shops, or interactive campaigns that allow consumers to experience the brand firsthand. These experiences create a lasting impact and foster positive brand associations.
Building brand awareness is an ongoing process that requires consistent effort and strategic planning. By focusing on creating a strong brand identity, delivering consistent messaging, utilizing multi-channel marketing, engaging in content marketing, leveraging influencer partnerships, gaining media coverage, and creating experiential marketing opportunities, businesses can effectively build brand awareness and establish a strong presence in the marketplace.
II. Target Market Identification
Target market identification is a critical role in marketing in business. It involves identifying the specific group of individuals or businesses that a company aims to serve with its products or services. Understanding the target market is essential for effective marketing strategies and successful business outcomes. Here are key reasons why target market identification is important:
- Focuses Marketing Efforts: Identifying the target market helps businesses focus their marketing efforts and resources on the most relevant audience. Instead of trying to reach everyone, businesses can tailor their messaging, advertising, and promotional activities to resonate with the specific needs, preferences, and demographics of their target market. This targeted approach increases the efficiency and effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Tailor’s Product or Service Offerings: Understanding the target market enables businesses to develop products or services that cater to their specific needs and desires. By conducting market research and gathering insights about the target audience, businesses can identify gaps in the market and create offerings that address those gaps. This customer-centric approach enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to long-term business success.
- Guides Communication and Branding: Target market identification helps businesses craft appropriate communication and branding strategies. By understanding the characteristics and preferences of the target market, businesses can determine the most effective channels, messaging tone, and communication style to connect with their audience. This ensures that marketing messages are relevant, compelling, and resonate with the target market, building stronger brand-customer relationships.
- Enables Market Segmentation: Identifying the target market allows businesses to segment the market based on different criteria such as demographics, psychographics, geographic location, or behavioral characteristics. Market segmentation helps businesses customize their marketing strategies for different segments, allowing for more personalized and targeted approaches. This enhances the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and enables businesses to reach specific customer groups with tailored messages and offerings.
- Improves Customer Acquisition and Retention: By understanding the target market, businesses can better identify and attract potential customers who are most likely to be interested in their offerings. This leads to improved customer acquisition rates. Furthermore, understanding the target market’s preferences, needs, and behaviors helps businesses tailor their products, services, and customer experiences to enhance customer satisfaction and retention. By meeting customer expectations, businesses can build long-term customer relationships and foster loyalty.
Target market identification is a crucial role of marketing in business. It allows businesses to focus their marketing efforts, tailor their offerings, guide communication and branding strategies, enable market segmentation, and improve customer acquisition and retention. By understanding and catering to the specific needs and preferences of their target market, businesses can position themselves for success and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
III. Product Development and Positioning:
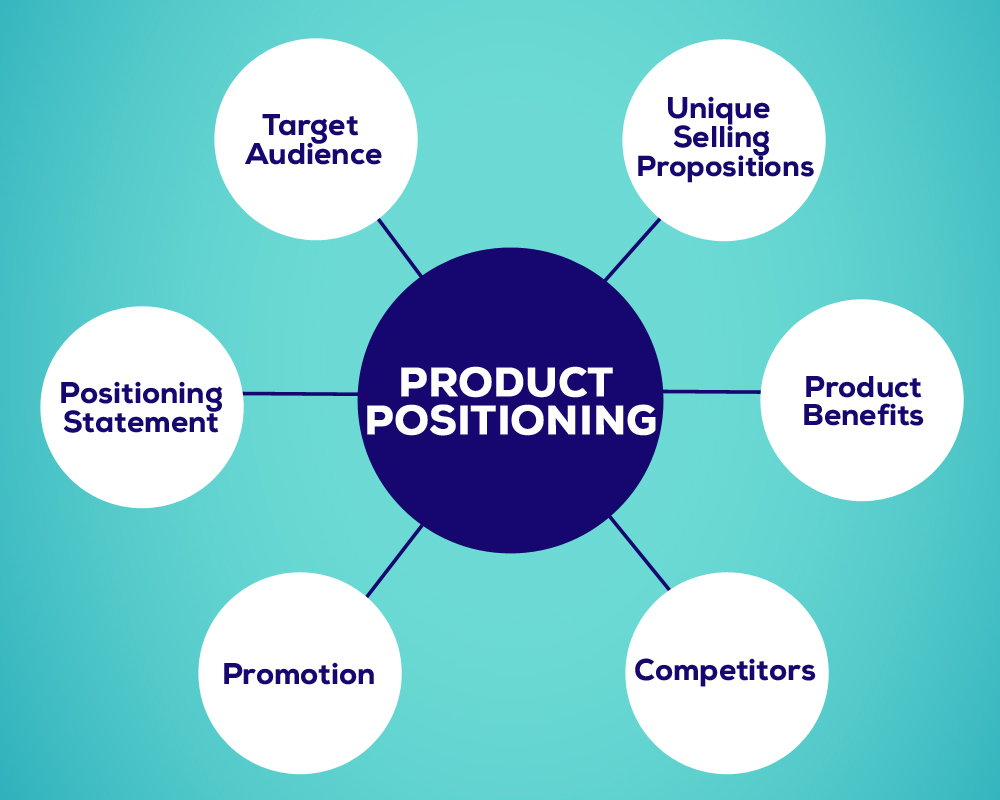
Product development and positioning are critical roles of marketing in business. They involve creating and refining products or services that meet customer needs and effectively positioning them in the market. Here are key aspects of product development and positioning:
A. Identifying Customer Needs: The first step in product development is understanding customer needs and preferences. Through market research, customer surveys, and feedback, marketing teams gather insights to identify gaps in the market and determine what customers are looking for in a product or service. This information guides the development process and ensures that the product addresses the target market’s specific needs.
B. Concept Development and Innovation: Once customer needs are identified, marketing teams work with product development teams to conceptualize and design new products or services. This may involve brainstorming sessions, prototyping, and testing to ensure that the product aligns with the identified needs and provides a unique value proposition. Innovation is a key aspect of product development, as it allows businesses to differentiate themselves and meet evolving customer demands.
C. Product Testing and Refinement: Before launching a new product, marketing teams conduct thorough testing to assess its functionality, quality, and performance. This may involve internal testing, focus groups, or beta testing with a select group of customers. Feedback from these tests helps identify areas for improvement and refine the product to ensure it meets customer expectations.
D. Product Positioning: Once the product is developed, marketing plays a crucial role in positioning it effectively in the market. Product positioning involves identifying the product’s unique features, benefits, and value proposition and communicating them to the target audience in a way that differentiates it from competitors. Effective positioning considers the target market’s needs, preferences, and competitive landscape to create a compelling and differentiated positioning statement.
E. Target Market Segmentation: Marketing teams segment the target market based on demographic, psychographic, geographic, or behavioral factors. By understanding the different segments within the target market, businesses can tailor their product positioning and marketing strategies to resonate with each segment’s specific needs and preferences. This allows for more effective targeting and messaging.
F. Value Communication: Marketing plays a crucial role in effectively communicating the value and benefits of the product to the target audience. This includes developing marketing materials, such as product descriptions, sales collateral, and promotional campaigns that highlight the product’s unique features and how it solves customer problems or meets their desires. Effective value communication helps build customer interest and generates demand for the product.
G. Product Lifecycle Management: Marketing teams are responsible for managing the product lifecycle, which involves monitoring sales, customer feedback, and market trends to make necessary adjustments. They develop strategies to extend the product’s lifespan through product updates, enhancements, or new versions. Additionally, marketing teams assess opportunities for product diversification or expansion to capitalize on changing market dynamics.
Product development and positioning are crucial in meeting customer needs, staying competitive, and driving business growth. Through effective product development processes, identifying customer needs, positioning the product effectively, and managing the product lifecycle, marketing teams ensure that businesses deliver value to customers and create a strong market presence for their offerings.
IV. Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Customer Relationship Management is a vital role in marketing in business. It focuses on building and nurturing strong relationships with customers to enhance satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term value. CRM involves various strategies and activities to manage customer interactions and create personalized experiences. Here are the key aspects of CRM:
A. Customer Data Management: CRM relies on the effective management of customer data. Marketing teams collect and organize customer information, such as contact details, purchase history, preferences, and interactions. This data helps businesses gain insights into individual customers, segment them based on common characteristics, and tailor marketing efforts accordingly.
B. Customer Segmentation: CRM involves segmenting customers into distinct groups based on demographics, behavior, interests, or purchase patterns. This segmentation allows businesses to understand the unique needs and preferences of different customer segments, enabling them to personalize marketing messages, offers, and experiences for better engagement and satisfaction.
C. Personalization and Customization: A key aspect of CRM is personalizing interactions with customers. By utilizing customer data, businesses can deliver targeted and relevant messages, recommendations, and offers to each customer. This level of personalization enhances the customer experience, increases engagement, and fosters loyalty.
D. Customer Service and Support: CRM involves providing excellent customer service and support throughout the customer journey. This includes promptly addressing customer inquiries, resolving issues, and ensuring a seamless experience across various touchpoints. Effective customer service not only builds customer loyalty but also generates positive word-of-mouth and referrals.
E. Loyalty Programs and Rewards: CRM incorporates loyalty programs and rewards to incentivize repeat purchases and foster customer loyalty. These programs can include tiered membership levels, exclusive discounts, personalized offers, or points-based systems. By recognizing and rewarding customer loyalty, businesses strengthen relationships and encourage continued engagement.
F. Feedback and Surveys: CRM involves actively seeking customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and feedback mechanisms. This information helps businesses understand customer satisfaction levels, identify areas for improvement, and address any issues promptly. Feedback also provides insights for product development, marketing strategies, and enhancing the overall customer experience.
G. Cross-Selling and Upselling: CRM leverages customer data and insights to identify opportunities for cross-selling and upselling. By understanding customer preferences and purchase history, businesses can recommend relevant complementary products or upgrades that enhance the customer’s value and satisfaction while increasing sales revenue.
H. Customer Retention and Relationship Building: CRM focuses on building long-term relationships with customers. This involves ongoing communication, nurturing customer loyalty, and delivering consistent value. By prioritizing customer retention, businesses can reduce churn, increase customer lifetime value, and benefit from positive customer referrals.
CRM plays a crucial role in understanding, engaging, and retaining customers. By effectively managing customer data, segmenting customers, personalizing experiences, providing exceptional service, utilizing loyalty programs, gathering feedback, and focusing on long-term relationships, businesses can cultivate strong customer relationships that drive loyalty, advocacy, and business growth.
V. Market Analysis and Competitive Intelligence:
-png.png)
Market analysis and competitive intelligence are vital roles of marketing in business. These activities involve gathering and analyzing data about the market, industry trends, customer behavior, and competitors. Market analysis and competitive intelligence provide valuable insights that guide strategic decision-making and enable businesses to stay competitive. Here are the key aspects of these roles:
A. Market Research: Market analysis begins with conducting comprehensive market research. This involves gathering data on market size, growth potential, customer demographics, preferences, and buying behavior. Market research helps businesses understand their target market, identify market trends, and assess the viability of new products or services. It provides insights into customer needs, expectations, and competitive dynamics.
B. Competitor Analysis: Competitive intelligence involves studying competitors to gain insights into their strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. By analyzing competitors’ product offerings, pricing strategies, marketing tactics, distribution channels, and customer experiences, businesses can identify opportunities and develop effective competitive strategies. Competitor analysis helps businesses differentiate themselves and capitalize on market gaps.
C. SWOT Analysis: SWOT analysis is a framework used in market analysis to assess a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It helps businesses identify internal factors that give them a competitive advantage, areas for improvement, external opportunities to exploit, and potential threats to their market position. A SWOT analysis guides strategic decision-making and enables businesses to align their resources and capabilities with market opportunities.
D. Industry Trends and Market Insights: Market analysis involves tracking industry trends, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and emerging market dynamics. By staying updated on market insights, businesses can proactively identify new opportunities, anticipate customer demands, and adapt their strategies accordingly. Understanding industry trends helps businesses stay ahead of the curve and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
E. Customer Insights: Market analysis includes gathering customer insights through surveys, focus groups, interviews, and data analysis. Understanding customer preferences, needs, and buying behavior is crucial for developing effective marketing strategies and delivering personalized experiences. Customer insights enable businesses to tailor their offerings, messaging, and customer experiences to meet evolving customer expectations.
F. Market Segmentation: Market analysis helps identify distinct customer segments based on demographics, psychographics, behavior, or needs. By segmenting the market, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to specific customer groups, deliver targeted messages, and develop differentiated offerings. Market segmentation enhances marketing effectiveness and customer engagement.
G. Pricing and Positioning Strategies: Market analysis provides insights into pricing dynamics, competitor pricing strategies, and customer willingness to pay. It helps businesses determine optimal pricing levels, understand price sensitivity, and develop pricing strategies that align with market realities. Additionally, market analysis aids in positioning the business and its offerings effectively, considering competitor positioning, market gaps, and customer perceptions.
Market analysis and competitive intelligence enable businesses to make informed decisions, identify market opportunities, mitigate risks, and develop effective marketing strategies. By conducting thorough market research, analyzing competitors, understanding industry trends, gathering customer insights, and leveraging data-driven analysis, businesses can gain a competitive edge and drive sustainable growth in their respective markets.
VI. Pricing and Distribution Strategies:
Pricing and distribution strategies are important roles of marketing in business. These strategies determine how products or services are priced and distributed to reach target customers effectively. Proper pricing and distribution strategies can lead to increased sales, market share, and profitability. Here are the key aspects of these roles:
A. Pricing Strategies:
- Cost-Based Pricing: This strategy involves setting prices based on the production and operational costs of the product or service, along with desired profit margins. The pricing decision considers factors such as materials, labor, overhead expenses, and desired return on investment. Cost-based pricing ensures that prices cover expenses and generate profit but may not account for market demand or competition.
- Value-Based Pricing: Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of the product or service to customers. It considers the benefits, quality, uniqueness, and customer perception of value. Businesses using value-based pricing align their prices with the value customers derive from their offerings. This strategy requires understanding customer preferences, conducting market research, and effectively communicating the value proposition.
- Competitive Pricing: Competitive pricing involves setting prices based on the pricing strategies of competitors. Businesses monitor the pricing of similar products or services in the market and aim to position their prices competitively. This strategy may involve pricing below, at, or slightly above competitors to attract customers or differentiate based on perceived value.
- Dynamic Pricing: Dynamic pricing adjusts prices based on real-time market conditions, customer demand, or other factors. It leverages data and technology to optimize prices dynamically. For example, airlines and hotels use dynamic pricing to adjust prices based on factors such as seasonality, demand, or booking patterns. Dynamic pricing allows businesses to maximize revenue and respond to market fluctuations effectively.
B. Distribution Strategies:
- Direct Distribution: Direct distribution involves selling products or services directly to customers without intermediaries. This strategy gives businesses more control over the customer experience, pricing, and branding. It may include selling through company-owned stores, websites, or direct sales teams. Direct distribution allows for direct customer interaction, feedback collection, and relationship-building.
- Indirect Distribution: Indirect distribution involves using intermediaries, such as wholesalers, retailers, distributors, or agents, to reach customers. This strategy is suitable when businesses want to leverage the existing distribution networks and customer bases of intermediaries. Indirect distribution can expand market reach, enhance product availability, and reduce logistical challenges for businesses.
- Multi-Channel Distribution: Multi-channel distribution involves utilizing multiple channels to reach customers. This may include a combination of direct sales, online platforms, third-party retailers, and other distribution channels. Multi-channel distribution allows businesses to cater to diverse customer preferences, increase market penetration, and provide convenience and accessibility to customers.
- Exclusive Distribution: Exclusive distribution involves restricting the number of outlets or intermediaries that sell a product or service. This strategy is used for premium or luxury products to maintain exclusivity and control distribution. Exclusive distribution can enhance brand perception and create an aura of prestige around the product or service.
- Intensive Distribution: Intensive distribution aims to make a product or service available through as many outlets as possible. This strategy is commonly used for fast-moving consumer goods or products with high demand. Intensive distribution maximizes market coverage and ensures wide availability for customers.
Pricing and distribution strategies are essential for businesses to effectively position their offerings, reach target customers, and maximize sales and profitability. By carefully considering pricing approaches, analyzing market conditions, understanding customer preferences, and selecting appropriate distribution channels, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
VI. Promotional and Communication Strategies:

Promotional and communication strategies are crucial roles of marketing in business. These strategies involve creating awareness, generating interest, and persuading target customers to engage with a company’s products or services. Effective promotional and communication strategies help businesses build brand recognition, attract customers, and drive sales. Here are the key aspects of these roles:
A. Advertising:
- Print Advertising: Print advertising includes placing ads in newspapers, magazines, brochures, flyers, or direct mail. It allows businesses to reach specific target audiences and convey detailed information about their products or services. Print advertising can be cost-effective and impactful in reaching local or niche markets.
- Digital Advertising: Digital advertising involves online channels such as search engine ads, display ads, social media ads, and video ads. Digital advertising provides targeting capabilities, allowing businesses to reach specific demographics, interests, or behaviors. It offers precise tracking and measurement of ad performance, enabling optimization and cost control.
- Broadcast Advertising: Broadcast advertising refers to television and radio ads. Television ads allow businesses to visually showcase their products or services to a broad audience, while radio ads provide an opportunity for audio-based messaging. Broadcast advertising can reach a large audience and create high brand exposure.
B. Public Relations (PR):
- Media Relations: PR involves building relationships with journalists and media outlets to secure favorable media coverage. This can be done through press releases, media pitches, media interviews, or participation in industry events. Positive media coverage enhances brand credibility and visibility.
- Crisis Management: PR plays a crucial role in managing and mitigating the impact of crises or negative situations. It involves timely communication, transparency, and addressing concerns to protect the brand’s reputation and maintain customer trust.
C. Sales Promotion:
- Discounts and Coupons: Offering discounts, coupons, or promotional codes can incentivize customers to make a purchase. These promotions create a sense of urgency and value, driving immediate sales and attracting new customers.
- Loyalty Programs: Loyalty programs reward customers for repeat purchases or brand loyalty. They encourage customer retention, increase engagement, and generate ongoing sales. Loyalty programs can include point systems, exclusive discounts, or special rewards.
D. Direct Marketing:
- Email Marketing: Email marketing involves sending targeted promotional messages or newsletters to a customer’s inbox. It allows businesses to personalize messages, nurture customer relationships, and drive repeat purchases.
- Direct Mail: Direct mail includes sending physical promotional materials, such as brochures, catalogs, or postcards, directly to customers’ mailboxes. Direct mail can be highly targeted and personalized, creating a tangible and memorable brand experience.
E. Digital Marketing:
- Content Marketing: Content marketing involves creating and sharing valuable and relevant content to attract and engage target customers. This can include blog articles, videos, infographics, or social media posts. Content marketing positions businesses as industry experts, builds brand authority and drives customer engagement.
- Social Media Marketing: Social media marketing utilizes platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, or YouTube to connect with target audiences, build brand awareness, and engage customers. It involves creating engaging content, fostering community interactions, and running targeted ad campaigns.
F. Influencer Marketing:
Influencer marketing leverages the reach and influence of individuals with a significant online following. Businesses collaborate with influencers to promote their products or services through authentic and trusted endorsements. Influencer marketing can help reach niche audiences and build credibility.
Promotional and communication strategies play a vital role in creating brand awareness, attracting customers, and driving sales. By employing a mix of advertising, public relations, sales promotions, direct marketing, digital marketing, and influencer marketing, businesses can effectively reach target audiences, convey their value proposition, and build strong relationships with customers.
VII. Measuring and Evaluating Marketing Efforts:
Measuring and evaluating marketing efforts is a critical role of marketing in business. It involves monitoring and assessing the effectiveness of marketing strategies, campaigns, and initiatives. By analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and gathering relevant data, businesses can make data-driven decisions, optimize their marketing efforts, and achieve better results. Here are key aspects of measuring and evaluating marketing efforts:
A. Defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Sales Revenue: Tracking sales revenue helps assess the direct impact of marketing efforts on the company’s financial performance. It provides insights into the effectiveness of marketing campaigns in driving revenue growth.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculating ROI helps determine the profitability of marketing initiatives by comparing the cost of marketing activities to the generated revenue or customer acquisition. ROI analysis helps prioritize and allocate resources to the most effective marketing channels or campaigns.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): CAC measures the cost incurred to acquire a new customer. By comparing CAC to customer lifetime value (CLTV), businesses can assess the efficiency and profitability of their marketing investments.
- Website and Social Media Metrics: Monitoring website traffic, conversion rates, bounce rates, time spent on site, and social media engagement metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of digital marketing efforts. These metrics help assess brand visibility, user engagement, and the impact of content and campaigns.
B. Market Research and Surveys:
- Customer Surveys: Conducting surveys and collecting customer feedback helps assess customer satisfaction, brand perception, and the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. Surveys provide qualitative and quantitative insights into customer preferences, needs, and purchasing behavior.
- Market Analysis: Ongoing market analysis provides insights into market trends, competitive landscape, and customer preferences. This analysis helps evaluate the positioning of the business and its offerings within the market and identify areas for improvement or market opportunities.
C. Tracking and Analytics:
- Web Analytics: Utilizing web analytics tools, such as Google Analytics, provides valuable data on website traffic, user behavior, conversions, and campaign performance. Web analytics helps identify website strengths and weaknesses, track marketing campaign effectiveness, and optimize conversion funnels.
- Social Media Analytics: Social media platforms offer analytics tools that provide insights into reach, engagement, click-through rates, and conversions. Social media analytics helps assess the effectiveness of social media strategies, content performance, and audience behavior.
D. A/B Testing and Experimentation:
- A/B Testing: A/B testing involves comparing two or more variations of a marketing element, such as email subject lines, website designs, or ad creatives, to determine the most effective version. A/B testing helps optimize marketing materials and strategies based on data-driven insights.
- Controlled Experiments: Conducting controlled experiments, such as split testing or pilot programs, helps evaluate the impact of specific marketing initiatives on key metrics. Controlled experiments provide valuable insights into the causal relationships between marketing activities and outcomes.
E. Continuous Improvement and Adaptation:
Regularly reviewing and analyzing marketing data allows businesses to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions. Evaluating marketing efforts helps optimize strategies, refine targeting, adjust messaging, and allocate resources effectively.
F. Competitive Analysis:
Analyzing competitors’ marketing activities, campaigns, and performance helps benchmark against industry standards and identify areas of competitive advantage or differentiation. Competitive analysis provides insights into market share, positioning, and potential opportunities or threats.
Measuring and evaluating marketing efforts is crucial for understanding the impact of marketing initiatives, identifying areas for improvement, and optimizing marketing strategies. By monitoring KPIs, conducting market research, tracking analytics, performing A/B testing, and adapting based on insights, businesses can make informed decisions, improve marketing effectiveness, and achieve better results.
Conclusion
Marketing is the lifeblood of business, driving growth, differentiation, and customer engagement. Throughout this article, we explored its vital roles, including understanding customers, building brands, creating value, and fostering customer relationships. Strategic marketing aligns efforts with business goals, enabling businesses to stand out, adapt to changing trends, and make data-driven decisions.
Looking ahead, marketers must embrace digital transformations, personalized experiences, technology integration, sustainability, and ethical considerations. These evolving trends and challenges shape the marketing landscape, requiring businesses to stay agile and relevant.
In conclusion, marketing is the driving force behind business success, connecting businesses with their audience, nurturing loyalty, and achieving goals. By harnessing the power of strategic marketing and staying ahead of industry shifts, businesses can navigate the ever-changing marketplace and thrive in an era of constant adaptation.

