What Is The Importance Of Marketing Mix
In today’s dynamic business landscape, achieving marketing success requires a strategic approach. One such approach that has stood the test of time is the concept of the marketing mix. From multinational corporations to small businesses, understanding and effectively utilizing the marketing mix can be the difference between triumph and obscurity. In this section, we will delve into the essence of the marketing mix, its significance in achieving marketing objectives, and how it can be a game-changer for businesses of all sizes.
Imagine a master chef preparing a gourmet dish. They carefully select the finest ingredients, balance the flavors, and present them in an appealing manner. Similarly, in the realm of marketing, the marketing mix acts as the recipe for success, blending various elements to create a winning strategy. Let’s explore why mastering the marketing mix is essential for businesses looking to thrive in today’s competitive marketplace.
What is Marketing Mix?
The marketing mix refers to a set of strategic elements that businesses combine to achieve their marketing goals. These elements, commonly known as the 4Ps, include Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Each P represents a distinct aspect of marketing, and when harmoniously integrated, they form a powerful framework that drives business success.
The Importance of the Marketing Mix
The marketing mix plays a crucial role in achieving marketing objectives for several reasons:
- Comprehensive Strategy: The marketing mix ensures a holistic approach to marketing, considering various aspects that collectively contribute to a successful campaign. By addressing all elements, businesses can create a well-rounded strategy that resonates with their target audience.
- Customer-Centric Approach: The marketing mix encourages businesses to understand their customers’ needs, preferences, and purchasing behavior. By aligning the mix with customer insights, businesses can tailor their offerings to meet customer expectations, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Effective Resource Allocation: With limited resources, businesses must allocate their budgets wisely. The marketing mix helps in optimizing resource allocation by identifying the most impactful strategies within each element. This ensures that investments are made where they will have the greatest impact.
- Competitive Advantage: A well-executed marketing mix can differentiate a business from its competitors. By crafting a unique value proposition through the mix, businesses can stand out in crowded markets, attract target customers, and gain a competitive edge.
- Strategic Adaptability: Markets are constantly evolving, and customer preferences can change rapidly. The marketing mix provides businesses with a framework for adaptability. By monitoring market trends and adjusting the mix accordingly, businesses can stay relevant and responsive to ever-changing market dynamics.
In conclusion, the marketing mix is an indispensable tool for businesses seeking marketing success. By strategically integrating the 4Ps, businesses can create a compelling value proposition, effectively communicate with their target audience, and achieve their marketing objectives. In the following sections, we will explore each element of the marketing mix in detail and unveil the strategies that can unlock its full potential.
The Elements of the Marketing Mix
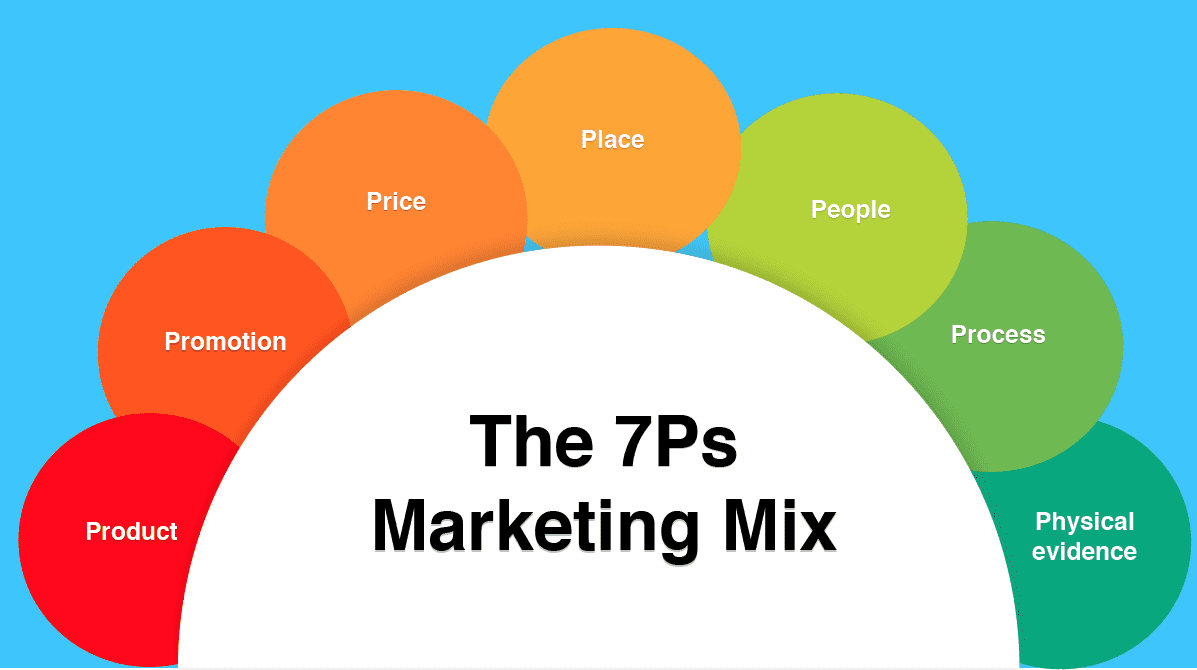
In this section, we will delve into the four key elements of the marketing mix: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. We will explore the significance of each element and how they collectively contribute to a successful marketing strategy.
1. Product:
The product element of the marketing mix refers to the tangible or intangible offering that a company provides to meet the needs or wants of its target market. It encompasses the features, design, branding, packaging, and quality of the product. The significance of the product element lies in its ability to satisfy customer needs, create value, and differentiate the company from its competitors.
Product development is the process of designing and creating new products or modifying existing ones to meet market demands. It involves conducting market research, generating ideas, concept development, prototype testing, and final production. Effective product development ensures that the company stays competitive and relevant in the market.
Features are the characteristics and attributes of a product that deliver specific benefits to the customer. These can include functionality, performance, design, durability, and other qualities that differentiate the product from its competitors. Companies must identify and emphasize the features that resonate with their target market to create a unique selling proposition.
Branding plays a crucial role in product differentiation and customer perception. A brand represents the overall image, reputation, and personality of a product or company. It helps establish trust, loyalty, and recognition among customers. Branding involves creating a unique name, logo, tagline, and visual identity that aligns with the target market’s preferences and values.
Packaging refers to the physical or visual presentation of a product. It serves multiple purposes, including protection, convenience, information communication, and promotion. Effective packaging attracts attention, enhances the product’s perceived value, and communicates important details such as ingredients, usage instructions, and branding. Packaging can also contribute to sustainability and environmental considerations.
Product differentiation and positioning impact marketing strategies significantly. Product differentiation refers to the unique qualities and features that set a product apart from its competitors. By highlighting these distinctive attributes, companies can position their products in the market to appeal to specific target segments. This positioning determines the marketing message, pricing strategy, distribution channels, and promotional activities employed to reach and influence the target market.
For example, if a company differentiates its product as a high-end luxury item, it would position it in the market accordingly, targeting affluent customers and employing premium pricing, exclusive distribution channels, and sophisticated promotional campaigns. On the other hand, a company focusing on product differentiation based on affordability and convenience would position its product for a broader market segment and utilize cost-effective pricing, widespread distribution, and targeted promotional activities.
The marketing strategy should align with the unique selling proposition derived from product differentiation and positioning. By understanding customer needs, desires, and preferences, companies can tailor their marketing efforts to effectively communicate the value proposition of their products and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
2. Price:
The price element of the marketing mix refers to the monetary value that customers are willing to pay for a product or service. Price plays a significant role in shaping customer perceptions, influencing demand, and determining the company’s profitability. Setting the right price is crucial for achieving business objectives and satisfying customer expectations.
Pricing strategies can vary depending on factors such as costs, competition, and perceived value. Cost-based pricing involves setting the price based on the production and distribution costs, along with a desired profit margin. Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of the product in the eyes of the customer, considering factors such as quality, benefits, and customer willingness to pay. Competition-based pricing involves setting the price in line with or slightly below the prices of competitors to gain market share.
The relationship between price and perceived value is vital for customers. Customers evaluate the benefits they expect to receive from a product or service and compare it to the price. If the perceived value exceeds the price, customers perceive the product as a good deal and are more likely to make a purchase. On the other hand, if the price exceeds the perceived value, customers may perceive the product as too expensive and seek alternatives. Therefore, it is crucial for companies to align their pricing with the perceived value of their products to attract and retain customers.
3. Place:
The place element of the marketing mix refers to the distribution channels and methods used by a company to make the product available to customers. It involves decisions regarding how the product will be stored, transported, and delivered to the target market. The significance of the place element lies in its ability to ensure that the product reaches the right customers at the right time and in the right condition.
Distribution channels can include direct, indirect, or online channels. Direct channels involve selling products directly from the manufacturer to the end customers, bypassing intermediaries. Indirect channels involve the use of intermediaries such as wholesalers, retailers, and distributors to reach the end customers. Online channels refer to the use of e-commerce platforms and websites to sell products directly to customers.
The selection of distribution channels is essential for reaching target markets efficiently. Companies must consider factors such as market coverage, customer convenience, cost-effectiveness, and control over the marketing mix variables. The choice between direct and indirect channels depends on various factors such as the complexity of the product, target market characteristics, competition, and company resources.
Logistics plays a crucial role in the place element. It involves managing the movement and storage of products throughout the supply chain, ensuring timely delivery and efficient inventory management. Logistics activities include transportation, warehousing, inventory control, order processing, and customer service. Efficient logistics practices help minimize costs, reduce lead times, and enhance customer satisfaction.
4. Promotion:
The promotion element of the marketing mix refers to the activities and tools used by companies to communicate with and persuade customers. It aims to inform, educate, persuade, and remind the target market about the company’s products or services. Effective promotion helps create awareness, generate interest, and ultimately drive sales.
Promotional tools can include advertising, sales promotion, public relations, and personal selling. Advertising involves paid, non-personal communication through various media channels such as television, radio, print, online platforms, and social media. Sales promotion includes short-term incentives and discounts aimed at stimulating immediate sales. Public relations involve managing the company’s reputation, building positive relationships with stakeholders, and generating favorable publicity. Personal selling involves one-on-one communication between the salesperson and potential customers to address their specific needs and influence purchase decisions.
Integrated marketing communications (IMC) is crucial for effective promotion. It involves coordinating and integrating various promotional tools to deliver a consistent and unified message to the target market. By aligning the messages across different channels, companies can enhance brand consistency, avoid confusion, and reinforce their value proposition. Consistent messaging helps build brand awareness, credibility, and customer trust.
In conclusion, the elements of the marketing mix, namely product, price, place, and promotion, are essential components of a company’s marketing strategy. They work together to create value for customers, differentiate the company from competitors, and influence customer buying decisions. Understanding and effectively managing these elements are key to developing successful marketing strategies and achieving business objectives.
Case Studies and Examples
In this section, we will explore real-world case studies and examples of successful marketing mix strategies. By analyzing how different companies implemented the marketing mix to achieve their objectives, we can gain valuable insights into the versatility and effectiveness of this strategic framework.
Example 1: Apple’s Product Innovation and Branding
Apple is widely regarded as a prime example of successful marketing mix implementation. By focusing on product innovation and differentiation, Apple has consistently maintained a competitive edge in the technology industry. Their marketing mix strategies have been instrumental in shaping their success.
- Product: Apple’s product development focuses on creating innovative and user-friendly devices, such as the iPhone, MacBook, and Apple Watch. Their sleek design, cutting-edge features, and seamless user experience have set them apart from competitors.
- Price: Apple adopts a premium pricing strategy, positioning its products as high-end and exclusive. By associating their brand with quality and luxury, they have successfully justified higher price points.
- Place: Apple strategically utilizes both direct and indirect distribution channels. Their brick-and-mortar stores provide a unique customer experience, while online channels enable global accessibility. This omnichannel approach ensures wider market reach.
- Promotion: Apple’s marketing communications emphasize their products’ unique features and benefits through integrated campaigns. Their iconic “Think Different” and “Shot on iPhone” campaigns have resonated with customers and reinforced their brand identity.
Example 2: Coca-Cola’s Effective Promotion and Branding

Coca-Cola’s marketing mix strategies have played a pivotal role in establishing its iconic brand and achieving global success. Through effective promotion and branding efforts, Coca-Cola has become a household name.
- Product: Coca-Cola offers a range of refreshing beverages that cater to diverse consumer preferences. From the classic Coca-Cola soda to Diet Coke and Coca-Cola Zero, they have successfully expanded their product portfolio.
- Price: Coca-Cola employs competitive pricing strategies to make its products affordable and accessible to a wide range of customers. Their pricing aligns with the perceived value and affordability expectations of their target market.
- Place: Coca-Cola has developed a robust distribution network that ensures its products are available in various channels, including supermarkets, convenience stores, restaurants, and vending machines. This extensive reach maximizes their market penetration.
- Promotion: Coca-Cola’s promotional efforts are synonymous with engaging storytelling and emotional connection. Through memorable advertising campaigns, such as the “Share a Coke” campaign and the Coca-Cola polar bears, they have successfully connected with consumers on a deep emotional level.
Example 3: Amazon’s Customer-Centric Approach and Convenience
Amazon’s marketing mix strategies have revolutionized the e-commerce industry. By prioritizing customer-centricity and convenience, Amazon has become a dominant force in online retail.
- Product: Amazon offers a vast selection of products across various categories, providing customers with a wide range of choices. They also developed their own line of products, such as Amazon Echo and Kindle, to further expand their offerings.
- Price: Amazon utilizes dynamic pricing strategies, optimizing prices based on market demand and competition. Their competitive pricing, coupled with special deals and discounts, attracts price-sensitive customers.
- Place: Amazon’s distribution strategy focuses on fast and reliable delivery. With fulfillment centers strategically located worldwide, they can provide quick shipping to customers globally. Their Prime membership program further enhances convenience and customer loyalty.
- Promotion: Amazon’s marketing communications emphasize the ease of shopping, personalized recommendations, and customer reviews. Their targeted advertising, email campaigns, and affiliate marketing contribute to building customer trust and loyalty.
These case studies demonstrate how different companies, across various industries, have effectively implemented the marketing mix to achieve their objectives. By understanding their strategies and adapting them to specific business contexts, businesses can leverage the marketing mix to drive success in their respective industries.
Conclusion
The marketing mix is the secret recipe for business success. With its seven P’s, it forms a comprehensive strategy to influence customers, optimize sales, and differentiate from competitors. By constantly evaluating and aligning the marketing mix with business goals, companies can reach the right customers with the right offering, at the right time and price. Embrace the power of the marketing mix to unlock your business’s full potential and pave the way for sustained growth and profitability.

