Importance Of Micro Environment In Marketing
While macroeconomic trends and global influences undoubtedly hold sway, it is the often-overlooked microenvironment that forms the intricate tapestry upon which marketing strategies are woven. This article delves into the significance of the microenvironment in marketing, shedding light on how factors within a company’s immediate sphere of influence can wield a profound impact on its ability to thrive and adapt in an ever-evolving marketplace.
What is MicroEnvironment in Marketing?
The microenvironment in marketing encapsulates the immediate surroundings and influences that directly affect a business entity. Unlike the broader macro environment, which encompasses factors like economic trends and political forces, the microenvironment focuses on those elements that are closer to home and have a direct and immediate impact. These factors are often dynamic and can vary greatly from one industry to another.
Importance of Understanding the Micro Environment
Gaining a deep comprehension of the microenvironment is akin to wielding a magnifying glass over the details that can make or break a business. In this fiercely competitive era, businesses need to anticipate changes, challenges, and opportunities that arise from within their industry niche. Such foresight empowers companies to tailor their strategies, enhance their offerings, and refine their approach to cater precisely to their target audience’s needs.
Components of the MicroEnvironment
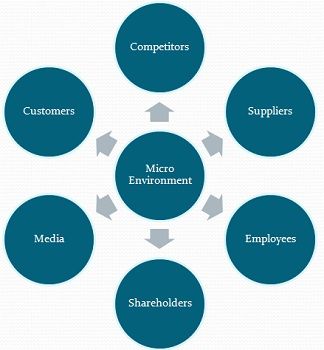
In the microenvironment, the components that intricately shape a company’s ability to serve its customers and achieve its marketing objectives come into play. A deep understanding of these components is pivotal for crafting effective marketing strategies that resonate with the intended audience. Let’s delve into the key factors that make up this dynamic microenvironment.
A. Customers
When it comes to the microenvironment in marketing, few components are as vital and influential as customers. Customers are not just the end consumers of products and services; they are the lifeblood of any business, and their behavior, needs, and preferences hold a central place in shaping marketing strategies. In this article, we delve into the intricate relationship between customers and the microenvironment, highlighting why understanding and engaging with this critical component is essential for the success and sustainability of any business.
1. Identification of Target Customers
Identifying and defining the target customers is the foundational step in any marketing endeavor. This involves segmenting the market to pinpoint specific groups of individuals who share common characteristics and are most likely to be interested in the offerings. From demographics such as age, gender, and location to psychographics like interests and lifestyle, the process of target customer identification refines the marketing approach and guides all subsequent decisions.
2. Customer Needs, Preferences, and Behaviors
In the realm of marketing, the customer’s voice reigns supreme. Understanding the needs, desires, and pain points of the target customers is paramount. This involves conducting thorough market research to uncover insights into what motivates their purchasing decisions. Unveiling customer preferences, whether related to features, pricing, or convenience, provides the basis for tailoring products and messages that resonate on a personal level.
3. Influence of Customer Buying Patterns on Marketing Strategies
Customer buying patterns serve as invaluable guides for shaping marketing strategies. By studying historical data, businesses can discern patterns related to when, where, and how customers make purchasing decisions. This insight informs decisions such as the timing of promotions, the channels used for communication, and even the development of new products or services. Adapting to these patterns ensures that marketing efforts are not only effective but also aligned with the customer’s journey.
In today’s hyper-competitive landscape, understanding and leveraging the nuances of the microenvironment is pivotal for crafting laser-focused marketing strategies. By identifying target customers, comprehending their needs, preferences, and behaviors, and adapting to their buying patterns, businesses can create campaigns that resonate deeply, fostering lasting customer relationships and sustainable success.
B. Competitors
Competitors play a pivotal role in shaping a company’s marketing environment, influencing pricing strategies, product development, and overall market positioning. Understanding and strategically responding to both direct and indirect competitors are essential for maintaining a competitive edge. Let’s delve into the key aspects of dealing with competitors in the ever-evolving marketing landscape.
1. Analysis of Direct and Indirect Competitors
Thoroughly analyzing both direct and indirect competitors is the cornerstone of effective competitor intelligence. Direct competitors are those offering similar products or services to the same target audience. Indirect competitors, on the other hand, might provide alternative solutions that satisfy the same customer needs. Conducting a comprehensive analysis involves studying their strengths, weaknesses, market share, pricing strategies, and unique selling propositions.
2. Competitive Positioning and Differentiation
Positioning your brand effectively in the market vis-à-vis your competitors is paramount. This involves identifying your company’s unique value proposition and differentiators that set you apart. By highlighting these differentiators, whether they relate to quality, pricing, customer service, or innovation, you can carve out a distinct space in the market that resonates with your target audience.
3. Strategies for Monitoring and Responding to Competitor Actions
In the dynamic marketing environment, vigilance is key. Regularly monitoring your competitors’ activities, such as product launches, pricing changes, and marketing campaigns, provides invaluable insights. By staying attuned to their movements, you can proactively respond to emerging trends and competitive threats. This might involve adjusting your pricing, enhancing your product offerings, or refining your marketing messages to maintain a competitive advantage.
Moreover, staying on top of competitor actions empowers you to seize opportunities that arise from missteps or gaps in the market. Swift, well-informed responses can position your brand as the go-to choice for customers seeking value and innovation.
In summary, competitors are integral components of the marketing environment, driving businesses to innovate, adapt, and refine their strategies. By conducting thorough competitor analysis, strategically positioning your brand, and proactively monitoring and responding to competitor actions, you can create a robust marketing strategy that not only withstands competition but also thrives in the face of it.
C. Suppliers

Suppliers play a critical role in the marketing process, significantly influencing a company’s ability to deliver value to its customers. Their role extends beyond providing products and services; they contribute to the overall success and competitive advantage of a business. Let’s explore the multifaceted aspects of suppliers’ involvement in the marketing process.
1. Role of Suppliers in the Marketing Process
Suppliers are essential partners in the marketing process, contributing in various ways:
- Product Quality: The quality of the materials and components supplied by suppliers directly affects the quality of the final product. High-quality inputs result in better-end products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Innovation: Collaborative relationships with innovative suppliers can lead to the introduction of new ideas, materials, and technologies, enhancing product offerings and competitiveness.
- Timely Delivery: Reliable suppliers ensure the timely delivery of materials, enabling companies to meet production schedules and deliver products to customers as promised.
- Cost Efficiency: Efficient and cost-effective supply chains contribute to competitive pricing, which can attract price-sensitive customers and boost sales.
- Customization: Suppliers that offer customization options can help businesses tailor products to meet specific customer needs and preferences.
2. Dependence on a Reliable and Efficient Supply Chain
A reliable and efficient supply chain is crucial for the success of a business. A breakdown in the supply chain can lead to delays in production, product shortages, and missed delivery deadlines. This can have a domino effect, impacting customer satisfaction, damaging the company’s reputation, and even causing financial losses.
Establishing strong relationships with suppliers, based on trust and clear communication, helps ensure a smooth and uninterrupted supply chain. Companies that maintain such relationships are better positioned to respond quickly to market demands and changes, leading to increased customer satisfaction and sustained growth.
3. Impact of Supplier Relationships on Product Quality and Pricing
Supplier relationships directly impact product quality and pricing:
- Product Quality: Reliable suppliers that consistently deliver high-quality materials contribute to the production of superior products. This, in turn, enhances the company’s reputation and customer loyalty. A lapse in product quality due to subpar inputs can lead to customer complaints, returns, and decreased trust.
- Pricing: Supplier costs directly influence a company’s production costs and, subsequently, its pricing strategy. Companies with strong supplier relationships may negotiate better terms, volume discounts, or exclusive deals, leading to cost savings that can be passed on to customers in the form of competitive pricing.
- Innovation and Differentiation: Collaborating with innovative suppliers can lead to the development of unique products and features that differentiate a company’s offerings in the market. This can create a competitive advantage and justify premium pricing.
Suppliers are integral to a company’s marketing process. They contribute to product quality, innovation, timely delivery, cost efficiency, and customization. A reliable and efficient supply chain is essential for meeting customer demands and maintaining a competitive edge. Building strong supplier relationships can positively impact product quality, pricing, and differentiation, ultimately enhancing a company’s success in the market.
D. Distributors
Effective distribution channels and collaboration with distributors are essential components of a successful marketing strategy. Distributors play a pivotal role in ensuring that products reach the intended customers efficiently and that the brand maintains consistent visibility in the market. Let’s delve into the significance of distribution channels, collaboration with distributors, and the importance of consistent product availability and visibility.
1. Importance of Effective Distribution Channels
Distribution channels, also known as marketing channels, refer to the various intermediaries involved in the process of getting products from the manufacturer to the end consumer. Effective distribution channels are crucial for several reasons:
- Wider Market Reach: Distributors help reach a broader audience by covering a larger geographical area. They have established networks, allowing products to reach places that might be challenging for the manufacturer to access directly.
- Efficiency: Distributors specialize in logistics and warehousing, which can result in efficient storage, transportation, and delivery of products. This ensures that products are available when and where customers need them.
- Reduced Costs: Distributors often handle bulk orders, allowing manufacturers to benefit from economies of scale in production and shipping. This can lead to cost savings that can be passed on to customers.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Manufacturers can focus on product development, quality control, and marketing while leaving the distribution logistics to experts.
2. Collaboration with Distributors for Wider Market Reach
Collaborating with distributors offers several advantages:
- Market Expertise: Distributors have a deep understanding of local markets, customer preferences, and trends. They can provide valuable insights that help manufacturers tailor their products and marketing strategies for specific regions.
- Faster Market Entry: Distributors have established relationships with retailers, making it quicker for new products to enter the market. This is especially beneficial for companies looking to expand their product offerings.
- Risk Sharing: Distributors take on some of the financial risks associated with storing and selling products. This can provide manufacturers with greater stability and predictability.
3. Ensuring Consistent Product Availability and Visibility
Consistent product availability and visibility are critical for brand recognition and customer loyalty:
- Availability: Distributors help ensure that products are consistently available to consumers. This avoids instances of out-of-stock situations, which can lead to customer dissatisfaction and lost sales opportunities.
- Visibility: Distributors play a role in promoting and marketing products to retailers and consumers. They help maintain consistent product visibility through effective merchandising and promotional efforts.
- Brand Image: A strong and recognizable brand image is built over time through consistent product availability and visibility. Customers are more likely to trust and engage with brands that they frequently encounter.
- Impulse Purchases: Products that are readily available and visible can encourage impulse purchases. A well-placed product in a retail store, for example, can catch the eye of a consumer and lead to a purchase.
Distributors are key partners in a company’s marketing strategy. They help extend the brand’s reach, enhance efficiency, and provide market insights. Collaborating with distributors allows manufacturers to tap into their expertise and networks. Ensuring consistent product availability and visibility is essential for maintaining brand loyalty and attracting new customers. Together, effective distribution channels and distributor collaboration contribute to a successful marketing ecosystem.
E. Intermediaries
Intermediaries, such as agents, brokers, and wholesalers, play a significant role in the distribution process, helping to bridge the gap between manufacturers and consumers. Building strong intermediary relationships and effectively managing conflicts is crucial for maintaining smooth distribution and achieving marketing goals.
1. Role of Intermediaries like Agents, Brokers, and Wholesalers
Intermediaries serve as a link between producers and end consumers, adding value to the distribution process:
- Agents: Agents represent manufacturers or suppliers in the market. They facilitate transactions and negotiations between producers and buyers, often specializing in specific industries. Agents typically work on commission and can provide expertise and market insights to both parties.
- Brokers: Brokers, similar to agents, act as intermediaries who connect buyers and sellers. However, brokers are more focused on facilitating transactions, such as real estate deals or stock trading. They bring parties together and earn a commission for successful deals.
- Wholesalers: Wholesalers purchase products in bulk from manufacturers and then sell them in smaller quantities to retailers. They play a critical role in distribution by providing storage, bulk purchasing, and logistics services. Wholesalers help manufacturers reach a wider network of retailers efficiently.
2. Building Strong Intermediary Relationships
Building strong relationships with intermediaries is essential for a successful distribution strategy:
- Clear Communication: Effective communication is key to understanding each other’s needs and expectations. Regular communication helps avoid misunderstandings and aligns both parties toward common goals.
- Mutual Benefits: Intermediaries are more likely to work closely with manufacturers who offer mutual benefits. These benefits can include competitive pricing, reliable product availability, and marketing support.
- Training and Support: Providing training and support to intermediaries helps them better understand the products they are selling. This can lead to better customer service and enhanced product knowledge.
- Feedback Loop: Encourage intermediaries to provide feedback on market trends, customer preferences, and challenges they face. This information can help manufacturers refine their products and strategies.
3. Managing Conflicts and Ensuring Smooth Distribution
Conflict management is crucial for maintaining smooth distribution relationships:
- Open Dialogue: Address conflicts openly and constructively. Listen to the concerns of intermediaries and work together to find solutions that benefit both parties.
- Mediation: In case of disputes, consider involving a neutral third party to mediate and help find a resolution. This can prevent conflicts from escalating and damaging the relationship.
- Clear Agreements: Establish clear agreements and contracts that outline responsibilities, terms, and expectations. Having these documents in place can help prevent misunderstandings.
- Performance Evaluation: Regularly evaluate the performance of intermediaries. If issues arise, identify the root causes and work collaboratively to address them.
Intermediaries play a vital role in the distribution process, connecting manufacturers to end consumers. Building strong relationships with intermediaries involves clear communication, mutual benefits, and support. Conflict management strategies ensure that conflicts are resolved without damaging the distribution network. Effective collaboration with intermediaries contributes to efficient distribution and successful marketing outcomes.
F. Publics
Publics are groups of individuals or entities that have a legitimate interest in or impact on a company’s operations, decisions, and reputation. Publics play a crucial role in shaping a company’s image and can influence marketing strategies and brand perception. Managing public perception and reputation is essential for building a positive brand image and successful marketing strategies.
1. Identification of Relevant Publics (Media, Financial, Government, etc.)
Different types of public can have varying levels of impact on a company’s operations. Some common types of publics include:
- Media Public: This includes newspapers, magazines, blogs, social media platforms, and other forms of media that can report on a company’s activities. Media coverage can significantly influence public perception and brand image.
- Financial Public: Financial publics include entities such as banks, investors, shareholders, and financial analysts. The financial health and performance of a company can affect its relationships with these stakeholders.
- Government Public: Government agencies and regulators have a direct impact on a company’s operations through laws, regulations, and policies. Maintaining positive relationships with government bodies is crucial for compliance and reputation.
- General Public: The general public’s opinions, preferences, and perceptions about a company’s products, services, and actions can influence its success. Social media and consumer reviews play a significant role in shaping public opinions.
2. Managing Public Perception and Reputation
Managing public perception and reputation is essential for building a positive brand image:
- Transparency: Being transparent in communication with the public builds trust. Companies should provide accurate and timely information about their products, services, and operations.
- Crisis Management: Effective crisis management is crucial in handling situations that could damage the company’s reputation. Responding promptly, taking responsibility, and offering solutions can mitigate negative perceptions.
- Engagement: Engaging with the public, especially through social media, can humanize the company and create a positive connection. Responding to feedback and addressing concerns demonstrates the company’s commitment to its customers.
- Consistency: Consistency in messaging across various platforms and interactions helps establish a strong brand identity and reinforces positive perceptions.
3. Impact of Public Opinions on Brand Image and Marketing Strategies
Public opinions can significantly impact a company’s brand image and marketing strategies:
- Brand Image: Positive public opinions can enhance a company’s brand image, while negative opinions can tarnish it. Public perceptions about a company’s values, ethics, and social responsibility can influence customer loyalty.
- Marketing Strategies: Public opinions can shape marketing strategies. Companies often tailor their campaigns to align with public sentiments and values to resonate with their target audience.
- Viral Effects: In today’s digital age, public opinions can spread rapidly through social media and online platforms. Viral content, whether positive or negative, can have a far-reaching impact on a company’s reputation.
- Long-Term Impact: Consistently positive public opinions can lead to long-term customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth, while negative opinions can result in decreased sales and market share.
The public plays a vital role in shaping a company’s image and influencing marketing strategies. Identifying relevant publics, managing public perception, and responding to public opinions are essential for building a positive brand image and successful marketing efforts. Companies that prioritize transparency, engagement, and responsiveness can create strong relationships with various publics and ultimately drive business success.
Impact on Marketing Strategies
The profound influence of customers as a key component of the microenvironment on marketing strategies cannot be overstated. Indeed, understanding the nuances of customer behavior, preferences, and feedback is central to the development of effective marketing strategies. Here, we explore how customers shape and impact marketing strategies, emphasizing the critical role they play in guiding businesses toward success.
A. Customer-Centric Approach

A customer-centric approach in marketing emphasizes placing the customer at the center of all marketing efforts. This approach recognizes the significance of understanding customer needs, preferences, and behaviors to create tailored products and build lasting customer relationships.
1. Tailoring Products to Meet Customer Needs
Understanding customer needs and preferences is essential for developing products that address specific market demands. By analyzing customer feedback, conducting market research, and staying attuned to industry trends, companies can identify opportunities to create products that fulfill customer needs more effectively.
2. Customizing Marketing Messages for Target Segments
Effective communication is crucial in reaching and resonating with target audiences. Customizing marketing messages involves crafting content that speaks directly to the unique needs, interests, and preferences of different customer segments. By tailoring messages to specific demographics, psychographics, and behaviors, companies can enhance the relevance and impact of their marketing campaigns.
3. Building Long-Lasting Customer Relationships
Building enduring relationships with customers is a cornerstone of successful marketing. Satisfied and loyal customers not only make repeat purchases but also act as brand advocates, spreading positive word-of-mouth and contributing to a company’s reputation. Companies achieve this by delivering consistent value, personalized experiences, exceptional customer service, and addressing customer feedback.
A customer-centric approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also fosters brand loyalty, positive brand perception, and sustainable business growth. By aligning marketing strategies with customer needs and preferences, companies can differentiate themselves in competitive markets and create a strong foundation for long-term success.
B. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis is a vital component of marketing strategy that involves evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of competitors in the market. By understanding the competitive landscape, businesses can formulate effective strategies to differentiate themselves, capitalize on opportunities, and address challenges.
1. Leveraging Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
Studying competitors’ strengths and weaknesses provides valuable insights for shaping a company’s marketing approach. By identifying what competitors excel at, a business can learn from their successful tactics and potentially incorporate similar strategies. Similarly, recognizing their weaknesses can help a business identify gaps in the market where they can excel. For instance, if a competitor is known for quality but lacks in customer service, a business could emphasize exceptional customer support to stand out.
2. Innovating to Stay Ahead in the Market
Competition often drives innovation. To maintain a competitive edge, businesses must continually innovate by developing new products, services, or marketing approaches. By observing the strategies and offerings of competitors, companies can identify areas where they can introduce novel solutions that cater to customer needs. Innovation can help create a distinct market position, attract new customers, and enhance brand loyalty.
3. Pricing and Promotional Strategies in Response to Competition
Competitor actions can impact a company’s pricing and promotional decisions. If a competitor lowers prices or offers attractive promotions, a business might need to adjust its pricing or promotional strategies to remain competitive. On the other hand, if a company has unique value propositions that set it apart, it may be able to maintain premium pricing. Adapting pricing and promotions based on competitor actions helps businesses retain customer interest and avoid losing market share.
Competitive analysis is an ongoing process that requires businesses to monitor competitors, assess market trends, and respond proactively to changes. By leveraging competitor insights, companies can refine their marketing strategies, enhance customer value, and strengthen their market position.
C. Supplier Collaboration
Supplier collaboration is a crucial aspect of effective supply chain management and plays a significant role in ensuring the success of a business. Collaborating with suppliers can lead to improved product quality, cost efficiency, and risk mitigation.
1. Ensuring Timely and Quality Supplies for Consistent Product Quality
Suppliers provide the raw materials, components, and resources necessary for a company to manufacture its products. Collaborating closely with suppliers helps ensure a steady and timely supply of these materials. This, in turn, contributes to maintaining consistent product quality. By establishing clear communication channels and quality standards, businesses can work together with suppliers to ensure that the materials provided meet the required specifications, leading to better end products.
2. Negotiating Favorable Terms to Maintain Cost-Efficiency
Supplier collaboration also involves the negotiation of terms and contracts that benefit both parties. Companies can work with suppliers to negotiate favorable pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Effective negotiation can lead to cost savings, which can have a positive impact on the company’s profitability. Collaborative relationships can also lead to volume discounts and other cost-efficiency measures that benefit both the business and the supplier.
3. Mitigating Risks Through Diversified Supplier Relationships
Relying on a single supplier can pose risks to a company’s supply chain, especially if that supplier faces disruptions or challenges. Collaborating with multiple suppliers and diversifying sourcing options helps mitigate these risks. In case one supplier experiences issues, the business can still maintain its operations by relying on alternative sources. Supplier collaboration involves building strong relationships with multiple suppliers, fostering competition, and ensuring a more stable supply chain.
Effective supplier collaboration requires open communication, trust, and a shared commitment to achieving mutual goals. By working together, businesses and suppliers can optimize their operations, enhance product quality, reduce costs, and minimize risks, ultimately contributing to the overall success of both parties.
D. Channel Management

Channel management is a critical component of a company’s marketing strategy, involving the selection, coordination, and management of distribution channels to effectively deliver products or services to customers. Efficient channel management helps ensure that products reach the right customers at the right time and in the most cost-effective manner.
1. Optimal Distribution Channel Selection
Selecting the right distribution channels is a crucial decision in channel management. Businesses need to determine the most suitable channels to reach their target audience efficiently. These channels can include direct sales, wholesalers, retailers, e-commerce platforms, and more. The choice of distribution channels depends on factors such as the nature of the product, the target market’s preferences, geographic considerations, and the company’s resources. Optimal distribution channel selection ensures that products are available where and when customers want them.
2. Supporting and Training Distributors for Effective Representation
Effective channel management involves building strong relationships with distributors, wholesalers, and retailers. Businesses need to provide adequate support and training to their channel partners to ensure that they are well-informed about the product, its features, and benefits. This enables distributors to represent the product accurately and answer customer queries effectively. Regular training sessions, product updates, and marketing collateral can help channel partners become more successful in promoting and selling the company’s products.
3. Minimizing Channel Conflicts to Ensure Seamless Delivery
Channel conflicts can arise when different distribution channels compete or overlap, leading to inefficiencies and customer dissatisfaction. Effective channel management aims to minimize these conflicts and ensure a seamless delivery process. This involves clear communication, setting clear roles and responsibilities for each channel, and addressing any disputes or issues promptly. When channel partners work harmoniously, the distribution process becomes smoother, leading to improved customer experiences.
Channel management is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires monitoring, evaluation, and adjustments as needed. By optimizing distribution channels, supporting channel partners, and minimizing conflicts, businesses can enhance their market reach, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately achieve their marketing objectives.
E. Intermediary Coordination
Intermediaries play a crucial role in a company’s distribution network, connecting producers with customers and helping products reach the market efficiently. Effective intermediary coordination is essential for ensuring a smooth distribution process, aligning goals, and resolving conflicts to maintain a strong distribution network.
1. Facilitating Effective Communication and Cooperation
Intermediary coordination involves establishing clear lines of communication and fostering cooperation between a company and its intermediaries, which can include wholesalers, retailers, distributors, and agents. Open and effective communication helps both parties understand each other’s needs, expectations, and challenges. By sharing information about product availability, changes in marketing strategies, and customer preferences, intermediaries can better serve customers, and companies can make informed decisions. Effective communication ensures that products are delivered to the right places at the right times, minimizing delays and improving customer satisfaction.
2. Aligning Intermediary Goals with Overall Marketing Objectives
Intermediaries are independent entities with their own goals and interests. For successful intermediary coordination, it’s important to align these intermediary goals with the company’s overall marketing objectives. This alignment ensures that intermediaries are motivated to promote and sell the company’s products effectively. Companies can achieve this by offering incentives, rewards, and training programs that encourage intermediaries to prioritize the company’s products and work toward shared marketing goals. When intermediary goals are in line with the company’s objectives, the distribution process becomes more efficient and productive.
3. Resolving Conflicts to Maintain a Smooth Distribution Network
Conflicts can arise in any business relationship, including those between companies and their intermediaries. Effective intermediary coordination involves promptly addressing and resolving these conflicts to maintain a strong and smooth distribution network. Conflicts might arise due to issues such as pricing disagreements, delivery delays, communication breakdowns, or differing expectations. When conflicts are left unresolved, they can disrupt the distribution process, impact customer satisfaction, and harm relationships. By actively identifying and resolving conflicts, companies can ensure that the distribution network remains intact and efficient.
Intermediary coordination is an ongoing effort that requires a proactive approach from both the company and its intermediaries. By fostering communication, aligning goals, and addressing conflicts, companies can build strong relationships with intermediaries, enhance the efficiency of their distribution network, and ultimately deliver better value to their customers.
F. Public Relations and Image
Public relations (PR) plays a pivotal role in shaping a company’s image, managing relationships with different publics, addressing concerns, and maintaining transparency. Navigating public opinions effectively is crucial to protect and enhance a brand’s reputation.
1. Engaging with Different Publics to Shape a Positive Image
Publics refer to groups or individuals with a legitimate interest in a company’s operations and activities. Engaging with the public in a positive and proactive manner is a key aspect of public relations. Companies need to establish and maintain positive relationships with various stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, regulators, communities, and the media. By effectively engaging with the public, companies can shape a positive image, build trust, and establish themselves as responsible and ethical entities. This involves open communication, responsiveness, and addressing concerns promptly.
2. Addressing Public Concerns and Maintaining Transparency
Public relations involves addressing concerns and issues that may arise within the various publics associated with a company. This could include addressing customer complaints, responding to negative media coverage, and managing the aftermath of a product recall, among other things. Maintaining transparency is vital in these situations. Companies should provide accurate and timely information, take responsibility when necessary, and communicate their actions to resolve the issues. Transparency helps build credibility and trust, even in challenging situations.
3. Navigating Public Opinions to Protect Brand Reputation
Public opinion can have a significant impact on a company’s brand reputation. Public relations professionals must actively monitor and analyze public sentiment toward the company, its products, and its actions. By understanding the prevailing opinions, companies can adjust their messaging, strategies, and actions to align with public expectations. This proactive approach helps prevent potential reputation crises and enables companies to navigate challenges while maintaining their credibility and goodwill.
In summary, public relations and image management are essential components of a company’s overall marketing strategy. By engaging with different publics, addressing concerns transparently, and adapting to public opinions, companies can establish and maintain a positive brand image, build trust, and foster long-term relationships with stakeholders. Effective public relations can help companies weather storms, recover from setbacks, and position themselves as responsible and ethical players in their industries.
Case Studies
A. Real-world Examples Showcasing the Impact of Micro Environment on Marketing
Microenvironment factors play a significant role in shaping a company’s marketing strategies and outcomes. Here are some real-world examples that illustrate the impact of microenvironment factors on marketing:
- Apple Inc.: Customer-Centric Approach Apple’s microenvironment strategy revolves around its customer-centric approach. By understanding its customers’ needs and preferences, Apple designs products that cater to their desires, leading to a strong brand following and customer loyalty. The company’s unique retail stores provide personalized customer experiences, differentiating it from competitors. Apple’s success demonstrates how understanding and adapting to customer preferences can drive marketing success.
- Starbucks: Leveraging Suppliers and Intermediaries Starbucks’ success is not just attributed to its coffee but also to its strong relationships with suppliers and intermediaries. The company focuses on ethical sourcing and building sustainable relationships with coffee bean farmers. This commitment to responsible sourcing enhances Starbucks’ brand image and resonates with environmentally conscious customers.
- Coca-Cola vs. Pepsi: Competitive Rivalry The rivalry between Coca-Cola and Pepsi is a classic example of how competitors impact marketing strategies. Both companies continuously innovate their products, engage in aggressive advertising campaigns, and adjust pricing to gain market share. The competition between these two giants demonstrates how understanding competitors’ strategies and strengths is crucial for success in a competitive market.
B. Lessons Learned from Successful and Unsuccessful Strategies
- Nike: Successful Brand Building Nike’s microenvironment-focused strategy of aligning its brand with athletes and active lifestyles has propelled it to success. The company’s endorsements by sports icons and its commitment to innovation have created a strong brand image that resonates with consumers. Nike’s lesson is that consistent branding and a strong connection to target customers can lead to long-term success.
- Kodak: Failure to Adapt Kodak’s failure to adapt to the changing microenvironment is a cautionary tale. As the digital camera and smartphone industries emerged, Kodak, a pioneer in photography, struggled to keep up. Despite having the necessary technology for digital photography, the company did not anticipate market trends and failed to pivot its business model. This failure to adapt to changing customer preferences and technological advancements led to Kodak’s decline.
- Blockbuster: Ignoring Market Shifts Blockbuster’s downfall serves as an example of a company that did not respond to changes in the microenvironment. Despite the rise of streaming services and digital rentals, Blockbuster continued to focus on its brick-and-mortar rental model. The failure to embrace digital distribution and changing consumer behavior ultimately led to Blockbuster’s bankruptcy.
Key Takeaways from Case Studies:
- Customer-Centric Approach: Understanding and catering to customer needs and preferences can drive success in marketing.
- Supplier Relationships: Building ethical and sustainable relationships with suppliers can enhance brand image.
- Competitive Rivalry: Monitoring and responding to competitors’ strategies is crucial in a competitive market.
- Consistent Branding: Establishing a strong brand identity and maintaining it over time contributes to brand loyalty.
- Adaptation to Change: Failure to adapt to changing customer preferences and market trends can lead to decline or failure.
These case studies highlight the importance of staying attuned to microenvironment factors and adapting marketing strategies accordingly to achieve long-term success.
Conclusion
Marketing success is not solely reliant on creative advertising and promotions. Instead, it stems from a deep understanding of the microenvironment and the ability to tailor marketing strategies accordingly. By leveraging insights from the microenvironment, businesses can craft compelling value propositions, engage customers effectively, and differentiate themselves in the market.
In essence, the microenvironment is the foundation upon which successful marketing strategies are built. By recognizing its significance and continually adapting to its dynamics, businesses can navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and achieve sustainable marketing success.
So, as you embark on your marketing journey, remember that while the big picture of the macroenvironment is important, the microenvironment is where you can make a direct impact and drive positive outcomes for your business.
Are you ready to take your marketing strategies to the next level by mastering the microenvironment? Start by understanding your customers, building strong relationships with suppliers, analyzing competitor moves, and staying connected to the ever-changing needs and preferences of your target audience. The microenvironment is your playing field—use it strategically to achieve marketing excellence.