The Importance Of Distribution Channels In Marketing
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective marketing and distribution strategies are cHave you ever wondered how products reach you from manufacturers or producers? The answer lies in distribution channels â the unsung heroes of the marketing world. Welcome to “The Importance of Distribution Channels in Marketing,” where we unravel the essential role these channels play in getting products into the hands of consumers.
In this article, we will explore the significance of distribution channels, their various types, and how they streamline the journey of products from production to the final buyer. Join us as we unveil the hidden power behind successful marketing and discover how distribution channels drive business success in today’s interconnected world.
Understanding Distribution Channels
Distribution channels, also known as marketing channels or trade channels, refer to the pathways through which products or services move from the manufacturer to the end consumer. It encompasses all the intermediaries involved in this journey, facilitating the flow of goods or services from the point of production to the point of consumption.
There are various types of distribution channels, each serving a specific purpose in the marketing ecosystem. These channels can be direct, indirect, or a combination of both, depending on the nature of the product, target market, and business goals.
The Role of Distribution Channels in Marketing
Distribution channels play a pivotal role in the marketing mix, alongside product, price, and promotion. They serve as a critical link between the producer and the consumer, providing several key functions:
I. Market Reach and Accessibility: Distribution channels enable businesses to extend their market reach and make products or services accessible to a wider audience. By tapping into established networks of wholesalers, retailers, and distributors, companies can overcome geographical barriers and cater to diverse customer segments.
II. Inventory Management and Storage: Distribution channels assist in managing inventory levels and storage. Manufacturers can produce goods in bulk and distribute them strategically, minimizing excess inventory and associated costs. On the other hand, retailers can maintain stock based on demand fluctuations.
III. Enhancing Customer Convenience: An efficient distribution channel ensures that products are available at the right place and at the right time, enhancing customer convenience. Customers can find what they need easily, leading to a positive shopping experience and fostering brand loyalty.
IV. Market Feedback and Insights: Distribution channels serve as a valuable source of market feedback and insights. Intermediaries interact directly with customers, gaining valuable information about preferences, trends, and demands. This data can be utilized to improve products or services and develop effective marketing strategies.
V. Promotion and Marketing Support: Distribution partners often engage in marketing and promotional activities to boost sales. They may run localized advertising campaigns, offer discounts, or provide in-store promotions to create awareness and drive customer interest.
The Evolution of Distribution Channels
Over the years, the landscape of distribution channels has undergone significant changes, adapting to the advancements in technology and consumer behavior. Let’s explore how distribution channels have evolved and the impact of these changes on the marketing industry.
Traditional Distribution Channels
Traditional distribution channels have been the backbone of product distribution for decades. These channels involve a linear flow of products from manufacturers to wholesalers, then to retailers, and finally reaching the end consumers. The key characteristics of traditional distribution channels include:
I. Physical Presence: Traditional channels rely on physical stores, warehouses, and distribution centers to store and distribute products. Customers need to visit these physical locations to make purchases.
II. Limited Reach: These channels are geographically bound, and businesses face challenges in reaching customers in distant regions or international markets.
III. Longer Lead Times: The time taken for products to move through the traditional distribution network can be relatively longer, leading to delayed deliveries.
IV. High Overhead Costs: Maintaining physical stores and managing inventory incurs substantial overhead costs for businesses.
Emergence of Digital Distribution Channels
The advent of the internet and digital technologies has revolutionized the way products are distributed. Digital distribution channels have emerged as powerful alternatives to traditional methods, offering various advantages for businesses and consumers alike:
I. Online Marketplaces: E-commerce platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Etsy have created virtual marketplaces that connect sellers with customers worldwide. These platforms allow businesses to expand their reach beyond physical boundaries.
II. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Model: Digital channels enable businesses to adopt a DTC model, bypassing intermediaries and selling directly to customers. This approach provides greater control over branding and customer relationships.
III. Personalization and Targeting: Digital channels allow businesses to gather valuable customer data and preferences, enabling personalized marketing and targeted promotions.
IV. Faster Transactions: Online purchasing offers convenience and speed, reducing lead times and ensuring faster delivery to customers.
The Impact of E-commerce on Distribution
E-commerce has been a game-changer in the world of distribution channels, reshaping the entire marketing landscape:
I. Global Reach: E-commerce platforms have facilitated cross-border trade, allowing businesses to enter international markets without the need for physical presence.
II. Disruption of Traditional Retail: Brick-and-mortar retailers face intense competition from e-commerce platforms, leading to a shift in consumer buying behavior.
III. Market Accessibility: E-commerce has enabled small businesses and entrepreneurs to access a wider audience, leveling the playing field with larger competitors.
IV. Logistics Advancements: E-commerce has driven innovations in logistics and fulfillment services, making last-mile delivery more efficient.
V. Seamless Customer Experience: E-commerce platforms focus on user experience and convenience, leading to a seamless shopping journey for customers.
As the digital age continues to evolve, businesses must adapt their distribution strategies to stay competitive in the ever-changing market. A mix of traditional and digital distribution channels may be necessary to cater to diverse customer preferences and maximize market reach. Understanding the evolution of distribution channels and embracing technological advancements can position businesses for success in the dynamic world of marketing.
Types of Distribution Channels
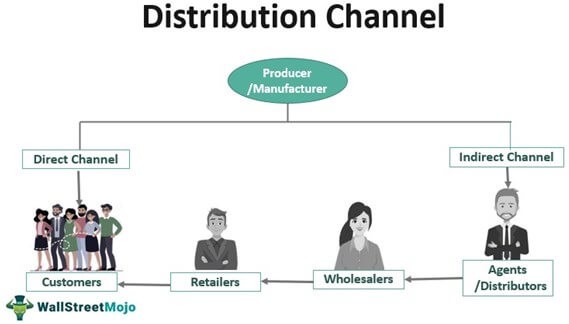
Distribution channels play a crucial role in delivering products from manufacturers to end consumers. These channels can vary based on the number of intermediaries involved and the level of control businesses seek over their product’s journey. Let’s explore the three main types of distribution channels: Direct Distribution Channels, Indirect Distribution Channels, and Hybrid Distribution Channels.
1. Direct Distribution Channels
Direct distribution channels involve a direct link between the manufacturer and the end consumer, without any intermediaries in between. In this model, businesses take complete control over the distribution process and interact directly with customers.
Characteristics:
- The manufacturer sells products directly to customers.
- Limited or no intermediaries involved.
- Direct communication and relationship with customers.
- Provides better control over product positioning and brand image.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Greater control: Businesses have full control over their product’s distribution and customer interactions.
- Direct feedback: Direct channels facilitate direct feedback from customers, enabling quick adjustments and improvements.
- Higher profit margins: Eliminating intermediaries can lead to higher profit margins for the manufacturer.
Cons:
- High costs: Setting up and maintaining a direct distribution network can be expensive.
- Limited reach: Direct channels may have limitations in reaching a wide audience, especially in distant or international markets.
- Time-consuming: Direct distribution requires significant time and effort to manage customer relationships and logistics.
2. Indirect Distribution Channels
Indirect distribution channels involve the presence of intermediaries between the manufacturer and the end consumer. These intermediaries, such as wholesalers, retailers, or distributors, play a significant role in product distribution.
Characteristics:
- Products move through multiple intermediaries before reaching the end consumer.
- Intermediaries handle tasks like storage, promotion, and delivery.
- Broader market reach due to the established network of intermediaries.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Wider market coverage: Indirect channels allow businesses to reach a larger audience through the established network of intermediaries.
- Reduced logistical burden: Intermediaries handle tasks like inventory management and distribution, easing the burden on the manufacturer.
- Cost-effective: Sharing distribution responsibilities with intermediaries can be cost-effective compared to managing the entire process independently.
Cons:
- Less control: Businesses may have less control over product presentation and customer interactions through indirect channels.
- Higher distribution costs: Each intermediary adds to the distribution costs, potentially reducing profit margins.
- Slower feedback: Feedback from customers may take longer to reach the manufacturer due to multiple layers of intermediaries.
3. Hybrid Distribution Channels
Hybrid distribution channels combine elements of both direct and indirect distribution models. In this approach, businesses use a combination of direct selling and the involvement of intermediaries to optimize their distribution strategy.
Characteristics:
- Manufacturers sell directly to certain customers while using intermediaries for other segments.
- Offers flexibility and adaptability in reaching different customer groups.
- Enables businesses to maintain some level of control while leveraging the advantages of intermediaries.
Examples in Real-world Business
Examples of hybrid distribution channels include:
- Companies sell products through their website (direct) while also distributing through retail stores (indirect).
- Brands offering exclusive products or services through their own physical stores (direct) and selling other products through authorized retailers (indirect).
Hybrid distribution channels allow businesses to tailor their distribution strategy based on market dynamics, customer preferences, and business objectives. By adopting a hybrid approach, companies can strike a balance between maintaining control and leveraging the strengths of intermediaries for enhanced market reach and customer satisfaction.
The Significance of an Efficient Distribution Network
An efficient distribution network plays a vital role in the success of any business. It enables products to reach the right customers at the right time and in the right condition. Let’s explore the significance of having an efficient distribution network and how it benefits businesses.
1. Enhancing Reach and Market Penetration
One of the primary advantages of an efficient distribution network is that it enhances the reach of products to a wider audience. Through various distribution channels like retailers, wholesalers, and online marketplaces, businesses can access different geographic locations and target diverse customer segments. This increased market penetration allows businesses to tap into new markets, reach potential customers, and expand their customer base.
An effective distribution network also helps businesses reach remote or inaccessible areas, providing access to customers who may not have easy access to physical stores. As a result, businesses can establish a strong presence in both urban and rural markets, increasing their overall market share.
2. Ensuring Product Availability and Convenience for Customers
An efficient distribution network ensures that products are readily available and accessible to customers when they need them. This is crucial in today’s fast-paced world, where customers expect convenience and immediate access to products.
With well-managed distribution channels, businesses can maintain sufficient inventory levels to meet customer demand. This helps in preventing stockouts and ensures that customers do not face disappointments due to unavailability. Providing a seamless and convenient shopping experience contributes to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Minimizing Costs and Maximizing Profits
An optimized distribution network helps in reducing costs associated with inventory management, transportation, and warehousing. By streamlining the supply chain and minimizing unnecessary intermediaries, businesses can cut down on operational expenses, resulting in higher profit margins.
Efficient distribution also aids in reducing lead times, thereby improving cash flow. Faster movement of products from production to consumption ensures that businesses can quickly generate revenue and reinvest in their operations.
4. Strengthening Customer Relationships
A well-organized distribution network fosters better customer relationships by providing timely deliveries, high-quality products, and excellent customer service. When customers receive their orders promptly and in perfect condition, they are more likely to trust the brand and become repeat buyers.
Moreover, distribution channels allow businesses to gather valuable feedback from customers. This feedback helps in understanding customer preferences, demands, and pain points. Armed with this information, businesses can make necessary improvements to their products and services, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
An efficient distribution network is a critical aspect of any successful business strategy. It enables businesses to reach a broader customer base, ensures product availability and convenience, reduces costs, and strengthens customer relationships. By investing in an optimized distribution network, businesses can stay competitive, improve market penetration, and drive overall growth and success in the marketplace.
Key Players in Distribution Channels
A distribution channel involves various key players who play essential roles in ensuring the smooth flow of products from manufacturers to end customers. Let’s explore the key players in distribution channels and their roles:
1. Manufacturers and Producers
Manufacturers and producers are the initial players in the distribution channel. They are responsible for producing goods and ensuring their quality and availability. Manufacturers create products and package them for distribution to wholesalers, retailers, or directly to consumers, depending on the distribution strategy they choose.
The manufacturers’ role is to:
- Produce high-quality products that meet consumer demands.
- Decide on the most appropriate distribution strategy for their products.
- Package and label products for easy identification and transportation.
- Work closely with wholesalers and retailers to promote and sell their products effectively.
2. Wholesalers and Distributors
Wholesalers and distributors act as intermediaries between manufacturers and retailers or other businesses. They purchase products in bulk from manufacturers and store them in large quantities in warehouses. Their main role is to distribute products to retailers in smaller quantities, ensuring a steady supply chain and availability of products in the market.
The wholesalers’ and distributors’ role is to:
- Buy products in bulk from manufacturers at discounted prices.
- Store products in warehouses and manage inventory.
- Break down large quantities of products into smaller lots for retailers.
- Offer credit facilities to retailers to help them manage their cash flow.
- Provide market information to manufacturers about customer preferences and demands.
3. Retailers and Resellers
Retailers and resellers are the last players in the distribution channel before products reach the end consumers. They purchase products from wholesalers or directly from manufacturers and sell them to individual consumers. Retailers can operate physical stores, online platforms, or both, depending on their business model.
The retailers’ and resellers’ role is to:
- Display products in an attractive manner to attract customers.
- Provide a convenient shopping experience for consumers.
- Offer additional services like customer support, warranties, and after-sales services.
- Maintain a wide range of products to cater to different customer needs.
- Promote products and create marketing campaigns to drive sales.
4. The Role of E-commerce Platforms
In recent years, e-commerce platforms have become significant players in distribution channels. These online marketplaces provide a digital platform for manufacturers and retailers to showcase and sell their products directly to consumers. E-commerce platforms have enabled businesses to reach a global audience and expand their market presence without the need for physical stores.
The role of e-commerce platforms is to:
- Provide a user-friendly interface for consumers to browse and purchase products.
- Facilitate secure online transactions and payment processing.
- Offer a vast product range from various manufacturers and sellers.
- Enable businesses to reach a broader customer base and increase sales.
- Provide data analytics and insights to help businesses optimize their marketing strategies.
The key players in distribution channels, including manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and e-commerce platforms, work together to ensure that products reach the end consumers efficiently and effectively. Each player’s role is essential in creating a seamless supply chain that satisfies customer demands and contributes to the success of businesses in the market. As technology continues to evolve, e-commerce platforms have become a crucial component of distribution channels, providing new opportunities for businesses to grow and thrive in the digital age.
Selecting the Right Distribution Channel Strategy
Choosing the appropriate distribution channel strategy is crucial for businesses to effectively reach their target market and achieve their marketing objectives. Here are the factors to consider and the various channel options for selecting the right distribution channel strategy:
Factors to Consider
I. Target Market Analysis: Understanding the characteristics, preferences, and behavior of the target market is essential. Different customer segments may have varying preferences for how they want to purchase products, which influences the choice of distribution channels.
II. Product Characteristics: The nature of the product also plays a significant role in determining the distribution channel. For example, perishable products may require a fast and direct distribution approach, while durable products may benefit from wider distribution through retailers.
III. Competitor Analysis: Analyzing the distribution strategies of competitors can provide valuable insights. It helps in identifying potential gaps in the market and understanding the effectiveness of different distribution channels in the industry.
IV. Geographical Considerations: The geographical reach of the target market and the availability of distribution infrastructure in specific regions influence the choice of distribution channels. Some products may require localized distribution networks, while others can have broader geographic coverage.
Evaluating Channel Options
I. Intensive Distribution: Intensive distribution involves making the product available in as many outlets as possible. It aims to maximize market coverage and reach a broad customer base. This strategy is suitable for products with high demand and mass appeal, such as consumer goods and everyday products.
Advantages of Intensive Distribution:
- Widespread availability and accessibility to customers.
- Increased brand visibility and market share.
- Potential for higher sales volume.
Disadvantages of Intensive Distribution:
- Reduced control over the product’s presentation and positioning.
- Potential cannibalization of sales among different channels.
- Higher logistical and management complexity.
II. Selective Distribution: Selective distribution involves distributing products through a limited number of carefully chosen intermediaries. This strategy is suitable for products that require specific brand positioning and a certain level of customer service, such as high-end consumer goods or specialized products.
Advantages of Selective Distribution:
- Better control over product positioning and presentation.
- Focus on providing better customer service and support.
- Reduced channel conflict and better relationships with intermediaries.
Disadvantages of Selective Distribution:
- Limited market coverage compared to intensive distribution.
- Potential loss of sales opportunities in some regions or markets.
- Higher dependency on the performance and commitment of selected intermediaries.
III. Exclusive Distribution: Exclusive distribution involves granting exclusive rights to a single intermediary or a limited number of intermediaries to sell the product. This strategy is suitable for luxury products, premium brands, or products with limited availability.
Advantages of Exclusive Distribution:
- Strong control over brand image and product positioning.
- Higher perceived value and exclusivity for customers.
- Close collaboration and support from exclusive intermediaries.
Disadvantages of Exclusive Distribution:
- Limited market coverage and potential loss of sales in certain regions.
- Potential difficulty in finding the right exclusive partners.
- Higher risks if the exclusive intermediary underperforms or loses interest.
Selecting the right distribution channel strategy requires careful consideration of various factors, including target market analysis, product characteristics, competitor analysis, and geographical considerations. Each distribution channel option has its advantages and disadvantages, and businesses must weigh these factors to determine the most effective strategy for their products and market objectives. A well-chosen distribution channel strategy can lead to increased market reach, improved customer satisfaction, and ultimately, business success.
Challenges and Obstacles in Distribution Channels

Distribution channels play a vital role in the success of a business, but they also come with their fair share of challenges and obstacles. Here are some of the common challenges that businesses may face in managing distribution channels:
1. Inventory Management and Supply Chain Issues:
Effective inventory management is crucial in distribution channels to ensure that products are available when and where customers demand them. Some of the inventory and supply chain challenges include:
- Overstocking or understocking: Finding the right balance between having enough inventory to meet demand without excessive carrying costs or stockouts can be challenging.
- Demand forecasting: Accurately predicting customer demand is essential to avoid excess inventory or stock shortages.
- Logistics and transportation: Managing the transportation of products from manufacturers to retailers or end customers can be complex, especially when dealing with multiple locations and different transportation methods.
2. Channel Conflict and Cooperation:
Channel conflict can arise when there is competition or disagreement among different intermediaries in the distribution channel. Some common channel conflict issues include:
- Price competition: Retailers or distributors may engage in price wars to attract customers, leading to reduced profitability for manufacturers.
- Territory disputes: Conflicts can arise when two or more intermediaries claim exclusive territories, causing inefficiencies in distribution.
- Lack of cooperation: Lack of communication and cooperation between channel partners can result in delays, misunderstandings, and ultimately, customer dissatisfaction.
3. Adapting to Technological Advancements:
The rapid advancements in technology have significantly impacted distribution channels. Businesses need to adapt to these changes to remain competitive. Some technology-related challenges include:
- E-commerce integration: Embracing online sales and incorporating e-commerce platforms into existing distribution channels can be challenging for traditional brick-and-mortar retailers.
- Data management: Leveraging data for demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and customer insights requires sophisticated data management systems and analytics capabilities.
- Customer expectations: With the rise of technology, customers have higher expectations regarding the speed and convenience of product delivery, which puts pressure on distribution channels to meet these demands.
4. Global Distribution Challenges:
For businesses operating in international markets, global distribution comes with its own set of challenges. Some common global distribution challenges include:
- Trade regulations and customs: Navigating different trade regulations and customs procedures in various countries can be complex and time-consuming.
- Cultural and language barriers: Understanding cultural differences and addressing language barriers is essential for effective communication and customer satisfaction.
- Supply chain complexities: Managing supply chains across different countries and time zones requires careful coordination and logistics planning.
Managing distribution channels can be a complex task, and businesses must be prepared to face various challenges and obstacles. Inventory management, channel conflict, adapting to technological advancements, and global distribution challenges are some of the key areas where businesses need to focus their efforts to ensure efficient and effective distribution of products to customers. Overcoming these challenges can lead to improved customer satisfaction, increased sales, and a competitive edge in the market.
Case Studies of Successful Distribution Channel Strategies
In the world of business, successful distribution channel strategies can make or break a company’s growth and success. Let’s take a look at three case studies of companies that have implemented effective distribution channel strategies:
1. Apple Inc.: Seamless Omni-Channel Experience
Apple Inc. is known for its seamless and integrated omnichannel distribution strategy. Apple’s distribution channels include online sales through its official website and the Apple Store app, as well as offline sales through Apple Stores, authorized retailers, and carriers. Here’s why Apple’s distribution strategy is successful:
Retail Presence: Apple has a strong retail presence with its iconic Apple Stores, strategically located in high-traffic areas. These stores offer a unique and immersive customer experience, allowing customers to try out products before making a purchase.
Online Sales: Apple’s official website and the Apple Store app offer a user-friendly online shopping experience. Customers can easily browse products, view specifications, and make purchases with just a few clicks.
Authorized Retailers: Apple partners with authorized retailers to expand its reach to a wider audience. These retailers offer Apple products in their stores, making it more convenient for customers to access and purchase Apple products.
Carrier Partnerships: Apple collaborates with various carriers to sell its products through its stores. This partnership enables Apple to tap into the carrier’s customer base and increase sales.
Customer Service: Apple focuses on providing exceptional customer service through its knowledgeable and helpful staff at Apple Stores. This ensures a positive customer experience, leading to increased customer loyalty and word-of-mouth referrals.
2. Amazon: Revolutionary E-commerce Distribution
Amazon has revolutionized the e-commerce distribution landscape with its innovative approach. Amazon’s distribution channels are primarily online, but the company has also ventured into physical retail with Amazon Go stores and its acquisition of Whole Foods. Here’s why Amazon’s distribution strategy is successful:
Vast Product Range: Amazon offers an extensive range of products, including electronics, books, clothing, and groceries, among others. This vast product selection attracts a diverse customer base and encourages repeat purchases.
Efficient Fulfillment Centers: Amazon’s network of fulfillment centers ensures quick and reliable order processing and delivery. This enables Amazon to offer fast shipping options like Amazon Prime, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Amazon Prime Membership: The Amazon Prime membership program provides members with benefits like free two-day shipping, access to streaming services, and exclusive deals. This loyalty program encourages customer retention and frequent purchases.
Digital Distribution: Amazon’s Kindle platform for e-books and Amazon Music and Prime Video for digital content distribution have further expanded the company’s distribution channels, offering customers more choices.
3. Coca-Cola: Global Distribution Network
Coca-Cola has built a robust global distribution network, making its products available almost everywhere in the world. Coca-Cola’s distribution channels are diverse, including bottlers, distributors, and retail outlets. Here’s why Coca-Cola’s distribution strategy is successful:
Bottling Partners: Coca-Cola operates through a franchised bottling system, partnering with local bottlers worldwide. This allows Coca-Cola to produce and distribute its products locally, ensuring freshness and reducing transportation costs.
Distribution Partnerships: Coca-Cola collaborates with various distributors to reach retailers, restaurants, and convenience stores globally. These distribution partnerships help Coca-Cola reach a vast customer base efficiently.
Localized Marketing: Coca-Cola tailors its marketing and product offerings to suit local preferences and cultural nuances. This localized approach enhances customer relevance and brand appeal in different regions.
Global Branding: Coca-Cola’s iconic branding and advertising campaigns create a strong brand identity, making it one of the most recognized and valuable brands globally.
The success of these companies distribution channel strategies lies in their ability to provide a seamless and convenient customer experience. Apple’s omnichannel approach, Amazon’s revolutionary e-commerce distribution, and Coca-Cola’s global distribution network all highlight the importance of understanding customer needs, adapting to technological advancements, and building strong partnerships. By focusing on these key factors, businesses can develop effective distribution channel strategies that contribute to their growth and market leadership.
Leveraging Digital Marketing in Distribution Channels
In today’s digital age, leveraging digital marketing in distribution channels has become crucial for businesses to reach and engage with their target audience effectively. Let’s explore four key digital marketing strategies that can enhance distribution channels:
1. Social Media Marketing
Social media marketing involves promoting products and services on various social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and more. It provides an opportunity for businesses to connect with their customers directly and build brand awareness. Here’s how social media marketing can benefit distribution channels:
Increased Reach: Social media platforms have billions of active users, making it an excellent channel for expanding the reach of products and services to a wide audience.
Engagement: Businesses can engage with customers through social media by responding to comments, addressing queries, and providing personalized support, creating a positive customer experience.
Targeted Advertising: Social media platforms allow businesses to run targeted advertising campaigns based on demographics, interests, and behaviors, ensuring that the right audience sees their products.
Influencer Partnerships: Partnering with social media influencers who have a large following in a particular niche can help businesses reach a highly targeted audience and gain credibility.
Real-time Updates: Social media provides a platform for real-time updates on new product launches, promotions, and events, keeping customers informed and engaged.
2. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of optimizing a website to rank higher in search engine results pages. By implementing SEO strategies, businesses can improve their visibility in search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. Here’s how SEO can enhance distribution channels:
Increased Online Visibility: A higher search engine ranking makes it more likely for potential customers to discover the business, its products, and its services.
Organic Traffic: SEO drives organic traffic to the website, which can lead to higher conversions and sales.
Local SEO: For businesses with physical locations, local SEO strategies can help attract customers in specific geographical areas.
Keyword Targeting: By targeting relevant keywords, businesses can align their website content with what their target audience is searching for, leading to more qualified leads.
Content Optimization: Creating high-quality and informative content can establish the business as an authority in its industry and drive more traffic to the website.
3. Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing involves collaborating with individuals who have a large and engaged following on social media or other online platforms. These influencers promote products or services to their audience, driving awareness and sales. Here’s how influencer marketing can leverage distribution channels:
Authentic Recommendations: Influencers build trust with their followers, and their recommendations can have a significant impact on purchasing decisions.
Targeted Audience: Businesses can choose influencers whose audience aligns with their target demographic, ensuring the marketing message reaches the right people.
Diverse Platforms: Influencers can create content on various platforms, including social media, blogs, YouTube, and podcasts, increasing the brand’s exposure.
Product Reviews: Influencers can provide honest reviews and demonstrations of products, offering valuable insights to potential customers.
Brand Affiliation: Long-term partnerships with influencers can establish a strong brand affiliation, leading to increased brand loyalty among their followers.
4. Content Marketing
Content marketing involves creating and distributing valuable and relevant content to attract and engage the target audience. It can include blog posts, videos, infographics, e-books, and more. Here’s how content marketing can be utilized in distribution channels:
Educating Customers: Informative content can educate customers about the product’s features, benefits, and usage, helping them make informed purchasing decisions.
Search Engine Visibility: High-quality content can improve SEO and drive organic traffic to the website.
Lead Generation: Content marketing can generate leads by offering valuable resources in exchange for contact information, allowing businesses to nurture potential customers.
Thought Leadership: Creating authoritative and valuable content establishes the business as a thought leader in the industry, enhancing brand reputation.
Social Sharing: Engaging and shareable content can be shared across social media platforms, expanding its reach and visibility.
Leveraging digital marketing in distribution channels has become essential for businesses to stay competitive in the digital landscape. Social media marketing, SEO, influencer marketing, and content marketing are powerful strategies that can enhance distribution channels, increase brand awareness, and drive sales. By integrating these digital marketing tactics into their distribution strategies, businesses can effectively connect with their target audience and achieve their marketing goals.
Future Trends in Distribution Channels

The landscape of distribution channels is constantly evolving, driven by changing consumer behaviors and technological advancements. Here are some future trends in distribution channels that businesses should keep an eye on:
1. The Rise of Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Brands
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) brands are companies that sell their products directly to consumers without relying on traditional retail intermediaries. This trend is gaining momentum due to the following reasons:
Cutting Out Middlemen: DTC brands can cut out wholesalers and retailers, allowing them to have more control over their pricing, branding, and customer experience.
Enhanced Customer Relationships: By selling directly to consumers, DTC brands can establish direct relationships with their customers, gathering valuable data and feedback for product improvement and personalized marketing.
E-commerce and Social Media: DTC brands leverage e-commerce platforms and social media to reach a global audience, enabling them to compete with larger established brands.
Subscription Models: Many DTC brands adopt subscription-based models, offering convenience and regular revenue streams.
2. Personalization and Customization
Consumers are increasingly seeking personalized and customized products and experiences. Businesses that incorporate personalization and customization into their distribution channels can benefit in the following ways:
Increased Customer Loyalty: Personalized experiences create emotional connections with customers, leading to higher retention rates and brand loyalty.
Higher Conversion Rates: Customized products and recommendations cater to individual preferences, leading to higher conversion rates and sales.
Data-Driven Insights: Personalization requires data analysis, and businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences.
Mass Customization: Advancements in technology, such as 3D printing, enable mass customization, allowing businesses to efficiently produce personalized products.
3. Embracing Sustainability and Ethical Distribution
As consumer awareness about sustainability and ethical practices grows, businesses are expected to adopt greener and more ethical distribution channels:
Eco-Friendly Packaging: Using sustainable and eco-friendly packaging materials reduces the environmental impact of product distribution.
Carbon-Neutral Shipping: Companies are exploring carbon-neutral shipping options to offset the carbon emissions associated with transporting goods.
Ethical Sourcing: Businesses are expected to ensure that their products are sourced ethically, with a focus on fair trade and responsible supply chain practices.
Local and Circular Economies: Emphasizing local production and circular economy principles can reduce the carbon footprint of distribution and create a more sustainable ecosystem.
Social Responsibility: Consumers prefer to support brands that demonstrate social responsibility and contribute positively to society and communities.
The future of distribution channels is shaped by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and sustainability concerns. The rise of Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) brands, the emphasis on personalization and customization, and the adoption of sustainability and ethical distribution practices are key trends to watch. Businesses that embrace these trends and adapt their distribution strategies accordingly can stay ahead in the competitive market and meet the evolving needs of their customers.
Conclusion
Distribution channels are the backbone of successful marketing strategies, ensuring products reach customers efficiently. They bridge gaps, deliver on time, and expand market reach, making them indispensable for businesses.
Key takeaways include the rise of Direct-to-Consumer brands, the importance of personalization, and the need for sustainability. To stay ahead, businesses must embrace digitalization, optimize logistics, and harness data analytics.
As we navigate the changing landscape, collaboration, and innovation will drive success. By understanding the pivotal role of distribution channels and embracing advancements, businesses can thrive in the dynamic world of marketing.

