Types Of Market Penetration Strategy
Are you looking to boost your business’s presence in the market and reach a wider audience? If so, understanding the various market penetration strategies can be a game-changer. Market penetration is a critical aspect of a company’s growth, and employing the right strategies can lead to remarkable success. In this article, we delve into the different types of market penetration strategies, offering insights that will empower your business to penetrate new markets, expand your customer base, and drive sustainable growth. Let’s explore the dynamic world of market penetration and discover the strategies that can take your business to new heights.
Understanding Market Penetration Strategy
Market penetration strategy is a crucial concept in business that revolves around gaining a larger share of an existing market with the current products or services offered. This strategy aims to increase the market share of a company by attracting more customers or convincing existing customers to purchase more.
What is a Market Penetration Strategy?
Market penetration strategy involves implementing various tactics to penetrate deeper into the target market. It focuses on achieving growth within the same market and among the existing customer base. The core idea is to create a stronger presence and visibility in the market to drive higher sales and revenue.
Importance of Market Penetration Strategy for Businesses
Market penetration is an essential element of a comprehensive business strategy, and its significance lies in the numerous benefits it offers:
- Increased Market Share: By effectively implementing market penetration strategies, businesses can gain a larger portion of the market, outpacing competitors, and solidifying their position as a market leader.
- Higher Sales Volume: By reaching out to a broader audience and encouraging more frequent purchases from existing customers, businesses can experience a surge in sales volume, ultimately boosting their revenue.
- Enhanced Brand Awareness: Successful market penetration leads to increased brand visibility and recognition, ensuring that the target audience is well aware of the company’s offerings.
- Cost Efficiency: Compared to market development or product diversification, market penetration typically involves lower costs as it leverages existing resources and infrastructure.
- Competitive Advantage: A strong market penetration strategy enables businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors and create a competitive advantage in the market.
Overview of How Market Penetration Strategy Helps Increase Market Share
Market penetration can be achieved through a variety of approaches, each tailored to suit the company’s products, target audience, and industry. Some common methods include:
- Aggressive Pricing: Offering products at competitive prices or providing special discounts can attract price-sensitive customers and encourage them to switch from competitors.
- Promotional Campaigns: Well-designed marketing campaigns, both online and offline, can effectively showcase the benefits of the products and draw more customers toward the brand.
- Product Bundling: Combining products or services into bundles can entice customers with added value, encouraging them to make larger purchases.
- Increased Distribution Channels: Expanding the reach by utilizing multiple distribution channels can help the brand connect with a wider audience.
- Improved Customer Service: Exceptional customer service can lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty, resulting in repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth.
In conclusion, understanding market penetration strategy is vital for businesses looking to expand their market share and solidify their position in the industry. By implementing effective tactics, businesses can drive growth, increase revenue, and achieve sustainable success in their chosen markets.
Key Objectives of Market Penetration Strategy
Market penetration strategy aims to increase a company’s market share within its existing market by targeting current customers or attracting new customers from competitors.
The Primary Goals of Market Penetration Strategy
The key goals of the market penetration strategy are as follows:
- Increased Market Share: The primary objective of market penetration is to gain a larger share of the market, surpass competitors, and become a dominant player in the industry.
- Higher Sales Volume: By attracting more customers or encouraging existing customers to make repeat purchases, businesses can experience a surge in sales volume, leading to increased revenue.
- Enhanced Brand Visibility: Successful market penetration results in higher brand awareness and recognition among the target audience, helping to establish a strong brand presence.
- Cost Efficiency: Market penetration strategies often involve lower costs compared to other market entry approaches, making it a cost-effective method to drive growth.
- Competitive Advantage: Effectively implementing market penetration tactics can create a competitive advantage for businesses, making it challenging for competitors to replicate their success.
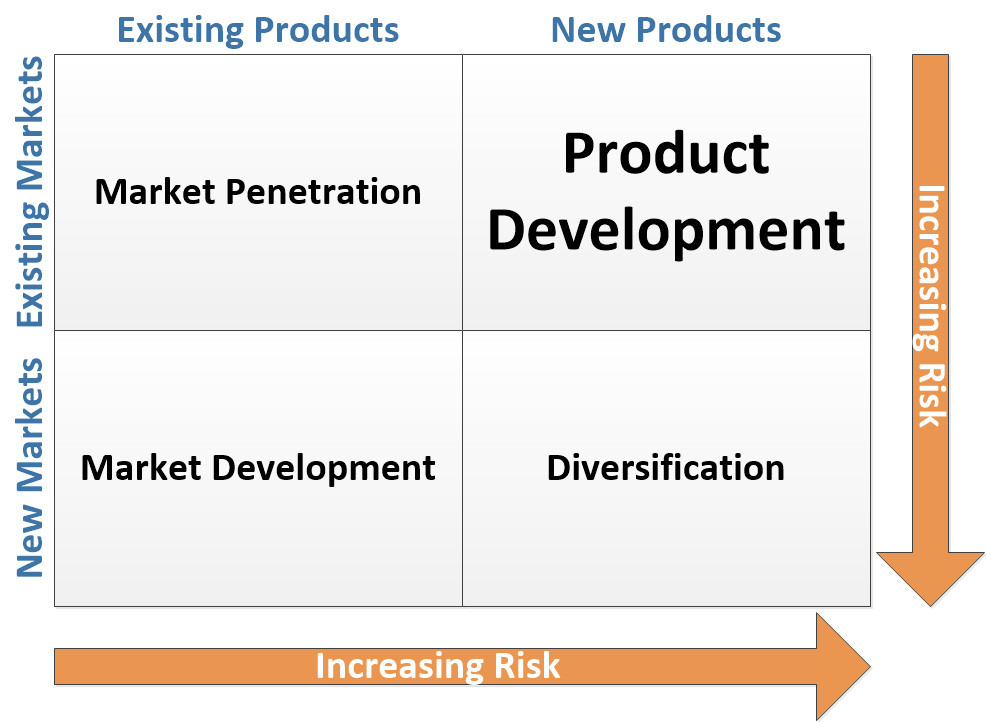
How Market Penetration Differs from Other Market Entry Approaches
Market penetration differs from other market entry approaches in the following ways:
- Market Penetration vs. Market Development: Market penetration focuses on increasing market share within the existing market by selling current products to existing customers. On the other hand, market development involves selling existing products to new markets or customer segments.
- Market Penetration vs. Product Development: While market penetration concentrates on selling existing products, product development involves creating new products for the existing market.
- Market Penetration vs. Diversification: Diversification entails launching new products for new markets, while market penetration centers on increasing market share with existing products.
Real-Life Examples of Successful Market Penetration Strategies
- Apple iPhone: Apple utilized a market penetration strategy by introducing the iPhone to the existing smartphone market. The company captured a significant market share by offering a unique and user-friendly product.
- Amazon Prime: Amazon successfully penetrated the market by offering its Prime membership program. By providing benefits such as free shipping and exclusive access to content, Amazon attracted a large customer base and increased sales.
- McDonald’s Value Menu: McDonald’s implemented a price adjustment strategy by introducing a value menu with affordable options. This tactic attracted price-conscious customers and contributed to higher sales and market share.
In conclusion, market penetration strategy plays a crucial role in a company’s growth and success. By understanding its objectives and differentiating it from other market entry approaches, businesses can make informed decisions and develop effective strategies to achieve their market penetration goals. Real-life examples serve as inspiration for companies looking to implement successful market penetration tactics and boost their market presence.
Overview of Market Analysis and Target Audience Identification
Before implementing a market penetration strategy, businesses must conduct a thorough market analysis. This analysis helps in understanding the current market conditions, identifying growth opportunities, and evaluating the potential demand for the products or services.
Key aspects of market analysis include:
- Market Size and Potential: Determine the size of the target market and assess its growth potential. Analyze market trends, demand patterns, and market dynamics.
- Competitor Analysis: Identify and analyze competitors’ market shares, strategies, strengths, and weaknesses. Understanding the competitive landscape can help in developing effective penetration tactics.
- Customer Segmentation: Segment the target audience based on demographics, preferences, needs, and buying behavior. This segmentation aids in tailoring marketing efforts for specific customer groups.
Understanding the Target Audience and Their Needs for Effective Penetration
A successful market penetration strategy requires a deep understanding of the target audience. Understanding customer needs, preferences, pain points, and expectations is crucial to develop products and marketing messages that resonate with the target customers.
Key steps for understanding the target audience:
- Customer Surveys and Feedback: Conduct surveys and gather feedback from existing and potential customers to understand their preferences and pain points.
- Market Research: Utilize market research to gain insights into customer behavior, purchase patterns, and brand perception.
- Data Analysis: Analyze customer data, such as purchase history and behavior, to identify trends and patterns.
Utilizing Data-Driven Insights to Develop a Targeted Approach
Data-driven insights play a pivotal role in developing a targeted approach for market penetration. Utilize the information gathered from market analysis and customer understanding to craft a targeted marketing and sales strategy.
Key components of a data-driven approach:
- Segment-Specific Marketing: Tailor marketing campaigns and promotions to specific customer segments based on their preferences and needs.
- Personalization: Utilize customer data to personalize product recommendations and marketing messages for individual customers.
- Continuous Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor the performance of market penetration efforts and use data insights to optimize strategies for better results.
Effective market analysis and understanding of the target audience are vital for successful market penetration. By leveraging data-driven insights, businesses can develop targeted strategies that resonate with customers and drive growth in the new market.
Types Of Market Penetration Strategy
Market penetration strategies are designed to increase a company’s market share within its existing market. There are various types of market penetration strategies that businesses can employ to achieve this objective. Here are some common types:
1. Market Penetration through Product Development
Market penetration through product development involves introducing new or improved products to the existing market with the aim of increasing market share and attracting more customers. This strategy leverages the company’s current customer base and distribution channels to promote the new products.
I. Product Differentiation and Value Proposition
Creating a Unique Selling Proposition (USP) to Stand Out in the Market
In a competitive market, product differentiation is essential for successful market penetration. A Unique Selling Proposition (USP) is a distinct feature or benefit that sets a product apart from its competitors and makes it attractive to the target audience. Creating a compelling USP helps businesses to stand out, capture customers’ attention, and gain a competitive edge.
Key steps to create a strong USP:
- Identify Customer Needs: Understand the needs and pain points of the target audience. Identify what customers value the most in a product or service.
- Analyze Competitors: Research the offerings of competitors to identify gaps in the market and areas where your product can offer something unique.
- Highlight Unique Features: Determine the unique features or benefits of your product that solve customer problems or provide superior value.
- Craft a Clear Message: Communicate your USP in a clear and concise manner. Your message should resonate with customers and communicate the value they will receive from choosing your product.
- Consistency in Marketing: Ensure that your USP is consistently reflected in all marketing efforts, including advertisements, website content, and promotional materials.
Innovating Products to Meet Customer Demands and Expectations
Innovation is a key driver of market penetration through product development. By continuously innovating and improving products, businesses can cater to changing customer demands and expectations. Keeping pace with market trends and incorporating customer feedback is crucial for product development success.
Key strategies for product innovation:
- Customer Feedback and Surveys: Collect feedback from customers to understand their pain points and preferences. Use this data to identify areas for product improvement and innovation.
- Market Research: Conduct market research to identify emerging trends and unmet customer needs. Use this information to develop innovative products that address these gaps.
- Product Testing and Prototyping: Before launching a new product, conduct testing and create prototypes to gather feedback and make necessary improvements.
- Continuous Improvement: Emphasize continuous improvement in product development processes to ensure that your offerings remain relevant and competitive.
Addressing Consumer Pain Points to Improve Market Penetration
Addressing consumer pain points is essential to improve market penetration. When businesses understand and solve the challenges customers face, they build trust and loyalty. By offering products that effectively address pain points, businesses can attract more customers and increase market share.
Key steps to address consumer pain points:
- Customer Surveys and Feedback: Gather feedback from customers to identify common pain points they experience with existing products or services.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyze the offerings of competitors to identify areas where their products fall short in addressing customer needs.
- Innovative Solutions: Develop innovative solutions to address the identified pain points effectively. Think outside the box to provide unique and customer-centric solutions.
- Effective Communication: Clearly communicate how your product addresses consumer pain points through marketing messages and promotional materials.
- Customer Support: Provide excellent customer support to address any issues or concerns customers may have after purchasing your product.
In conclusion, market penetration through product development requires creating a strong Unique Selling Proposition (USP), continuous innovation, and addressing consumer pain points. By offering differentiated and customer-centric products, businesses can effectively penetrate the market and achieve growth and success.
II. Pricing Strategies for Market Penetration
Pricing is a critical element of market penetration strategies. Setting the right price can significantly impact a product’s success in a new or existing market. In this section, we will explore various pricing models and strategies that companies can employ for successful market penetration.
Analyzing Pricing Models for Successful Penetration
When entering a new market or aiming to increase market share, companies can choose from various pricing models. Each model has its advantages and is suitable for different business scenarios. Some common pricing models for market penetration are:
- Skimming Pricing: In skimming pricing, companies initially set a high price for their product. This strategy is suitable when a product has unique features or offers exceptional value to a specific target audience. Skimming pricing allows companies to maximize initial revenue and cater to early adopters. However, over time, the price is gradually reduced to attract a broader customer base.
- Penetration Pricing: Penetration pricing involves setting a low price for a product to quickly gain market share. This strategy aims to attract price-sensitive customers and build a large customer base. While penetration pricing may lead to lower initial profits, it can create brand awareness, establish a customer base, and deter potential competitors.
- Premium Pricing: Premium pricing positions a product as a high-quality, luxury item. Companies adopt this strategy when their product offers superior features, exceptional quality, or a unique value proposition. Premium pricing requires companies to invest in branding, marketing, and customer experience to justify the higher price.
- Value-Based Pricing: Value-based pricing focuses on setting prices based on the perceived value of the product to customers. Companies conduct market research to understand customer preferences and willingness to pay for specific features. Value-based pricing allows companies to align prices with customer expectations and the value they receive from the product.
- Dynamic Pricing: Dynamic pricing involves adjusting prices based on real-time market conditions, demand, and other factors. This strategy is common in industries like travel and e-commerce, where prices fluctuate based on factors like time of booking, inventory levels, or customer segments.
Competitive Pricing vs. Penetration Pricing: Pros and Cons
Both competitive pricing and penetration pricing are common strategies used for market penetration. Let’s explore the pros and cons of each approach:
Competitive Pricing:
Pros:
- Quick market entry: Competitive pricing allows companies to enter the market swiftly by matching or slightly undercutting competitors’ prices.
- Reduced risk: By pricing competitively, companies can avoid potential price wars and maintain a stable market position.
- Perceived value: Customers may perceive competitively priced products as offering good value for money.
Cons:
- Lower profit margins: Competitive pricing may lead to lower profit margins, especially if the market is price-sensitive and cost structures are high.
- Less differentiation: Pricing based solely on competition may limit opportunities to differentiate the product based on features or quality.
Penetration Pricing:
Pros:
- Market share gain: Penetration pricing can help companies quickly gain market share by attracting price-sensitive customers.
- Brand awareness: Lower prices can generate increased interest and word-of-mouth, leading to better brand recognition.
- The barrier to entry: Penetration pricing can make it challenging for new competitors to enter the market due to the established customer base.
Cons:
- Short-term profitability: Penetration pricing may lead to lower initial profits until market share increases significantly.
- Price perception: Customers may associate low prices with lower product quality, impacting brand perception.
- Unsustainable: Penetration pricing may not be sustainable in the long term if costs and competition increase.
Dynamic Pricing and Discounts to Attract New Customers
Dynamic pricing and discounts are effective tools for attracting new customers and encouraging purchase decisions. These strategies can be used in conjunction with other market penetration tactics to boost sales and expand the customer base.
- Dynamic Pricing: Dynamic pricing involves adjusting product prices in response to real-time market conditions, demand, and other factors. For example, online retailers may offer discounts during low-demand periods or increase prices during peak demand. Dynamic pricing helps optimize revenue and capture sales opportunities.
- Discounts and Promotions: Offering limited-time discounts, promotional offers, or special deals can create a sense of urgency and incentivize customers to make a purchase. Discounts for first-time buyers, volume discounts, or bundle offers can attract new customers and drive sales.
- Loyalty Programs: Implementing loyalty programs can encourage repeat purchases and foster customer loyalty. Rewarding loyal customers with exclusive discounts or points-based systems can increase customer retention and lifetime value.
In conclusion, pricing strategies play a crucial role in market penetration efforts. Companies can choose from various pricing models, including skimming, penetration, premium, and value-based pricing. Both competitive pricing and penetration pricing have their merits and drawbacks. Additionally, dynamic pricing and discounts are effective tools for attracting new customers and driving sales. The right pricing strategy should align with the company’s goals, target audience, and product positioning to achieve successful market penetration.
III. Packaging and Branding Strategies
Packaging and branding are crucial elements of market penetration strategies. They play a significant role in enhancing product visibility, building a strong brand image, and creating an emotional connection with customers. Let’s explore the importance of packaging and branding in successful market penetration.
The Role of Packaging in Enhancing Product Visibility
Packaging is more than just a way to contain and protect a product. It serves as a powerful marketing tool that can significantly impact a product’s visibility and appeal to customers. Here’s how packaging plays a vital role in market penetration:
- Attracting Attention: Eye-catching and innovative packaging designs can capture the attention of potential customers in a crowded marketplace. When launching a new product or entering a new market, unique packaging can differentiate the product from competitors and pique customers’ curiosity.
- Communicating Value: Packaging communicates vital information about the product, such as its features, benefits, and usage instructions. Clear and informative packaging helps customers understand the value proposition, leading to better-informed purchase decisions.
- Brand Representation: Packaging is often the first physical interaction customers have with a brand. Consistent and well-designed packaging reinforces the brand’s identity and helps customers recognize and recall the product easily.
- Creating Differentiation: In competitive markets, packaging can be a key differentiator. Unconventional packaging materials, shapes, or colors can set a product apart and create a memorable impression on consumers.
- Convenience and Functionality: Packaging that is easy to open, use, and store can enhance the overall customer experience. Convenience in packaging can lead to repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth.
- Environmental Considerations: Eco-friendly and sustainable packaging designs resonate with environmentally-conscious consumers. Adopting environmentally responsible packaging practices can appeal to a growing segment of socially-aware customers.
Building a Strong Brand Image to Gain Consumer Trust
Brand image is a critical aspect of market penetration. A strong and positive brand image helps companies gain consumer trust and loyalty. Here’s how branding contributes to successful market penetration:
- Consistent Branding: Consistent branding across all marketing channels, packaging, and communication materials create a cohesive and memorable brand identity. Customers are more likely to trust a brand that demonstrates consistency and reliability.
- Brand Storytelling: Telling a compelling brand story helps establish an emotional connection with customers. A well-crafted brand narrative can evoke emotions, values, and aspirations that resonate with the target audience.
- Customer Reviews and Testimonials: Positive customer reviews and testimonials build credibility and trust. Encouraging satisfied customers to share their experiences can strengthen the brand’s reputation.
- Brand Associations: Associating the brand with positive attributes and values can enhance its image. Aligning the brand with social causes or supporting meaningful initiatives can improve its standing in the eyes of consumers.
- Brand Loyalty Programs: Implementing loyalty programs and rewards for repeat customers can foster brand loyalty. Loyal customers are more likely to repurchase and recommend the brand to others.
Leveraging Branding to Create an Emotional Connection with Customers
Emotional branding is a powerful tool in market penetration strategies. By connecting with customers on an emotional level, brands can build deeper relationships and drive brand loyalty. Here’s how branding can create an emotional connection with customers:
- Brand Personality: Giving the brand a distinct personality and character can make it relatable and endearing to customers. A brand that exhibits human-like traits and values is more likely to resonate with consumers.
- Storytelling and Customer Engagement: Sharing authentic and relatable stories about the brand’s journey, values, and impact can evoke emotions and engage customers on a personal level.
- Personalization: Tailoring brand experiences and communication to individual customer preferences and needs can create a sense of personal connection and relevance.
- Community Building: Building a community of like-minded customers who share common values and interests can foster a sense of belonging and emotional attachment to the brand.
In conclusion, packaging and branding are integral components of successful market penetration. Innovative and informative packaging can enhance product visibility, while strong branding builds consumer trust and emotional connections. Companies should invest in creating consistent and appealing packaging designs and use branding to communicate their unique value proposition and create meaningful relationships with customers. By combining effective packaging and branding strategies, businesses can significantly improve their market penetration efforts and achieve long-term success in competitive markets.
2. Market Penetration through Distribution Channels
Market penetration through distribution channels involves utilizing existing or new distribution channels to increase a company’s market share within its current market. This strategy aims to reach more customers and improve product accessibility, ultimately driving higher sales and market dominance.
I. Channel Selection and Expansion
Distribution channels play a vital role in market penetration strategies. They are the pathways through which products reach consumers, and selecting the right channels and expanding them strategically can significantly impact a company’s success. In this section, we will explore the importance of channel selection and expansion in market penetration.
Evaluating Different Distribution Channels for Penetration
When entering a new market or aiming to increase market penetration, companies must carefully evaluate various distribution channels to determine the most effective ones for their products. Here are some factors to consider when evaluating distribution channels:
- Target Audience: Understanding the preferences and shopping habits of the target audience is crucial. For example, if the target audience prefers online shopping, e-commerce channels might be more effective.
- Product Nature: The nature of the product and its packaging can influence the choice of distribution channels. For instance, perishable items may require a more efficient and quick distribution network.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyzing how competitors distribute their products can provide valuable insights. Identifying gaps or areas of improvement in their distribution strategies can help create a competitive advantage.
- Cost and Efficiency: Assessing the cost and efficiency of different channels is essential. Balancing cost-effectiveness with timely delivery and customer satisfaction is vital for successful market penetration.
- Market Reach: The distribution channels’ geographical reach should align with the company’s target markets. Expanding distribution networks to cover untapped regions can open up new growth opportunities.
- Channel Partnerships: Building strong partnerships with distributors, wholesalers, retailers, and online platforms can enhance market penetration efforts. Collaborating with partners who have a well-established customer base can expedite market entry.
- Customer Support: Consider the customer support and after-sales service offered by the distribution channels. Positive customer experiences can lead to repeat purchases and brand loyalty.
Online vs. Offline Distribution: Choosing the Right Mix
In the digital age, companies often face the choice between online and offline distribution channels. While both options have their merits, finding the right mix is crucial for successful market penetration. Here’s how companies can choose the right distribution mix:
- Online Distribution: Online channels, such as e-commerce websites and online marketplaces, offer a vast reach and convenience for customers. They are especially suitable for tech-savvy and digitally engaged consumers.
- Offline Distribution: Offline channels, such as retail stores and brick-and-mortar outlets, provide a physical shopping experience. They can be effective for products that require demonstration, personal assistance, or immediate gratification.
- Omnichannel Approach: Adopting an omnichannel distribution strategy that combines online and offline channels can maximize market penetration. Customers can have a seamless shopping experience across various touchpoints.
- Data and Analytics: Utilize data and analytics to understand customer behavior and preferences in both online and offline channels. This data-driven approach can guide decision-making in channel selection.
- Testing and Iteration: Conduct testing and iterate on the distribution mix based on performance metrics. Flexibility is essential, as consumer preferences and market dynamics may change over time.
Expanding Distribution Networks to Reach New Markets
Expanding distribution networks is a key strategy for reaching new markets and increasing market penetration. Here are some considerations for expanding distribution networks:
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to identify potential new markets with untapped demand. Understanding the needs and preferences of consumers in these markets is crucial.
- Local Partnerships: Forge partnerships with local distributors or retailers in the new markets. Local partners can provide valuable insights and help navigate regulatory and cultural nuances.
- Logistics and Infrastructure: Ensure that the distribution infrastructure, including transportation and warehousing facilities, can support the expansion. Efficient logistics are vital for timely product delivery.
- Adaptation to Local Preferences: Tailor product packaging, marketing messages, and distribution strategies to align with local preferences and cultural norms. Localizing the approach can enhance acceptance and adoption.
- Pricing and Competitive Analysis: Analyze the pricing strategies of competitors in the new markets and set competitive pricing. Understanding the competitive landscape can guide pricing decisions.
- Promotional Campaigns: Launch targeted promotional campaigns to create awareness and generate demand in the new markets. Utilize digital marketing and local advertising platforms to reach potential customers effectively.
In conclusion, selecting the right distribution channels and strategically expanding distribution networks are critical components of successful market penetration. Companies must evaluate various channels based on their target audience, product nature, cost, efficiency, and market reach. Finding the right mix of online and offline distribution and considering an omnichannel approach can be advantageous. Moreover, expanding distribution networks to reach new markets requires thorough market research, local partnerships, adaptation to local preferences, and efficient logistics. By making informed decisions and focusing on customer needs, companies can effectively penetrate new markets and achieve sustainable growth.
II. Partnering and Collaborations
Partnering and collaborations play a crucial role in accelerating market penetration strategies. By forging strategic alliances with other companies, businesses can leverage each other’s strengths and resources to achieve mutual benefits. In this section, we will explore the significance of partnering and collaborations in market penetration.
Forging Strategic Partnerships to Accelerate Penetration
Strategic partnerships involve collaborating with other companies, organizations, or individuals to achieve common objectives. When aiming to penetrate a new market or expand market share, companies can benefit significantly from such partnerships. Here’s how strategic partnerships can accelerate market penetration:
- Access to New Markets: Partnering with a company that already has an established presence in the target market can provide access to a new customer base. This enables the penetrating company to reach potential customers more efficiently.
- Leveraging Expertise: Each partner in the strategic alliance brings unique expertise and resources to the table. By leveraging complementary skills, companies can enhance their overall capabilities and competitiveness.
- Shared Resources: Collaborating on resources like technology, distribution networks, marketing efforts, or research and development can lead to cost efficiencies and faster market entry.
- Risk Mitigation: In new markets or challenging environments, risks can be high. Partnering with a well-established company can help mitigate risks and increase the chances of success.
- Enhanced Credibility: Aligning with reputable and trusted partners can enhance the credibility and reputation of the penetrating company in the eyes of consumers and stakeholders.
Co-marketing and Co-branding Opportunities for Mutual Benefit
Co-marketing and co-branding are specific forms of strategic partnerships where two or more companies come together to promote and market products or services jointly. These collaborative efforts can lead to mutual benefits and stronger market penetration. Here’s how co-marketing and co-branding opportunities can be advantageous:
- Leveraging Each Other’s Audience: Co-marketing allows companies to reach a larger audience by tapping into each other’s customer bases. This increases brand exposure and awareness.
- Shared Marketing Costs: By sharing marketing costs, companies can run more extensive and impactful marketing campaigns that they might not be able to afford individually.
- Complementary Product Pairings: Co-branding involves combining two brands on a single product. When the brands have complementary offerings, it can create added value and appeal to customers.
- Expanding Market Reach: Companies can use co-marketing or co-branding to enter new markets or target different customer segments effectively.
The Importance of Maintaining Healthy Relationships with Partners
Building and maintaining healthy relationships with partners is essential for the long-term success of strategic alliances. Here are some factors that contribute to strong partnerships:
- Clear Communication: Effective communication is crucial to align goals, expectations, and strategies between partners. Regular communication helps resolve conflicts and ensures everyone remains on the same page.
- Mutual Trust and Respect: Trust and respect are the foundation of any successful partnership. Companies should honor commitments and act in each other’s best interests.
- Collaborative Decision-making: Involving all partners in decision-making processes fosters a sense of ownership and shared responsibility.
- Value Creation: The partnership should focus on creating value for both parties. A win-win approach ensures that each partner benefits from the collaboration.
- Conflict Resolution: Inevitably, conflicts may arise during the partnership. A proactive approach to resolving conflicts is essential to maintaining a healthy working relationship.
In conclusion, forging strategic partnerships and collaborations can significantly accelerate market penetration efforts. These alliances provide access to new markets, shared resources, risk mitigation, and enhanced credibility. Co-marketing and co-branding opportunities can also expand market reach and reduce marketing costs. However, the success of these partnerships depends on maintaining healthy relationships with partners through clear communication, mutual trust, collaborative decision-making, value creation, and proactive conflict resolution. By strategically selecting partners and nurturing these alliances, companies can achieve faster market penetration and sustainable growth.
3. Market Penetration through Promotional Strategies

Market penetration through promotional strategies involves using various marketing and advertising techniques to increase a company’s market share within its existing market. These strategies aim to attract more customers, boost sales, and enhance brand awareness.
I. Digital Marketing and Online Promotion
In today’s digital age, leveraging digital marketing and online promotion is essential for successful market penetration. Digital marketing encompasses various strategies and tools that can help businesses reach their target audience, increase brand awareness, and drive sales. In this section, we will explore the key components of digital marketing for market penetration.
Leveraging SEO, Content Marketing, and Social Media for Penetration
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): SEO is the practice of optimizing a website or online content to rank higher in search engine results. By strategically incorporating relevant keywords and improving website structure, businesses can increase their visibility in search engines. When customers search for products or services related to their industry, a well-optimized website is more likely to be discovered, leading to increased website traffic and potential customers.
- Content Marketing: Content marketing involves creating valuable and relevant content, such as blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, and more, to attract and engage the target audience. By providing valuable information and solutions to customers’ problems, businesses can build trust and credibility. Engaging content also encourages sharing and can lead to increased brand exposure and organic growth.
- Social Media Marketing: Social media platforms are powerful tools for market penetration. By maintaining an active presence on social media, businesses can interact with customers, share valuable content, and promote their products or services. Social media also allows for targeted advertising, enabling businesses to reach specific demographics and interests, further enhancing market penetration efforts.
Pay-per-click (PPC) Advertising and Its Role in Market Entry
- PPC Advertising: PPC advertising is a digital advertising model where businesses pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. It allows businesses to bid on specific keywords or target audience demographics, and their ads are displayed to users who are actively searching for relevant products or services. PPC ads can appear on search engines, social media platforms, and other websites, providing immediate visibility and driving traffic to the business website.
- Market Entry: PPC advertising is particularly valuable for market entry, especially in competitive markets. When entering a new market, businesses might face challenges in establishing organic visibility quickly. PPC allows them to place their ads at the top of search engine results and other high-traffic platforms, ensuring they are immediately visible to potential customers. This can help new entrants gain initial traction and compete with established players.
Analyzing the Effectiveness of Online Campaigns
Analyzing the effectiveness of online campaigns is crucial to optimize marketing efforts and ensure a positive return on investment (ROI). Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be identified to measure the success of digital marketing campaigns for market penetration. Some essential metrics to consider include:
- Website Traffic: Monitoring website traffic helps gauge the overall interest and engagement generated by digital marketing efforts. An increase in traffic indicates that the marketing strategies are driving users to the website.
- Conversion Rate: The conversion rate measures the percentage of website visitors who take a desired action, such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a form. A high conversion rate indicates that the marketing strategies are effectively driving actions.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): CPA measures the cost required to acquire a new customer. It helps assess the efficiency of marketing spending and the cost-effectiveness of the campaign.
- Social Media Engagement: Tracking social media engagement metrics, such as likes, shares, comments, and followers, provides insights into the effectiveness of social media marketing efforts.
- ROI on PPC Advertising: Analyzing the return on investment for PPC advertising ensures that the money spent on paid advertising generates profitable results.
By regularly analyzing these metrics and making data-driven decisions, businesses can refine their digital marketing strategies, enhance market penetration efforts, and achieve sustainable growth in the target market.
In conclusion, digital marketing and online promotion are essential components of successful market penetration strategies. Leveraging SEO, content marketing, and social media helps businesses attract and engage their target audience. PPC advertising plays a crucial role in market entry by providing immediate visibility and traction in competitive markets. To ensure the effectiveness of online campaigns, businesses should analyze relevant metrics and use insights to optimize their marketing efforts continuously. By combining these digital marketing tactics and staying agile in the online landscape, businesses can successfully penetrate new markets and achieve their growth objectives.
II. Traditional Marketing and Offline Promotion
While digital marketing has become increasingly prevalent, traditional marketing and offline promotion still play a significant role in market penetration. Traditional advertising methods encompass a range of strategies that can effectively reach target audiences through print media, television, radio, and other offline channels. In this section, we will explore the relevance of traditional advertising in modern market penetration and how businesses can utilize print media, TV, and radio for targeted outreach. Additionally, we will discuss the importance of measuring the impact of offline marketing efforts.
The Relevance of Traditional Advertising in Modern Market Penetration
Despite the rise of digital marketing, traditional advertising methods remain relevant for several reasons:
- Wide Reach: Traditional advertising, such as print ads in newspapers or magazines, TV commercials, and radio spots, can reach a broad audience, including individuals who may not be active online. This wide reach is particularly beneficial for businesses targeting a diverse demographic.
- Established Audiences: Traditional media outlets have well-established audiences, which can provide businesses with access to a loyal and engaged customer base. For instance, advertising during popular TV shows or radio programs can expose the brand to a large and relevant audience.
- Trust and Credibility: Some consumers still perceive traditional media, like print publications or TV channels, as more trustworthy and credible compared to online sources. Having a presence in reputable traditional media can enhance the brand’s credibility.
- Tangible Presence: Print media, such as brochures, flyers, and direct mail, provide a tangible presence that digital ads may lack. Tangible materials can create a lasting impression and serve as reminders of the brand and its offerings.
Utilizing Print Media, TV, and Radio for Targeted Outreach
- Print Media: Print media includes newspapers, magazines, brochures, flyers, and direct mail. To utilize print media for targeted outreach, businesses should identify publications or distribution channels that align with their target audience. For instance, if a company aims to reach local customers, advertising in regional newspapers or community magazines can be effective. Targeted print media campaigns allow businesses to focus their message on specific geographic locations or customer segments.
- Television (TV) Advertising: TV advertising offers an excellent platform for reaching a massive audience. Businesses can choose between national, regional, or local TV networks based on their target market. TV commercials allow for storytelling, visual impact, and emotional appeal, making them ideal for creating brand awareness and leaving a lasting impression. Careful selection of TV channels and time slots ensures that the ads reach the intended audience.
- Radio Advertising: Radio advertising is a cost-effective option for targeted outreach, especially for local businesses. Radio spots can be strategically placed during peak commuting hours or specific program segments that align with the target audience’s interests. With radio ads, businesses can effectively communicate their brand message and promote time-sensitive offers.
Measuring the Impact of Offline Marketing Efforts
Measuring the impact of offline marketing efforts is essential to understand the effectiveness of traditional advertising campaigns and ensure a positive ROI. Here are some methods to measure the impact:
- Coupon Codes and Promotions: Including unique coupon codes or promotions in offline marketing materials allows businesses to track the number of redemptions. This data provides insights into the success of the campaign and helps calculate the conversion rate.
- QR Codes and Short URLs: QR codes and short URLs can be added to print materials, directing customers to specific landing pages on the website. Analyzing website traffic from these sources reveals the success of offline marketing efforts.
- Surveys and Customer Feedback: Conducting surveys or gathering customer feedback through phone calls or in-store interactions can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of offline advertising. Customer feedback helps assess brand recall and customer sentiment after exposure to traditional ads.
- Call Tracking: Using call tracking numbers in offline ads enables businesses to monitor incoming calls generated by specific campaigns. This data helps understand the impact of TV or radio advertising on lead generation.
By measuring the impact of offline marketing efforts, businesses can optimize their strategies, allocate resources effectively, and ensure that traditional advertising complements their digital marketing initiatives. A cohesive approach that integrates both traditional and digital marketing ensures comprehensive market penetration and maximizes the brand’s reach and impact.
In conclusion, traditional marketing and offline promotion remain relevant and valuable components of market penetration strategies. Print media, TV, and radio provide businesses with opportunities to reach a broad audience, establish credibility, and create a tangible presence. By effectively targeting the right audience and measuring the impact of offline marketing efforts, businesses can capitalize on traditional advertising to enhance their market penetration and achieve sustainable growth.
Measuring and Evaluating Market Penetration

Measuring and evaluating market penetration is essential to assess the effectiveness of the strategies employed and the success of increasing a company’s market share within its existing market.
Key Metrics for Assessing Market Penetration
Measuring and evaluating market penetration is essential to understand the success of the strategies implemented and to make informed decisions for further growth. Key metrics help businesses assess the effectiveness of their market penetration efforts and identify areas for improvement. In this section, we will discuss three essential key metrics for evaluating market penetration: sales data and revenue growth, market share analysis, and customer retention and loyalty metrics.
1. Sales Data and Revenue Growth as Indicators of Success
Sales data and revenue growth are crucial indicators of the success of market penetration strategies. Monitoring the sales performance and revenue generated after implementing market penetration tactics provides insights into whether the strategies are effectively increasing product demand and market share.
To measure sales data and revenue growth:
- Sales Volume: Track the number of products sold over a specific period. Comparing sales volumes before and after implementing market penetration tactics helps identify the impact on product demand.
- Revenue Increase: Calculate the percentage increase in revenue generated from the targeted market. An increase in revenue indicates that the market penetration strategies have been successful in capturing a larger market share.
- Customer Segmentation: Analyze sales data based on customer segmentation, such as geographic location, demographics, or purchasing behavior. This analysis helps identify the most profitable customer segments and target them more effectively.
- Customer Acquisition Cost: Measure the cost incurred in acquiring new customers through market penetration efforts. A lower customer acquisition cost signifies cost-effectiveness in reaching and converting new customers.
2. Market Share Analysis and Comparison with Competitors
Market share analysis is crucial for understanding a company’s position in the market relative to its competitors. A growing market share indicates successful market penetration, as it means the company is capturing a larger portion of the market compared to its rivals.
To analyze market share:
- Market Share Calculation: Calculate the company’s market share by dividing its total sales revenue by the total market sales revenue and multiplying the result by 100. Regularly tracking this metric helps identify trends and changes in market share over time.
- Competitor Comparison: Compare the company’s market share with that of its competitors. This analysis provides insights into whether the market penetration efforts are helping the company gain a competitive edge.
- Market Share Growth: Monitor the growth in market share over specific periods, such as quarterly or annually. Positive growth indicates successful market penetration, while declining market share may signify the need for strategy adjustments.
3. Customer Retention and Loyalty Metrics
Customer retention and loyalty metrics are essential for assessing the effectiveness of market penetration strategies in building long-term customer relationships. A successful market penetration strategy not only attracts new customers but also retains them and fosters loyalty.
To measure customer retention and loyalty:
- Customer Retention Rate: Calculate the percentage of customers who continue to do business with the company over a specific period. A high customer retention rate indicates that the market penetration strategies are meeting customer needs and expectations.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Determine the total revenue generated from a customer over their entire relationship with the company. CLV helps identify the most valuable customers and guides efforts to retain and upsell to them.
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys: Conduct customer satisfaction surveys to gather feedback on their experience with the company and its products. Positive survey results indicate customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Repeat Purchase Rate: Measure the percentage of customers who make repeat purchases. A high repeat purchase rate signifies customer loyalty and the effectiveness of market penetration in building brand loyalty.
By analyzing these key metrics, businesses can gain valuable insights into the success of their market penetration strategies. It allows them to adjust their tactics, target specific customer segments more effectively, and focus on retaining and nurturing long-term customer relationships. Ultimately, a comprehensive evaluation of market penetration efforts leads to continuous improvement and sustainable growth in the target market.
Analyzing Market Penetration Challenges
Market penetration, while an effective growth strategy, comes with its own set of challenges. In this section, we will discuss the obstacles and barriers to penetration, how to address market saturation and competitive pressures, and strategies to overcome challenges and sustain growth.
1. Identifying Obstacles and Barriers to Penetration
When implementing market penetration strategies, businesses may encounter various obstacles and barriers that hinder their efforts to gain a larger market share. Some common obstacles include:
- Customer Loyalty: Existing customers may be loyal to established brands, making it challenging to convince them to switch to a new product or service.
- Competitor Resistance: Competitors may respond aggressively to new market entrants, making it difficult to gain a foothold in the market.
- Limited Resources: Small businesses or startups may face resource constraints, limiting their ability to invest in aggressive marketing or pricing strategies.
- Inadequate Marketing Efforts: Insufficient marketing efforts can lead to low awareness of the new product, hindering its adoption in the market.
- Regulatory Barriers: Some industries may have strict regulations or licensing requirements, making it challenging for new entrants to penetrate the market.
To overcome these obstacles, businesses must conduct thorough market research and develop strategies that address the specific challenges they face.
2. Addressing Market Saturation and Competitive Pressures
Market saturation occurs when a market is flooded with similar products or services, leading to intense competition and price wars. In such scenarios, gaining market share becomes difficult, and businesses must find innovative ways to differentiate themselves and attract customers. To address market saturation and competitive pressures:
- Differentiation: Focus on unique selling points and value propositions that set your product apart from competitors. Highlight the product’s superior features, quality, or customer service.
- Innovation: Constantly innovate and improve your product to stay ahead of competitors. Introducing new features or technology can attract customers and revitalize interest in the product.
- Targeted Marketing: Identify niche segments or untapped markets where the competition is relatively low. Concentrate your marketing efforts on these segments to build a strong customer base.
- Pricing Strategies: Implement pricing strategies that provide value to customers without compromising profitability. Offer discounts, bundle packages, or loyalty programs to entice customers.
3. Strategies to Overcome Challenges and Sustain Growth
To sustain growth and overcome market penetration challenges, businesses can adopt the following strategies:
- Customer Education: Educate customers about the benefits of the new product or service through targeted marketing campaigns. Demonstrating the product’s value and usefulness can persuade customers to try it.
- Partnerships and Alliances: Form strategic partnerships or alliances with other businesses to expand the reach of your product. Collaboration can help access new markets and increase brand visibility.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously gather feedback from customers and make improvements based on their preferences and needs. This iterative process ensures that the product remains relevant and competitive.
- Customer Retention: Focus on building strong customer relationships and providing excellent customer service to retain existing customers. Satisfied customers are more likely to recommend the product to others, leading to organic growth.
- Agile Adaptation: Monitor market trends and be prepared to adapt quickly to changing market conditions. Agility allows businesses to seize new opportunities and stay ahead of competitors.
- Long-term Vision: While market penetration may provide immediate growth, businesses should also have a long-term vision for sustained success. Plan for future product extensions, market expansions, or diversification to ensure continued growth.
By understanding the challenges and implementing effective strategies, businesses can overcome obstacles to market penetration and achieve sustained growth in the target market. Market research, customer feedback, and a proactive approach to innovation are essential elements in successfully navigating the complexities of market penetration and staying competitive in the market.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve unveiled the power of market penetration strategies to drive business growth and success. Let’s recap the key methods:
- Price Adjustment: Lowering prices to gain a competitive edge and attract customers.
- Distribution Channels: Expanding into new channels for wider market reach.
- Product Improvement: Enhancing product quality to appeal to customers and boost sales.
- Upsurge Usage: Encouraging increased product usage through effective marketing.
- Knowing Risk and Growth: Strategically managing risks while aiming for growth.
- Create Barriers to Entry: Preventing competitors from entering the market.
- Be Unique and Think Differently: Innovating and adding value to stand out.
- Diversification: Introducing new products for new markets and adapting to change.
- Strategic Alliances: Partnering for efficient market entry.
To thrive in the future, remember to embrace market research, digital transformation, agility, customer-centricity, innovation, and social responsibility. Market penetration offers an opportunity for rapid expansion, but a thoughtful and adaptive approach is key to sustained success in today’s dynamic marketplace. By staying attuned to market trends and refining strategies, businesses can unlock their full potential and stay ahead in the competitive landscape. Empower your business with market penetration and seize every opportunity for growth and profitability.
