Types Of Marketing Strategy By Philip Kotler
Are you looking to delve into the world of marketing strategy and explore the brilliant insights of one of the industry’s pioneers? Join us as we unveil the various types of marketing strategy as proposed by none other than the renowned marketing guru, Philip Kotler. In this article, we will take you on a captivating journey through the diverse strategies that have shaped the marketing landscape and empowered businesses worldwide. From segmentation to differentiation, positioning to diversification, Kotler’s invaluable contributions have revolutionized the way companies approach their marketing endeavors. So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready to unravel the genius of Philip Kotler’s marketing strategies!
Overview of Marketing Strategies
Marketing strategy is a fundamental aspect of any successful business. It involves a set of well-thought-out plans and actions designed to achieve specific marketing objectives. A robust marketing strategy not only helps businesses reach their target audience but also enables them to stand out from competitors and drive growth. In this section, we will delve deeper into the concept of marketing strategies and explore their significance in the business world.
What is a Marketing Strategy?
At its core, a marketing strategy is a comprehensive plan that outlines the steps a company will take to promote its products or services to its target market. It involves a careful analysis of the market, understanding customer needs and preferences, and formulating tactics to achieve the company’s marketing goals. A well-defined marketing strategy acts as a roadmap, guiding the company’s marketing efforts and ensuring that resources are used efficiently.
Importance of Marketing Strategy in Business
In the ever-evolving business landscape, having a solid marketing strategy is more crucial than ever. A well-crafted marketing strategy provides several key benefits to a business:
- Market Penetration: By understanding the market and its dynamics, a marketing strategy helps businesses identify opportunities to expand their reach and gain a larger market share.
- Competitive Advantage: A well-executed marketing strategy allows a company to differentiate its products or services from competitors, creating a unique selling proposition that attracts customers.
- Resource Allocation: Effective marketing strategies help allocate resources wisely, ensuring that marketing efforts are focused on activities that yield the highest return on investment.
- Brand Building: A consistent and well-communicated marketing strategy contributes to building a strong brand identity, which is essential for customer loyalty and trust.
- Adaptability: Market conditions are subject to change, and a marketing strategy provides a framework for adapting to new trends, technologies, and customer behaviors.
Role of Philip Kotler in Shaping Modern Marketing Strategy
When discussing a marketing strategy, it is impossible not to mention the influential role of Philip Kotler. Regarded as the “Father of Modern Marketing,” Philip Kotler is an eminent marketing guru whose work has left a profound impact on the field of marketing. His innovative ideas and insights have helped shape marketing practices worldwide. Let’s explore how Philip Kotler has contributed to the evolution of marketing strategy.
Understanding Philip Kotler’s Contribution to Marketing Strategy
Brief Biography of Philip Kotler
Philip Kotler, born on May 27, 1931, in Chicago, Illinois, is an American marketing author, consultant, and professor. He earned his Master’s degree in Economics from the University of Chicago and a Ph.D. in Economics from MIT. Kotler is currently the S.C. Johnson Distinguished Professor of International Marketing at the Kellogg School of Management, Northwestern University. With a career spanning over five decades, Kotler has been instrumental in promoting marketing as a scientific discipline and elevating its status in the business world.
Kotler’s Influence on Marketing Concepts and Practices
Philip Kotler’s contributions to marketing are extensive and diverse. Some of his most significant influences include:
- Marketing Management: Kotler’s groundbreaking book, “Marketing Management: Analysis, Planning, Implementation, and Control,” has become the standard marketing textbook and is widely used in business schools worldwide. The book introduced essential marketing concepts and frameworks that are still widely applied in businesses today.
- Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP): Kotler’s work on STP has been pivotal in helping businesses identify and understand their target markets, tailor their marketing efforts to specific customer segments, and establish a unique market position.
- Social Marketing: Kotler’s research and advocacy for social marketing have spurred initiatives to address social issues and promote behavioral change for the betterment of society.
Key Works and Publications by Philip Kotler in the Marketing Field
Throughout his illustrious career, Philip Kotler has authored numerous books, research papers, and articles on various marketing topics. Some of his notable works include:
- Marketing Management: This seminal book is now in its 15th edition and has been translated into multiple languages, making it one of the most widely read marketing books globally.
- Principles of Marketing: Another influential textbook by Kotler that covers the fundamental principles of marketing and is widely adopted in academic settings.
- Marketing Insights from A to Z: In this book, Kotler provides practical insights and advice on a wide range of marketing issues, from branding to customer relationship management.
- Marketing 4.0: Co-authored with Hermawan Kartajaya and Iwan Setiawan, this book explores how marketing has evolved in the digital age and how businesses can adapt to new consumer behaviors and trends.
Philip Kotler’s extensive body of work has not only shaped marketing education but also provided valuable guidance to marketers worldwide, helping them navigate the dynamic and ever-changing marketing landscape. His emphasis on customer-centricity, strategic thinking, and ethical marketing practices continues to inspire marketing professionals to this day.
The Concept of Marketing Strategy

Defining Marketing Strategy
A well-defined marketing strategy serves as a roadmap for businesses to achieve their marketing objectives effectively. It involves a series of carefully planned actions to reach target customers and create a sustainable competitive advantage. In this section, we will explore the core components of a marketing strategy and its relationship with overall business objectives.
Core Components of a Marketing Strategy
- Market Analysis: Before crafting a marketing strategy, it is essential to conduct a thorough analysis of the market, including customer needs, competitors, and industry trends. Understanding the market dynamics helps in identifying opportunities and challenges.
- Target Audience Identification: Defining the target audience is crucial for tailoring marketing efforts to specific customer segments. Understanding the preferences, behaviors, and pain points of the target audience allows for more effective communication and engagement.
- Value Proposition Development: A strong value proposition outlines the unique benefits and value that a product or service offers to customers. It helps in differentiating the brand from competitors and capturing the attention of potential customers.
- Marketing Mix Strategy: The marketing mix consists of the four Ps: Product, Price, Promotion, and Place. Crafting the right marketing mix ensures that the product or service meets customer needs, is priced competitively, reaches the target audience through effective promotions, and is available through appropriate distribution channels.
Relationship between Marketing Strategy and Business Objectives
A well-crafted marketing strategy aligns with the overall business objectives of a company. The marketing strategy should support and contribute to achieving the broader goals of the organization. By establishing clear connections between marketing initiatives and business objectives, companies can ensure that marketing efforts are directed toward growth and profitability.
Aligning Marketing Strategy with Overall Company Goals
To achieve successful alignment between marketing strategy and business objectives, consider the following steps:
- Collaboration with Key Stakeholders: Engage with key stakeholders, such as company executives and department heads, to understand the company’s long-term goals and vision. This collaboration ensures that marketing efforts are in line with the overall business direction.
- Defining Specific Marketing Goals: Set specific and measurable marketing goals that contribute to achieving broader business objectives. For example, increasing sales by a certain percentage, expanding market share, or entering new markets could be specific marketing goals.
- Regular Performance Evaluation: Continuously monitor and evaluate the performance of marketing initiatives against set goals. This assessment allows for adjustments and optimizations to keep marketing efforts on track.
Types of Marketing Strategies
In the dynamic business landscape, various marketing strategies exist to help companies achieve their unique goals and objectives. Understanding the different types of marketing strategies enables businesses to select the most suitable approach for their specific needs. Let’s explore some commonly used marketing strategies:
1. Differentiation Strategy
A differentiation strategy focuses on making a product or service distinct from competitors’ offerings. Companies employing this strategy emphasize unique features, superior quality, exceptional customer service, or brand reputation to attract customers willing to pay a premium for the added value.
2. Cost Leadership Strategy
A cost leadership strategy aims to be the low-cost producer in the industry. By offering products or services at a lower price than competitors, companies can appeal to price-sensitive customers and gain a competitive advantage.
3. Niche Marketing Strategy
Niche marketing involves targeting a specific segment of the market with specialized products or services. By focusing on a narrow and well-defined customer group, companies can tailor their offerings to meet specific needs, build brand loyalty, and reduce competition.
4. Growth Strategies (Market Penetration, Market Development, Product Development, Diversification)
Growth strategies involve expanding a company’s market presence or product offerings to drive business growth. These strategies include:
- Market Penetration: Increasing market share through aggressive marketing efforts to attract more customers from existing markets.
- Market Development: Expanding into new geographic regions or untapped market segments with existing products.
- Product Development: Introducing new products or product variations to meet evolving customer needs or preferences.
- Diversification: Entering new markets or industries unrelated to the company’s current offerings, either through related or unrelated diversification.
Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP)
Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP) is a fundamental marketing concept that involves a customer-centric approach to tailor marketing efforts effectively. Let’s explore each component of STP:
Understanding Market Segmentation
Market segmentation involves dividing the broad market into distinct customer groups based on common characteristics, needs, or behaviors. By segmenting the market, businesses can target specific customer segments with customized marketing strategies.
Selecting Target Market Segments
After segmenting the market, businesses must identify which customer segments are the most viable and relevant for their offerings. Target market selection ensures that marketing efforts are directed toward customers most likely to engage and convert.
Creating a Unique Market Positioning
Market positioning involves how a company positions its products or services in the minds of customers relative to competitors. Effective positioning communicates a unique value proposition and addresses the specific needs or desires of the target market. By establishing a distinct market position, businesses can differentiate themselves and build a strong brand identity.
Philip Kotler’s Framework for Developing Marketing Strategy
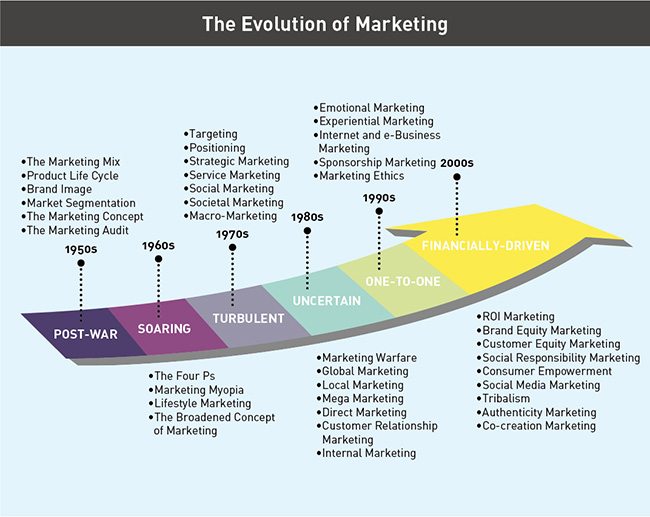
Philip Kotler, a renowned marketing expert, proposed a comprehensive framework for developing a marketing strategy. This framework, known as the “4 Ps of Marketing,” helps businesses design effective marketing plans by focusing on four key elements: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Let’s explore each component:
1. The 4 Ps of Marketing
Philip Kotler, one of the foremost authorities in marketing, developed the concept of the 4 Ps of marketing. These four elements form the foundation of a successful marketing strategy. Let’s explore each of them in detail:
Product: Designing Products That Meet Customer Needs
The product is the core offering that satisfies a customer’s need or wants. It includes the physical product itself, along with its features, design, quality, and packaging. In developing a marketing strategy, businesses must carefully consider their product’s attributes to meet customer expectations and stand out from competitors.
Price: Setting Competitive and Profitable Pricing Strategies
Pricing is a critical element in marketing strategy as it directly impacts customer perception and profitability. Businesses need to set prices that are competitive within the market while ensuring they can achieve their desired profit margins. Factors such as perceived value, competitor pricing, and cost of production must be considered when determining the right pricing strategy.
Promotion: Creating Effective Promotional Campaigns
Promotion involves the various marketing activities and communications used to promote and create awareness about a product or service. This includes advertising, public relations, sales promotions, direct marketing, and other promotional efforts. The goal is to reach the target audience effectively, influence their buying decisions, and create a positive brand image.
Place: Selecting Distribution Channels for Maximum Reach
The place, also known as distribution, refers to the process of getting the product to the customer. Choosing the right distribution channels is crucial for ensuring the product reaches the target audience efficiently. This can involve selling through retail stores, online platforms, wholesalers, or directly to consumers.
2. The 5 Product Levels
Philip Kotler also introduced the concept of the 5 product levels, which represent the different levels of a product that customers perceive. Understanding these levels can help businesses develop comprehensive marketing strategies to meet customer needs effectively. Let’s explore each of the product levels:
Core Product
The core product represents the essential benefit or value that the customer receives from using the product. For example, when purchasing a smartphone, the core product is the ability to communicate and access information conveniently.
Generic Product
The generic product refers to the basic features and functions that the product provides. In the case of a smartphone, it includes features like a camera, internet access, and messaging capabilities.
Expected Product
The expected product includes the attributes and features that customers expect from a product in a particular category. For a smartphone, customers may expect a high-quality display, reliable performance, and long battery life.
Augmented Product
The augmented product encompasses additional features or services that go beyond customer expectations. These features add value and differentiate the product from competitors. For a smartphone, augmented product features might include extended warranties, customer support, or exclusive software applications.
Potential Product
The potential product represents the future improvements or innovations that a company plans to introduce to the product. It includes possible enhancements and advancements that may be introduced to stay ahead of the market and meet future customer needs.
By understanding and incorporating the 4 Ps of marketing and the 5 product levels into their marketing strategy, businesses can develop comprehensive and customer-focused approaches to effectively position and promote their products in the market.
Developing a Comprehensive Marketing Plan
Developing a comprehensive marketing plan is essential for businesses to achieve their marketing objectives, reach their target audience, and drive growth. A well-structured marketing plan serves as a roadmap that outlines the strategies and tactics to be implemented, the resources required, and the metrics to measure success.
1. Market Research and Analysis
Before creating a marketing plan, it is essential to conduct thorough market research and analysis. This step involves gathering relevant market data and insights to understand the industry landscape, target audience, and competition. Here are the key components of market research and analysis:
Gathering Market Data and Insights
Market data and insights provide valuable information about customer preferences, market trends, and potential opportunities. Marketers should collect data through surveys, focus groups, interviews, and online research to gain a comprehensive understanding of the market.
Conducting Competitor Analysis
Analyzing competitors is crucial for identifying their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. By studying competitors, businesses can identify gaps in the market, understand consumer expectations, and develop strategies to differentiate themselves effectively.
Identifying Customer Needs and Preferences
Understanding customer needs and preferences is fundamental to creating a successful marketing plan. Marketers should conduct customer surveys, analyze feedback, and monitor social media to gain insights into what customers value and expect from products or services.
2. Setting Marketing Objectives
Once market research is complete, marketers can set clear and actionable marketing objectives. These objectives serve as the foundation for the marketing plan and help guide marketing efforts. Here are the key aspects of setting marketing objectives:
SMART Objectives: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-Bound
Marketing objectives should follow the SMART framework to ensure they are well-defined and attainable. SMART objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound, allowing marketers to track progress and assess the success of their efforts.
Aligning Objectives with Business Goals
Marketing objectives should align with the overall business goals of the organization. By aligning marketing goals with broader business objectives, marketers can ensure that their efforts contribute to the company’s success and growth.
3. Crafting Marketing Tactics
With clear marketing objectives in place, marketers can move on to developing effective marketing tactics. These tactics outline the strategies and activities that will be used to achieve the marketing goals. Here are the essential steps in crafting marketing tactics:
Selecting Appropriate Marketing Mix Strategies
The marketing mix refers to the combination of product, price, place, and promotion that a business uses to attract and satisfy customers. Marketers should carefully choose the right marketing mix strategies based on their target audience, product attributes, and market conditions.
Designing Promotional Activities
Promotional activities are crucial for creating awareness and interest in the products or services offered. These activities may include advertising, public relations, sales promotions, content marketing, and social media marketing. The promotional mix should align with the marketing objectives and resonate with the target audience.
Choosing the Right Marketing Channels
Selecting the appropriate marketing channels is essential for reaching the target audience effectively. Marketers should consider the preferences and behavior of their target customers when choosing channels such as social media, email marketing, search engine marketing, and traditional advertising.
By conducting thorough market research, setting clear marketing objectives, and crafting effective marketing tactics, businesses can develop a comprehensive marketing plan that maximizes their chances of success in the market.
Implementing and Evaluating Marketing Strategies

Implementing and evaluating marketing strategies is a crucial process that determines the success of your marketing efforts and helps you make data-driven decisions for future improvements.
1. Execution of the Marketing Plan
Once the marketing plan has been developed, it is time to implement it. Successful execution requires coordination and collaboration among different departments within the organization. Here are the key aspects of executing the marketing plan:
Coordination and Collaboration Among Departments
Effective marketing execution involves the seamless collaboration of various departments, such as marketing, sales, product development, and customer service. Each department plays a role in ensuring the successful implementation of the marketing strategies.
Monitoring Progress and Making Necessary Adjustments
Regularly monitoring the progress of marketing initiatives is crucial for identifying potential issues and opportunities. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and evaluating the results, marketers can make necessary adjustments to optimize the marketing plan’s effectiveness.
2. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Measuring Success
Measuring the success of marketing strategies is essential for understanding their impact and making informed decisions. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable metrics used to evaluate marketing performance. Here are the main categories of KPIs:
Sales Metrics
Sales metrics measure the impact of marketing efforts on the company’s revenue and sales performance. These metrics include sales revenue, conversion rates, average order value, and customer acquisition cost.
Customer Engagement Metrics
Customer engagement metrics assess how well marketing strategies are engaging the target audience. Metrics in this category may include website traffic, social media interactions, email open rates, and customer feedback.
ROI and Cost Metrics
ROI (Return on Investment) and cost metrics determine the efficiency and profitability of marketing campaigns. Marketers should analyze metrics such as marketing ROI, cost per lead, cost per acquisition, and customer lifetime value.
3. Analyzing and Improving Marketing Strategies
Analyzing the effectiveness of marketing strategies is a critical step in the continuous improvement process. By evaluating the results and gaining insights, marketers can enhance their future strategies. Here are the key components of analyzing and improving marketing strategies:
Evaluating Marketing Effectiveness
Evaluating marketing effectiveness involves comparing actual results with the initial marketing objectives. Marketers should analyze KPIs and other performance metrics to determine if the marketing strategies have achieved the desired outcomes.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
Marketing is an ever-evolving field, and continuous improvement is necessary to stay ahead of the competition. Marketers should embrace a culture of adaptation and learning, using data-driven insights to refine marketing strategies and tactics continuously.
By effectively executing marketing plans, measuring success through KPIs, and consistently analyzing and improving strategies, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts and achieve sustainable growth and success in the market.
Case Studies: Successful Marketing Strategies
Case Study 1: Company X – Market Penetration Strategy
Background and Objectives
Company X is a well-established manufacturer of consumer electronics, with a strong presence in its domestic market. However, the company faced increasing competition from both domestic and international players and wanted to strengthen its market position further. The primary objectives of the marketing strategy were to increase market share, attract new customers, and boost sales.
Implemented Strategies
- Product Diversification: Company X expanded its product line to cater to a broader customer base. They introduced new product variants and innovative features to attract different segments of consumers.
- Pricing Strategy: To gain a competitive edge, Company X adopted a penetration pricing strategy. They offered their products at lower prices than competitors, enticing price-sensitive customers and increasing sales volume.
- Promotions and Discounts: Aggressive marketing campaigns were launched to create awareness about the new product offerings. The company offered special discounts and limited-time promotions to encourage immediate purchases.
- Distribution Expansion: Company X extended its distribution network by partnering with new retail outlets and e-commerce platforms. This allowed them to reach untapped markets and increase their accessibility to customers.
Results and Outcomes
The market penetration strategy yielded significant results for Company X:
- Increased Market Share: By expanding its product range and adopting competitive pricing, the company successfully gained a larger share of the market.
- Growth in Customer Base: The marketing initiatives attracted new customers, especially those who were price-conscious and seeking value for money.
- Sales Growth: With the combination of product diversification, promotions, and wider distribution, Company X experienced a substantial increase in sales.
Case Study 2: Company Y – Differentiation Strategy
Background and Objectives
Company Y is a fashion apparel brand known for its premium quality and unique designs. While the brand had a loyal customer base, it aimed to stand out in the highly competitive fashion industry. The primary objectives of the marketing strategy were to differentiate their brand, enhance customer loyalty, and capture a premium market segment.
Implemented Strategies
- Unique Brand Identity: Company Y focused on creating a distinct brand identity by emphasizing its commitment to premium craftsmanship, sustainability, and exclusive designs.
- Premium Pricing: To position itself as a luxury brand, Company Y set higher prices for its products, targeting consumers who value quality and exclusivity.
- Limited Edition Collections: The brand introduced limited edition collections, creating a sense of urgency and exclusivity among customers.
- Influencer Marketing: Company Y collaborated with influential fashion bloggers and celebrities to showcase its products and build brand credibility.
- Personalized Customer Experience: The brand invested in personalized customer service and tailored shopping experiences to enhance customer loyalty.
Results and Outcomes
The differentiation strategy proved successful for Company Y:
- Enhanced Brand Perception: By emphasizing exclusivity and premium quality, the brand’s image improved, attracting high-end customers.
- Higher Profit Margins: The premium pricing strategy resulted in higher profit margins, compensating for the reduced sales volume.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: The personalized customer experience and limited edition collections fostered a loyal customer base, leading to repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth.
By implementing effective market penetration and differentiation strategies, Company X and Company Y achieved their marketing objectives, demonstrating the importance of thoughtful planning and execution in successful marketing endeavors.
Conclusion
Philip Kotler’s marketing philosophy has shaped the world of marketing strategy, emphasizing value creation, customer orientation, and integrated marketing. Developing a well-defined marketing strategy is essential for businesses, providing clear direction, resource allocation, and competitive advantage. Effective marketing strategies are a driving force behind business success, fostering customer connections and profitable actions. In today’s competitive landscape, a strategic approach is not just an advantage but a necessity for long-term prosperity. By following Kotler’s principles and remaining adaptable, businesses can leave a lasting impact on their industries and achieve their goals.
FAQs
Q1: What are the key principles of Philip Kotler’s marketing philosophy?
A: Philip Kotler, one of the most influential figures in marketing, has developed several key principles that form the foundation of his marketing philosophy. Some of these principles include:
- Creating Value: Marketing should focus on creating value for customers by understanding their needs, wants, and preferences. It involves delivering products or services that satisfy customer demands and provide benefits.
- Customer Orientation: Kotler emphasizes putting the customer at the center of marketing activities. Businesses should listen to their customers, engage with them, and build strong relationships based on trust and satisfaction.
- Integrated Marketing: Kotler advocates for an integrated approach to marketing, where all marketing activities work together to achieve common objectives. This includes coordination among different marketing channels and functions.
- Profitability: Marketing efforts should be designed to generate profits for the business. The goal is to create a sustainable competitive advantage that leads to long-term profitability.
- Social Responsibility: Kotler believes that marketing should not only focus on economic success but also take into account social and environmental impacts. Responsible marketing considers the well-being of society and the planet.
- Innovation: Successful marketing involves continuous innovation to adapt to changing customer needs, market trends, and technological advancements.
Q2: How does market segmentation help in crafting an effective marketing strategy?
A: Market segmentation is the process of dividing a larger market into distinct groups or segments based on common characteristics, needs, or behaviors. It is a crucial step in crafting an effective marketing strategy because it allows businesses to target specific customer groups with tailored messages and offerings. Here’s how market segmentation helps in marketing strategy:
- Understanding Customer Needs: Segmentation helps identify the unique needs and preferences of different customer groups. This understanding allows marketers to develop products and services that meet those specific needs.
- Focused Targeting: By dividing the market into segments, businesses can focus their resources on the most relevant and profitable customer groups. This reduces the wastage of resources on irrelevant audiences.
- Customized Messaging: Segmentation enables marketers to create personalized and relevant messages for each segment. Tailored communication is more likely to resonate with customers and drive engagement.
- Optimized Positioning: Different segments may have different perceptions of a brand. With market segmentation, businesses can position their products or services differently for each segment, enhancing their competitive advantage.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: By understanding the potential of each segment, businesses can allocate their marketing budget and efforts more efficiently to achieve better ROI.
- Adaptability: Market segmentation allows businesses to adapt their marketing strategies to changes in customer preferences and market dynamics.
Q3: Can you explain the concept of “The 4 Ps of Marketing” in detail?
A: The “4 Ps of Marketing,” also known as the marketing mix, is a fundamental concept in marketing. It refers to the four key elements that businesses need to consider when formulating their marketing strategies. These elements are:
- Product: This refers to the tangible or intangible goods and services that a business offers to its customers. It involves decisions about product design, features, quality, branding, packaging, and customer service.
- Price: Price refers to the amount of money customers are willing to pay for a product or service. Pricing decisions need to take into account production costs, competition, customer perception, and value proposition.
- Place: Place, also known as distribution, involves decisions about how and where products will be made available to customers. It includes considerations about distribution channels, retail locations, online platforms, and logistics.
- Promotion: Promotion includes all the activities that businesses use to communicate with their target audience and promote their products or services. This includes advertising, public relations, sales promotions, social media marketing, and other promotional efforts.
The 4 Ps of Marketing are interconnected and need to be harmonized to create a successful marketing strategy. The right combination of product, price, place, and promotion will help businesses effectively reach their target market and achieve their marketing objectives.
Q4: What are some common challenges in implementing marketing strategies?
A: Implementing marketing strategies can be complex and challenging for businesses. Some common challenges include:
- Market Competition: Competing with other businesses in a crowded market can be tough. Businesses need to find ways to differentiate their offerings and stand out from competitors.
- Limited Budget: Marketing activities often require financial investment and small businesses or startups may have limited budgets. Efficient allocation of resources becomes crucial.
- Changing Consumer Behavior: Customer preferences and behavior can be unpredictable, making it challenging to adapt marketing strategies to meet evolving needs.
- Measuring ROI: Determining the return on investment (ROI) of marketing efforts can be challenging, especially for activities like brand awareness campaigns.
- Technology and Data Management: Keeping up with technological advancements and effectively managing customer data can be overwhelming for businesses.
- Internal Coordination: Implementing marketing strategies may require coordination among different departments within the organization. Lack of alignment can hinder success.
- Regulatory Compliance: Businesses need to ensure that their marketing strategies comply with relevant laws and regulations, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- External Factors: Economic conditions, political changes, and other external factors can impact marketing strategies and require businesses to adapt quickly.
To address these challenges, businesses need to have a clear understanding of their target market, continuously monitor performance, and be agile in adjusting strategies as needed.
