Types Of Marketing Strategy In Agriculture
How does marketing strategy impact the world of agriculture? In the dynamic and ever-evolving agricultural sector, effective marketing strategies play a pivotal role in shaping success. From crop cultivation to agribusiness ventures, understanding the various types of marketing strategies is vital for farmers, agricultural businesses, and industry stakeholders alike. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse marketing approaches that drive growth and profitability in agriculture. Whether you’re a seasoned farmer or a newcomer to the field, this article will equip you with valuable insights to navigate the agricultural market with confidence and achieve sustainable success.
Understanding the Importance of Marketing in Agriculture
In the dynamic world of agriculture, effective marketing plays a pivotal role in driving growth, profitability, and sustainability for businesses operating in this sector. Gone are the days when agriculture was limited to mere production and distribution. Today, successful agricultural enterprises understand the significance of marketing strategies that go beyond traditional practices. In this section, we will delve into the evolution of agricultural marketing and explore how it has transformed to meet the demands of modern times.
The Evolution of Agricultural Marketing
Agricultural marketing has come a long way from the days of simple barter systems to sophisticated global trade networks. Historically, agriculture was primarily local, with farmers selling their produce directly to nearby communities. However, as transportation and communication improved, agricultural products started reaching distant markets, leading to the emergence of larger and more complex supply chains.
The Green Revolution of the mid-20th century further revolutionized agricultural practices by introducing advanced technologies and hybrid crops, resulting in increased productivity and surplus production. As a consequence, marketing became essential to manage the surplus and find new markets for agricultural products.
With the advent of the internet and digital technologies, agricultural marketing witnessed another significant shift. Farmers and agribusinesses now have access to a vast online marketplace, enabling them to reach consumers globally and engage in direct-to-consumer marketing.
Highlighting the Role of Marketing Strategies in Agricultural Growth
Agricultural growth depends not only on the efficiency of production but also on the ability to connect with the right markets and customers. This is where marketing strategies come into play. Effective marketing strategies help agricultural businesses:
- Identify and understand consumer preferences and demands.
- Develop products and services that meet market needs.
- Create strong brand identities that instill trust and loyalty.
- Reach new markets and expand the customer base.
- Maximize profitability and compete in a highly competitive landscape.
In today’s digital era, agricultural marketing strategies have become more diverse and data-driven than ever before. From traditional advertising methods to social media campaigns, search engine optimization, and content marketing, each approach offers unique opportunities to connect with consumers and build lasting relationships.
The Current Landscape of Agriculture Marketing
The agriculture industry, like many others, faces a range of challenges and opportunities in the contemporary world. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food and agricultural products is increasing rapidly. However, several factors impact the current landscape of agriculture marketing.
Overview of the Agriculture Industry and Its Challenges
The agriculture industry remains a critical sector that feeds the world’s population. However, it confronts challenges such as:
- Sustainable Agriculture: The need for sustainable and environmentally-friendly practices to preserve natural resources and ensure long-term viability.
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in commodity prices and demand, affect profitability and market access for farmers and businesses.
- Supply Chain Complexity: The intricacy of modern supply chains involving multiple stakeholders, from producers to distributors and retailers.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Shifting consumer preferences towards organic and locally-sourced products, necessitating adaptation by agricultural businesses.
Identifying Key Marketing Trends and Innovations in Agriculture
To thrive in today’s competitive landscape, agricultural businesses must stay ahead of marketing trends and embrace innovative approaches. Some noteworthy marketing trends in agriculture include:
- Digital Transformation: Embracing digital technologies to streamline operations, connect with customers, and optimize marketing efforts.
- E-commerce in Agriculture: The rise of online marketplaces and direct-to-consumer sales, provides new avenues for farmers to reach consumers.
- Sustainable Branding: Consumers increasingly value sustainability, leading to the rise of eco-friendly and socially responsible agricultural brands.
- Personalization and Data Analytics: Leveraging data analytics to understand customer behavior and preferences for targeted marketing campaigns.
In conclusion, understanding the importance of marketing in agriculture is essential for businesses seeking growth and success in a rapidly evolving industry. By recognizing the evolution of agricultural marketing and embracing the latest trends, agricultural enterprises can develop effective strategies to meet the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities in today’s market.
The Fundamentals of Agricultural Marketing

Agricultural marketing involves the process of buying, selling, and distributing agricultural products from producers to consumers. It is a critical aspect of the agricultural industry as it connects farmers and other agricultural stakeholders with the market. The fundamentals of agricultural marketing include various activities and strategies aimed at efficiently handling agricultural products and ensuring that they reach the intended consumers.
1. Defining Agricultural Marketing and Its Objectives
Clarifying the Concept of Agricultural Marketing
Agricultural marketing is a comprehensive process that involves the planning, execution, and control of activities related to the buying and selling of agricultural products. It goes beyond the mere exchange of goods and encompasses all the steps involved in bringing agricultural products from the farm to the end consumers.
At its core, agricultural marketing aims to create value by efficiently connecting producers with consumers and satisfying the demands of both parties. It encompasses activities such as product development, pricing, promotion, and distribution, all with the goal of ensuring that agricultural products reach the right markets at the right time.
One crucial aspect of agricultural marketing is understanding the needs and preferences of consumers, including farmers themselves, as well as end consumers. This requires thorough market research and data analysis to gain insights into customer behavior and market trends. By aligning product offerings with market demands, agricultural businesses can position themselves competitively and cater to the specific needs of their target audience.
Outlining the Primary Objectives of Agricultural Marketing
The primary objectives of agricultural marketing revolve around optimizing the value chain and maximizing the benefits for all stakeholders involved. These objectives include:
- Market Access and Expansion: Agricultural marketing aims to facilitate access to markets for farmers and agribusinesses. By identifying new market opportunities and potential customers, agricultural businesses can expand their reach and increase sales volumes.
- Price Stabilization: Fluctuations in commodity prices can significantly impact farmers’ income and profitability. Agricultural marketing strategies can help stabilize prices by efficiently managing supply and demand dynamics.
- Brand Awareness and Loyalty: Building a strong brand presence is crucial in today’s competitive agricultural landscape. Effective marketing efforts help create brand awareness, establish trust, and foster customer loyalty.
- Value Addition: Agricultural marketing focuses on adding value to agricultural products through branding, packaging, and differentiation. Value-added products are more attractive to consumers and can command premium prices.
- Efficient Distribution: Ensuring the efficient distribution of agricultural products is essential to minimize wastage, reduce transportation costs, and meet consumer demands promptly.
- Market Intelligence: Data-driven agricultural marketing provides valuable market intelligence to farmers and agribusinesses. By analyzing market trends and consumer preferences, businesses can make informed decisions and stay ahead of the competition.
- Sustainability and Social Responsibility: Agricultural marketing also involves promoting sustainable practices and social responsibility. Consumers increasingly prefer products from environmentally conscious and socially responsible brands.
In summary, agricultural marketing plays a crucial role in connecting producers with consumers and optimizing the value chain. By understanding the concept of agricultural marketing and its objectives, agricultural businesses can develop effective strategies to meet market demands and achieve sustainable growth.
2. Market Segmentation in Agriculture
Explaining the Need for Market Segmentation in Agriculture
Market segmentation is a critical concept in agricultural marketing that involves dividing the market into distinct and identifiable groups of customers with similar characteristics, needs, and preferences. The rationale behind market segmentation is to tailor marketing efforts to specific customer segments, enabling agricultural businesses to deliver targeted messages and solutions.
In agriculture, the customer base is diverse, with farmers having different farm sizes, crops, geographical locations, and production methods. Trying to appeal to all farmers with a single marketing strategy can be inefficient and ineffective. Market segmentation allows businesses to identify key customer segments and create specialized marketing campaigns for each group.
By segmenting the market, agricultural businesses can:
- Enhance Relevance: Tailored marketing messages resonate more with customers, as they directly address their specific challenges and requirements.
- Increase Conversion Rates: Segmentation enables businesses to offer solutions that precisely match the needs of each segment, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Improve Customer Satisfaction: Addressing the unique needs of each segment enhances customer satisfaction and fosters long-term loyalty.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: By focusing marketing efforts on high-potential segments, businesses can allocate resources more efficiently.
- Identify Growth Opportunities: Market segmentation can reveal underserved segments or new customer groups that present growth opportunities for agricultural products.
Identifying Different Market Segments and Their Characteristics
In the agricultural sector, various factors influence market segmentation. Some common market segmentation criteria include:
- Farm Size: Segmenting based on farm size, such as small, medium, and large-scale farms, allows businesses to offer tailored solutions suitable for the size and scope of operations.
- Crop Type: Different crops have distinct requirements and challenges. Segmentation based on crop type helps businesses create specialized offerings for specific crop growers.
- Geographical Location: Regional variations in climate, soil, and market demand necessitate geographic segmentation to cater to localized needs.
- Production Methods: Organic and conventional farmers may have different preferences and requirements, warranting segmentation based on production methods.
- Customer Behavior: Segmenting based on customer behavior, such as early adopters or price-conscious buyers, helps tailor marketing strategies accordingly.
Understanding the characteristics of each segment is vital in developing targeted marketing campaigns. By combining demographic, behavioral, and geographic data, agricultural businesses can create well-defined segments and craft messages that resonate with the unique needs of each group.
3. Targeting the Right Audience in Agriculture
Analyzing the Importance of Target Audience Selection
Target audience selection is a critical aspect of agricultural marketing that involves identifying and prioritizing specific customer segments to focus marketing efforts. Not all farmers will be interested in a particular product or service, and targeting the right audience ensures that marketing resources are utilized efficiently.
By selecting the right target audience, agricultural businesses can:
- Maximize ROI: Concentrating marketing efforts on high-potential segments leads to a higher return on investment.
- Minimize Wastage: Avoiding irrelevant marketing messages minimizes the risk of wasted marketing resources.
- Personalized Marketing Messages: Understanding the needs and preferences of the target audience allows businesses to deliver personalized marketing messages that resonate with potential customers.
- Build Brand Loyalty: Engaging with the right audience fosters brand loyalty and encourages repeat business.
Strategies to Identify and Reach the Ideal Customer in Agriculture
To identify and reach the ideal customer in agriculture, businesses can adopt several strategies:
- Data-driven Analysis: Utilize market research and data analysis to identify high-potential customer segments based on demographic, behavioral, and geographic criteria.
- Customer Surveys: Conduct surveys to gather insights directly from farmers about their needs, preferences, and pain points.
- Collaborate with Agronomists and Advisors: Partner with agronomists and agricultural advisors to gain industry insights and understand customer requirements better.
- Social Media and Online Platforms: Leverage social media and online platforms to engage with farmers and gather feedback, enabling better targeting and communication.
- Referral Programs: Implement referral programs to encourage satisfied customers to refer new customers from within their networks.
- Content Marketing: Create valuable and informative content that addresses specific customer needs, attracting the right audience to the brand.
By combining these strategies, agricultural businesses can refine their target audience selection process and develop effective marketing campaigns that resonate with the ideal customer, driving business growth and success.
Traditional Marketing Strategies in Agriculture

Traditional marketing strategies in agriculture involve conventional methods that have been used for generations to promote agricultural products and reach consumers. These strategies, although considered traditional, continue to play a vital role in the agricultural industry. Here are some of the key traditional marketing strategies in agriculture:
1. Print Advertising and Direct Mail
Utilizing Print Media for Agricultural Promotions
Print advertising has long been a staple in agricultural marketing strategies, and it continues to be an effective method for reaching farmers. By utilizing print media, agricultural businesses can engage with their target audience in a tangible and impactful way. Here are some key benefits of using print advertising in agricultural promotions:
- High Visibility: Print materials, such as agricultural magazines, newspapers, and brochures, are often displayed prominently in farm offices and facilities, ensuring high visibility among farmers.
- Targeted Reach: Agricultural publications are designed to cater to specific farming interests and regions, allowing businesses to target their ads to the most relevant audience.
- Credibility: Print media is often perceived as more trustworthy and credible by farmers, as compared to online ads that may be seen as intrusive.
- Longevity: Printed materials have a longer shelf life, and farmers can refer back to them for information when making purchasing decisions.
- Brand Recognition: Consistent print advertising can help build brand recognition and familiarity among farmers.
To make the most of print advertising, agricultural businesses should focus on creating visually appealing ads with compelling messages that resonate with their target audience. Additionally, tracking response rates and ROI can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of print campaigns.
The Effectiveness of Direct Mail in Agricultural Marketing
Direct mail is another traditional marketing strategy that remains relevant in agriculture due to its personalized approach. Sending physical mail directly to farmers’ mailboxes can be highly effective in capturing their attention and generating leads. Here’s why direct mail continues to be an important tool in agricultural marketing:
- Personalization: Direct mail allows businesses to tailor their messages and offerings to individual farmers, making the communication more relevant and engaging.
- Tangible Impact: Physical mail pieces create a tangible impact, providing farmers with a concrete representation of the product or service being offered.
- Less Competition: With the shift towards digital marketing, direct mail stands out as a less crowded advertising space, enabling businesses to reach farmers without facing the clutter of online ads.
- Measurability: Direct mail campaigns can be tracked and measured, providing valuable data on response rates and conversion metrics.
- Cross-Promotion: Direct mail can be combined with other marketing channels, such as online campaigns or special offers, to enhance its effectiveness.
To ensure the success of direct mail campaigns, agricultural businesses should invest in high-quality print materials, employ personalized messaging, and include clear calls to action. Additionally, incorporating unique identifiers or promotional codes in direct mail can help track response rates and measure campaign success.
In conclusion, traditional marketing strategies like print advertising and direct mail continue to play a crucial role in agricultural marketing. By leveraging the tangible impact and personalized approach of print media, agricultural businesses can effectively engage with their target audience and drive meaningful results.
2. Television and Radio Advertising
Harnessing the Power of Television in Agriculture
Television advertising remains a potent medium for reaching farmers and promoting agricultural products. With its widespread reach and visual impact, television offers several advantages for agricultural businesses. Here’s how you can harness the power of television in agriculture:
- Visual Engagement: Television allows you to showcase your agricultural products visually, making it easier for farmers to understand their features and benefits.
- Mass Reach: Television has broad viewership, enabling you to reach a large audience of farmers across different regions.
- Credibility: Farmers often trust the information presented on television, making it an effective medium for building brand credibility.
- Emotional Appeal: Television ads can evoke emotions, creating a connection with farmers and influencing their buying decisions.
- Repetition and Recall: Repeated airing of ads can reinforce your message and improve brand recall among farmers.
When using television advertising, it’s essential to tailor your commercials to resonate with the specific interests and needs of the agricultural audience. Consider showcasing real farm scenarios and success stories to create relatability and authenticity.
Leveraging Radio as a Marketing Channel for Agricultural Products
Radio advertising remains a relevant marketing channel in agriculture due to its accessibility and local reach. Radio ads can be an effective way to target farmers during their daily activities, such as while driving tractors or working in fields. Here’s how you can leverage radio as a marketing channel for agricultural products:
- Local Targeting: Radio stations often cater to specific regions, allowing you to target ads to farmers in specific geographic areas.
- Timely Messaging: Radio allows for quick dissemination of time-sensitive information, such as weather updates or limited-time offers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Radio advertising is generally more affordable than television, making it suitable for businesses with smaller marketing budgets.
- Audience Engagement: With well-crafted scripts and compelling storytelling, radio ads can capture farmers’ attention and keep them engaged.
- Frequency: Repeating radio ads at strategic times can reinforce your message and increase brand recall.
To make the most of radio advertising, ensure that your ad scripts are clear, concise, and impactful. Use sound effects and music that resonate with farmers and align with your brand identity.
3. Agricultural Trade Shows and Exhibitions
Showcasing Products and Building Networks at Trade Shows
Participating in agricultural trade shows and exhibitions offers a unique opportunity to showcase your products directly to farmers and industry professionals. Trade shows provide a platform for face-to-face interactions, product demonstrations, and networking. Here’s how you can make the most of agricultural trade shows:
- Booth Design: Create an eye-catching and inviting booth design that reflects your brand and attracts visitors.
- Product Displays: Highlight your agricultural products with informative displays and interactive demonstrations.
- Engagement Activities: Engage attendees with contests, quizzes, or hands-on experiences related to your products.
- Informative Materials: Provide brochures, flyers, and product catalogs for attendees to take with them.
- Networking: Use trade shows as an opportunity to connect with potential customers, distributors, and industry partners.
Tips for Successful Participation in Agricultural Exhibitions
To ensure a successful experience at agricultural exhibitions, consider the following tips:
- Preparation: Plan and prepare well in advance, including setting clear goals for the event.
- Promotion: Promote your participation in the trade show through social media, email marketing, and targeted invitations.
- Staff Training: Train your booth staff to be knowledgeable, approachable, and capable of answering attendees’ questions.
- Lead Capture: Have a system in place to capture leads and contact information of interested attendees.
- Follow-Up: Follow up with leads and contacts after the event to build relationships and convert potential customers.
Trade shows can be an excellent way to generate leads, gain market insights, and increase brand visibility within the agricultural industry.
In conclusion, traditional marketing strategies such as television and radio advertising, as well as participation in agricultural trade shows and exhibitions, continue to be effective means of reaching and engaging with the farming community. By leveraging the power of these traditional channels, agricultural businesses can complement their digital marketing efforts and create a comprehensive marketing approach to promote their products successfully.
Digital Marketing Strategies in Agriculture

Digital marketing strategies in agriculture have become increasingly important as technology continues to transform the way businesses reach and engage with consumers. These strategies leverage digital channels and online platforms to promote agricultural products, connect with customers, and enhance brand visibility.
1. Building an Online Presence for Agricultural Businesses
In today’s digital age, establishing a strong online presence is crucial for agricultural businesses to effectively reach and engage with their target audience. Building an online presence involves creating a user-friendly website and utilizing social media platforms strategically. Let’s explore these digital marketing strategies:
Creating a User-Friendly Agriculture Website
A well-designed website serves as the foundation of your online presence. It is often the first point of contact between your business and potential customers. Here are essential elements to consider when creating a user-friendly agriculture website:
- Responsive Design: Ensure that your website is mobile-friendly and adapts to various screen sizes. Many farmers access the internet through smartphones and tablets, so a responsive design is crucial.
- Clear Navigation: Keep the website’s navigation simple and intuitive. Visitors should be able to find the information they need quickly and effortlessly.
- Content Quality: Provide valuable and informative content related to your agricultural products and services. High-quality content establishes your expertise and builds trust with your audience.
- Visual Appeal: Use relevant images, videos, and infographics to make your website visually engaging and appealing to visitors.
- Contact Information: Make it easy for visitors to contact you by displaying your contact information prominently on the website.
- Call-to-Action (CTA): Include clear and compelling CTAs throughout your website to encourage visitors to take specific actions, such as requesting a quote or signing up for a newsletter.
- Testimonials and Reviews: Showcase customer testimonials and positive reviews to build credibility and demonstrate the value of your products or services.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Optimize your website with relevant keywords to improve its visibility on search engines and attract organic traffic.
Importance of Social Media Platforms for Agricultural Marketing
Social media has become a powerful tool for agricultural marketing, allowing businesses to connect directly with farmers and industry professionals. Here’s why social media platforms are essential for your digital marketing strategy:
- Targeted Advertising: Social media platforms offer sophisticated targeting options, allowing you to reach specific demographics, interests, and locations relevant to your agricultural products.
- Engagement and Interaction: Social media enables real-time engagement with your audience through comments, likes, and shares. Responding to inquiries and comments promptly shows that you value customer feedback.
- Showcasing Products and Success Stories: Use social media to showcase your agricultural products and share success stories from satisfied customers. Visual content can be particularly effective in capturing attention.
- Building a Community: Social media allows you to build an online community around your brand. Encourage discussions, share industry insights, and foster a sense of belonging among your followers.
- Promoting Events and Webinars: Use social media to promote agricultural events, webinars, or product launches. These platforms can help generate interest and registrations.
- Market Research: Social media provides valuable insights into customer preferences, challenges, and trends in the agricultural industry. Use this data to refine your marketing strategies.
- Influencer Marketing: Collaborate with agricultural influencers or industry experts to expand your reach and credibility.
When using social media, tailor your content to suit the platform and your audience. For example, use more visual content on Instagram and Facebook, while focusing on industry insights and discussions on LinkedIn.
By combining a user-friendly website and a strategic approach to social media marketing, you can effectively establish and grow your online presence in the agricultural industry. These digital marketing strategies will complement traditional marketing efforts, helping you reach a broader audience and achieve your business goals.
2. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) for Agriculture
In the digital landscape, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) plays a crucial role in enhancing the online visibility and reach of agricultural businesses. Understanding SEO and implementing best practices can significantly impact agriculture marketing. Let’s explore how SEO can benefit your agricultural business and how to implement it effectively:
Understanding SEO and Its Impact on Agriculture Marketing
SEO is the process of optimizing your website and online content to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). When farmers and potential customers search for agricultural products or services on search engines like Google or Bing, SEO helps your website appear prominently, increasing the likelihood of clicks and visits.
The impact of SEO on agriculture marketing is significant because:
- Increased Organic Traffic: SEO drives organic traffic to your website, meaning people find your website through non-paid (organic) search engine results. This targeted traffic consists of users genuinely interested in your agricultural products.
- Credibility and Trust: Websites that rank higher on search engine results are often perceived as more credible and trustworthy. Ranking well on SERPs can boost your brand’s credibility within the agricultural industry.
- Cost-Effective Marketing: Compared to paid advertising, SEO can be a cost-effective marketing strategy in the long run. Once you achieve higher rankings, the organic traffic flow continues without additional costs per click.
- Targeting Relevant Keywords: SEO allows you to target specific keywords related to your agricultural products or services. By optimizing your content around these keywords, you attract the right audience to your website.
- Local SEO for Farmers: If your agricultural business serves specific regions or localities, local SEO strategies help you connect with farmers in those areas more effectively.
Implementing SEO Best Practices for Improved Visibility
To enhance your agriculture marketing through SEO, follow these best practices:
- Keyword Research: Identify relevant keywords and phrases that farmers are likely to use when searching for agricultural products or services. Use keyword research tools to find popular and low-competition keywords.
- On-Page Optimization: Optimize your website’s pages for target keywords by including them in titles, headings, meta descriptions, and content. Ensure that your content is informative, engaging, and valuable to visitors.
- Mobile Optimization: As mobile usage in agriculture grows, ensure your website is mobile-friendly to provide a seamless experience to mobile users.
- Local SEO: If you have a physical presence or serve specific regions, optimize your website for local searches by creating location-based content and claiming your Google My Business listing.
- Link Building: Earn high-quality backlinks from reputable websites within the agricultural industry. Backlinks from authoritative sources improve your website’s credibility.
- Website Speed: Optimize your website’s loading speed, as slow-loading pages can negatively impact user experience and SEO rankings.
- Regular Content Updates: Keep your website’s content fresh and relevant by regularly publishing new blog posts, articles, and updates related to agriculture.
- Meta Tags and Alt Text: Use descriptive and keyword-rich meta tags and alt text for images to improve the accessibility and SEO of your website.
Remember that SEO is an ongoing process, and it may take time to see significant results. Regularly monitor your website’s performance, track keyword rankings, and make necessary adjustments to continuously improve your agriculture marketing through SEO.
By implementing effective SEO practices, you can increase your online visibility, attract a targeted audience of farmers, and ultimately grow your agricultural business.
3. Content Marketing in the Agricultural Industry
Content marketing is a powerful tool for agricultural brands to engage with their target audience, educate farmers, and attract potential customers. By creating valuable and engaging content, agricultural businesses can establish themselves as industry experts and build trust with their audience. Let’s explore how to develop compelling content for agricultural brands and leverage it to educate and attract customers:
Developing Engaging Content for Agricultural Brands
To create content that resonates with farmers and agricultural professionals, consider the following strategies:
- Understand Your Audience: Before creating content, gain insights into the needs, challenges, and interests of your target audience. Understand the problems farmers face and how your agricultural products or services can provide solutions.
- Focus on Value: Provide valuable and practical information in your content. Farmers appreciate content that offers insights, tips, best practices, and actionable advice they can apply to their farming operations.
- Diversify Content Types: Use a mix of content types to keep your audience engaged. This can include blog posts, articles, infographics, videos, podcasts, case studies, and more.
- Highlight Success Stories: Share success stories of farmers who have benefited from using your products or services. Real-life examples add credibility to your brand.
- Address Current Issues: Stay up-to-date with the latest trends and challenges in the agricultural industry. Address current issues and provide your audience with valuable solutions.
- Use Visuals: Incorporate visuals like images and infographics to enhance the visual appeal of your content. Visuals can make complex information easier to understand.
- SEO Optimization: Apply SEO best practices to your content to improve its visibility on search engines. Use relevant keywords and optimize meta tags and descriptions.
- Authenticity and Transparency: Be authentic in your content and showcase the human side of your brand. Transparency builds trust with your audience.
Leveraging Content to Educate and Attract Customers
Once you’ve created compelling content, leverage it effectively to educate and attract customers:
- Content Distribution: Share your content on various platforms, including your website, blog, social media channels, email newsletters, and industry forums. This widens your reach and attracts a broader audience.
- Social Media Engagement: Engage with your audience on social media platforms. Respond to comments, answer questions, and encourage discussions around your content.
- Email Marketing: Use email newsletters to keep your audience informed about new content, promotions, and updates. Email marketing is an effective way to nurture leads and retain customers.
- Collaborate with Influencers: Partner with agricultural influencers or experts in the industry to promote your content. Their endorsement can expand your content’s reach.
- Guest Blogging: Contribute guest posts to other agricultural websites or industry publications. This increases your brand’s visibility and establishes you as an authority in the field.
- Track Performance: Monitor the performance of your content through analytics. Measure engagement, click-through rates, and conversions to understand what content resonates best with your audience.
- Repurpose Content: Repurpose successful content into different formats. For example, turn a blog post into a video or create an infographic based on a comprehensive article.
- Stay Consistent: Consistently publish new content to maintain the interest of your audience. A regular content schedule builds anticipation and keeps your brand top-of-mind.
Content marketing in the agricultural industry allows you to educate farmers, demonstrate the value of your products or services, and attract potential customers. By providing valuable and engaging content, you can position your agricultural brand as a trusted resource within the industry and foster long-term relationships with your audience.
Sustainable Marketing Practices in Agriculture
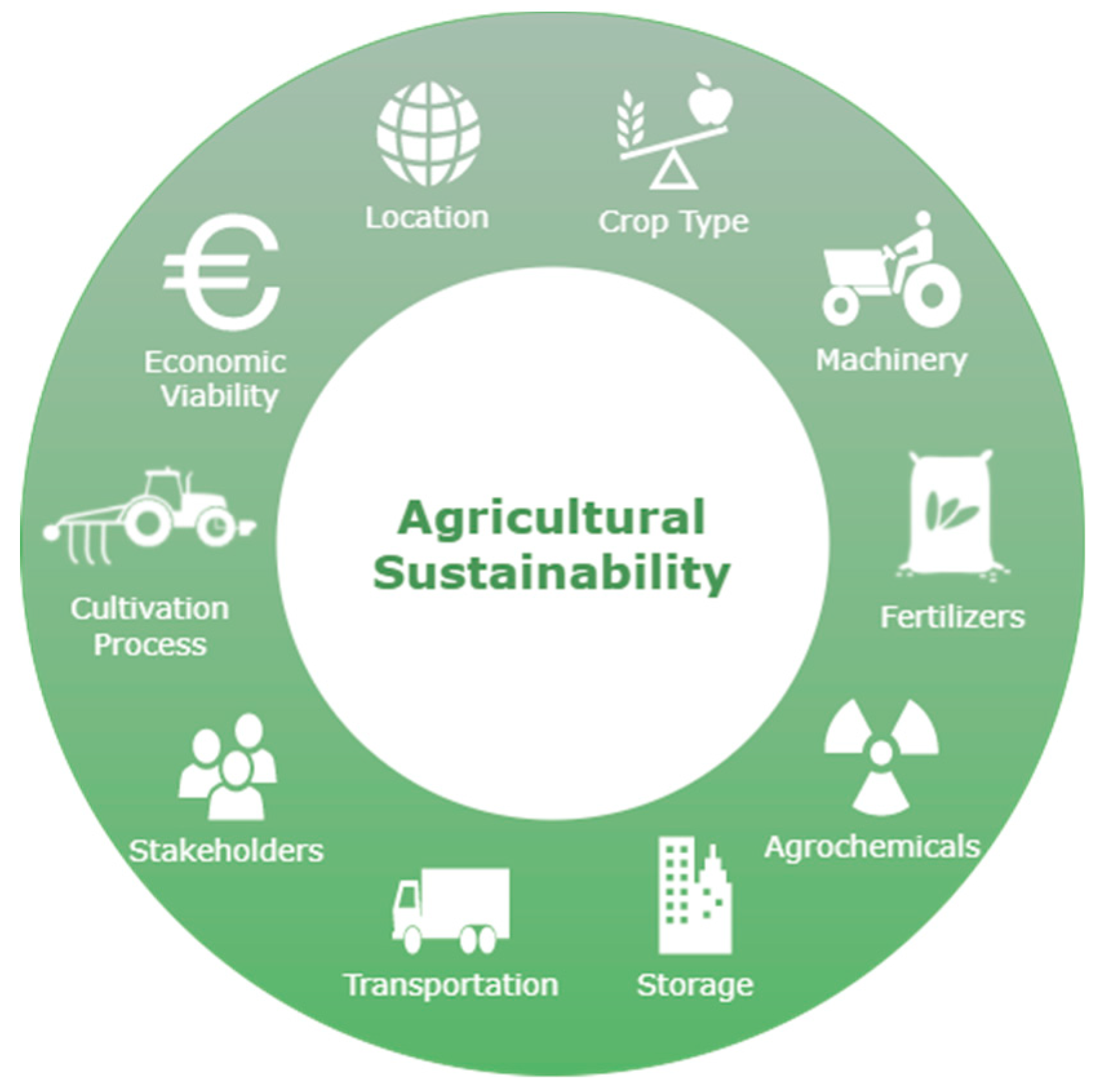
Sustainable marketing practices in agriculture focus on promoting environmentally and socially responsible approaches to farming and food production. These practices aim to minimize negative impacts on the environment, preserve natural resources, support local communities, and ensure the long-term viability of agriculture. Here are some key sustainable marketing practices in agriculture:
1. The Rise of Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture has become an increasingly important aspect of the agricultural industry, driven by the need to address environmental concerns, conserve natural resources, and meet consumer demand for more ethically produced products. In this chapter, we will explore the concept of sustainable agriculture, its benefits, and the rising consumer perception and demand for sustainable products.
Defining Sustainable Agriculture and Its Benefits
Sustainable agriculture can be defined as a farming approach that aims to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves farming practices that are environmentally responsible, economically viable, and socially equitable.
Key principles of sustainable agriculture include:
- Environmental Stewardship: Using farming practices that promote soil health, biodiversity, and conservation of natural resources. This includes practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced chemical inputs.
- Economic Viability: Ensuring the profitability and economic sustainability of farms, allowing farmers to maintain their livelihoods and reinvest in their operations.
- Social Equity: Treating farm workers, communities, and consumers ethically and fairly. Sustainable agriculture aims to support rural communities and promote social well-being.
- Climate Resilience: Adapting farming practices to mitigate the impacts of climate change and build resilience in the face of unpredictable weather patterns.
The benefits of sustainable agriculture are numerous and include:
- Environmental Preservation: Sustainable practices help protect soil health, conserve water, reduce pollution, and preserve biodiversity.
- Long-Term Productivity: By maintaining soil fertility and ecological balance, sustainable agriculture ensures the long-term productivity of farms.
- Cost Savings: Some sustainable practices, such as water conservation and integrated pest management, can lead to cost savings for farmers.
- Improved Public Health: Reduced use of synthetic chemicals in sustainable agriculture can have positive effects on public health and food safety.
Consumer Perception and Demand for Sustainable Products
Consumers worldwide are increasingly concerned about the environmental and social impact of the products they purchase, including food products. As a result, there is a growing demand for sustainably produced agricultural products.
Key factors driving consumer demand for sustainable agricultural products include:
- Environmental Awareness: Consumers are becoming more aware of environmental issues such as climate change, deforestation, and water pollution. They seek products that contribute to environmental preservation.
- Health and Safety Concerns: Consumers are paying more attention to the safety and quality of their food. They prefer products that are free from harmful chemicals and produced using eco-friendly methods.
- Ethical Considerations: Consumers are interested in the ethical treatment of farm workers and animals. They support products that are produced in a socially responsible manner.
- Transparency and Traceability: Consumers want to know where their food comes from and how it is produced. They value transparency in the supply chain and product traceability.
- Brand Reputation: Brands that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and social responsibility can gain a competitive edge and build trust with consumers.
In response to the rising demand for sustainable products, agricultural businesses are adopting sustainable practices, implementing eco-friendly certifications, and communicating their sustainability efforts to consumers. Sustainable marketing practices, such as eco-labeling and promoting sustainable initiatives, are becoming essential tools for connecting with environmentally conscious consumers.
In the following sections of this chapter, we will delve deeper into sustainable marketing strategies in the agricultural industry and explore how brands can effectively communicate their sustainability efforts to consumers.
2. Eco-Friendly Packaging and Labeling
Reducing Environmental Impact Through Packaging Choices
In recent years, eco-friendly packaging has gained significant attention in the agricultural industry as consumers and businesses alike seek ways to reduce their environmental impact. Sustainable packaging choices can play a crucial role in portraying a brand’s commitment to environmental stewardship and meeting the growing demand for sustainable products.
Here are some eco-friendly packaging options that agriculture businesses can consider:
- Biodegradable Packaging: Biodegradable packaging materials, such as bioplastics made from plant-based sources, break down naturally in the environment, reducing waste and pollution.
- Compostable Packaging: Compostable packaging is designed to decompose quickly and turn into compost under specific conditions, minimizing its impact on the environment.
- Recyclable Packaging: Using recyclable materials, such as cardboard and paper, allows consumers to recycle the packaging after use, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills.
- Reusable Packaging: Introducing reusable packaging options encourages consumers to return and reuse containers, reducing single-use packaging waste.
- Minimalist Packaging: Minimizing the amount of packaging material used for each product can significantly reduce waste and conserve resources.
- Packaging from Recycled Materials: Using packaging made from recycled materials reduces the demand for virgin resources and helps close the recycling loop.
- Smart Packaging Solutions: Implementing innovative packaging designs, such as vacuum-sealing or portion-controlled packaging, can extend the shelf life of products, reducing food waste.
By adopting eco-friendly packaging practices, agriculture businesses can align themselves with sustainability goals, appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, and contribute to a healthier planet.
Communicating Sustainability through Labels and Certifications
Clear and transparent communication about sustainability efforts is crucial to building trust with consumers and showcasing a brand’s commitment to environmental responsibility. One effective way to communicate sustainability is through product labels and certifications.
Here are some ways to effectively communicate sustainability through labels and certifications:
- Eco-Labels: Displaying eco-labels on product packaging helps consumers quickly identify sustainable products. Eco-labels may indicate attributes such as organic, biodegradable, recyclable, or carbon-neutral.
- Certifications: Obtaining recognized sustainability certifications, such as USDA Organic, Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, or non-GMO, provides third-party verification of a product’s environmental and ethical credentials.
- Transparency: Provide information on the packaging or product label about the sustainability practices used in the production process. This can include details about eco-friendly farming methods, water conservation efforts, or renewable energy use.
- QR Codes and URLs: Include QR codes or website URLs on packaging that direct consumers to more detailed information about the brand’s sustainability initiatives and practices.
- Educational Messages: Use packaging space to educate consumers about the importance of sustainable agriculture and the positive impact of their purchase decisions on the environment.
- Storytelling: Share the brand’s sustainability journey and initiatives through storytelling on packaging or marketing materials. Storytelling can create an emotional connection with consumers and strengthen brand loyalty.
- Sustainability Seals: Design a unique sustainability seal or logo that signifies the brand’s commitment to environmentally friendly practices and use it consistently across products and marketing materials.
By effectively communicating sustainability efforts through packaging and labels, agricultural brands can differentiate themselves in the market, attract environmentally conscious consumers, and contribute to the growing demand for sustainable products.
In the next section of this chapter, we will explore how agriculture businesses can leverage digital marketing channels to reach and engage with their target audience, especially those interested in sustainable products.
3. Promoting Agricultural Biodiversity and Conservation
Implementing Biodiversity Initiatives for Long-Term Growth
Agricultural biodiversity plays a critical role in ensuring the long-term sustainability and resilience of agricultural systems. By promoting biodiversity, agriculture businesses can enhance ecosystem services, improve crop productivity, and reduce vulnerability to pests and diseases. Here are some strategies for implementing biodiversity initiatives in agriculture:
- Crop Diversification: Encourage farmers to grow a variety of crops, including traditional and indigenous varieties, alongside mainstream crops. Diverse crop rotations can improve soil health, prevent soil erosion, and reduce the risk of crop failure due to climate variations.
- Preserving Native Seeds: Support the preservation and use of native seeds and heirloom varieties that are adapted to local conditions and have a long history of cultivation. Native seeds often require fewer inputs and are more resilient to local environmental challenges.
- Agroforestry: Promote the integration of trees, shrubs, or other perennial plants with crops in agroforestry systems. Agroforestry enhances biodiversity, provides habitat for beneficial organisms, and offers additional sources of income from tree products.
- Habitat Restoration: Collaborate with farmers to establish natural habitats, such as wildflower strips, hedgerows, and wetlands, to attract beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife that contribute to pest control and pollination.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Implement IPM practices that reduce reliance on chemical pesticides by incorporating natural predators, crop rotation, and other non-chemical control methods.
- Conservation Tillage: Encourage reduced or no-tillage practices to protect soil structure, increase organic matter, and promote beneficial soil organisms.
- Supporting Pollinators: Promote the conservation of pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, by providing nesting habitats and avoiding the use of harmful pesticides.
By actively participating in biodiversity initiatives, agriculture businesses can contribute to the conservation of native species, promote sustainable farming practices, and build a positive image as environmentally responsible partners.
Conservation Efforts and Their Positive Impact on Marketing
Conservation efforts in agriculture not only benefit the environment but also have a positive impact on marketing and brand reputation. Here’s how:
- Enhanced Brand Image: Consumers, especially those interested in sustainability, are more likely to support brands that actively engage in conservation and biodiversity initiatives. Promoting these efforts can enhance your brand’s image and attract environmentally conscious customers.
- Storytelling and Marketing Content: Conservation initiatives provide compelling stories and content for marketing materials, including websites, social media posts, and newsletters. Sharing stories of successful biodiversity projects can create emotional connections with consumers and increase engagement.
- Certifications and Labels: Participation in recognized biodiversity and conservation programs can lead to certifications and labels that demonstrate a brand’s commitment to sustainable practices. These certifications can be prominently displayed on packaging, further attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
- Educational Marketing: Use marketing campaigns to educate consumers about the importance of biodiversity and the positive impact of their support for sustainable agricultural practices. Educating consumers fosters trustand loyalty to the brand.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaborate with environmental organizations, conservation groups, or governmental agencies to showcase your commitment to conservation. Partnerships add credibility to your initiatives and increase visibility.
- Sustainable Sourcing: Highlight your use of sustainably sourced ingredients or products derived from biodiversity-friendly practices. This information can be featured on packaging and marketing materials to inform consumers of your ethical sourcing practices.
- Green Marketing Campaigns: Launch targeted green marketing campaigns that focus on your conservation efforts and the positive impact your brand has on the environment. Green marketing can attract environmentally conscious consumers seeking sustainable products.
By integrating conservation efforts into marketing strategies, agriculture businesses can differentiate themselves in the market, increase brand loyalty, and contribute to a more sustainable future for agriculture and the planet.
In the next section, we will explore the role of technology and digital marketing in promoting sustainable agriculture and reaching a wider audience of eco-conscious consumers.
Integrated Marketing Communications in Agriculture
Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) is a strategic approach to marketing that involves coordinating and integrating various communication channels and tools to deliver a consistent and unified message to the target audience. In the context of agricultural marketing, IMC aims to create a seamless and cohesive experience for farmers and agribusinesses across all touchpoints.
IMC recognizes that farmers are exposed to multiple communication channels, such as websites, social media, print media, direct mail, email, and more. Each of these channels can have a specific role in the marketing mix, and IMC seeks to ensure that the messages conveyed through these channels are harmonious and complementary.
By adopting an IMC approach, agriculture businesses can achieve the following benefits:
- Consistency: IMC ensures that the brand message, values, and positioning remain consistent across all marketing channels. This consistency builds trust and credibility with the target audience.
- Enhanced Impact: Coordinated communication efforts amplify the impact of marketing messages. When farmers receive consistent messages from different channels, the chances of message recall and positive reception increase.
- Efficiency: An integrated approach streamlines marketing efforts, reduces redundancy, and optimizes resource allocation. This leads to more efficient use of marketing budgets.
- Improved Customer Experience: IMC focuses on delivering a seamless and customer-centric experience. Farmers are more likely to engage with a brand that offers a unified experience across different touchpoints.
- Targeted Messaging: IMC allows for customized and targeted messaging based on specific segments of farmers. By tailoring messages to address the unique needs and interests of different farmer segments, businesses can increase relevancy and response rates.
- Brand Recognition: Consistent branding across channels helps in building brand recognition and recall. Farmers can easily identify the brand and its offerings, leading to better brand loyalty.
Benefits of an Integrated Approach for Agriculture Businesses
For agriculture businesses, embracing an integrated marketing communications approach can yield numerous advantages:
- Maximized Reach: By leveraging multiple communication channels, businesses can reach a broader and more diverse audience of farmers. This expanded reach can lead to increased market penetration and brand awareness.
- Strengthened Relationships: Consistent and well-coordinated communication fosters stronger relationships with farmers. A unified brand message builds trust and loyalty, encouraging farmers to choose the brand for their agricultural needs.
- Improved Marketing ROI: Integrated marketing allows businesses to allocate resources more effectively, focusing on channels and messages that deliver the best return on investment.
- Competitive Advantage: IMC enables agriculture businesses to stand out from competitors by presenting a cohesive and compelling brand identity. This differentiation can lead to a competitive advantage in the market.
- Agile Response: Integrated marketing facilitates a more agile response to market changes and trends. By monitoring performance across channels, businesses can adapt their strategies promptly.
- Measurable Results: With coordinated marketing efforts, businesses can more accurately measure the impact of their campaigns and marketing initiatives, allowing for data-driven decision-making.
- Long-Term Sustainability: An integrated approach to marketing supports the development of long-term relationships with farmers. Building a loyal customer base contributes to the long-term sustainability and success of the business.
In the following sections, we will explore how to develop an integrated marketing communications plan for agriculture products and the key elements to consider for effective implementation.
Creating a Unified Brand Image in Agriculture
Building a Consistent and Memorable Brand Identity
In the competitive landscape of agriculture, creating a strong and unified brand image is crucial for success. A brand identity is the visual and emotional representation of a company, product, or service that helps differentiate it from competitors and leaves a lasting impression on the target audience. Here are some key steps to build a consistent and memorable brand identity in agriculture:
- Define Your Brand’s Personality: Start by defining the personality of your brand. Consider the values, mission, and vision of your agriculture business. Are you a reliable and traditional brand, or do you want to be seen as innovative and cutting-edge? Understanding your brand’s personality will guide all aspects of your marketing communication.
- Create a Distinctive Logo: Your logo is the centerpiece of your brand identity. It should be unique, visually appealing, and representative of your brand’s values. A well-designed logo creates a strong visual association with your business and helps farmers recognize your brand easily.
- Choose Brand Colors and Fonts: Select a color palette and font styles that align with your brand personality. Consistency in colors and fonts across all marketing materials, including websites, social media, and print materials, helps reinforce brand recognition.
- Craft a Memorable Tagline: A memorable tagline can summarize your brand’s mission and benefits in a few words. A well-crafted tagline can evoke emotions and leave a lasting impression on farmers.
- Create Consistent Visual Assets: Ensure that all marketing materials, from brochures to digital ads, follow a consistent design language. Use the same color scheme, logo placement, and font style to reinforce brand identity.
- Tell Your Brand Story: Share your brand’s story with farmers. Use content marketing to communicate your values, history, and commitment to the agriculture industry. A compelling brand narrative can foster a deeper connection with your target audience.
- Be Authentic: Farmers appreciate authenticity and transparency. Be genuine in your communication and avoid over-promising. Deliver on your brand promises to build trust and credibility.
- Engage in Social Media: Social media platforms provide an excellent opportunity to showcase your brand personality and engage with farmers directly. Use social media to share valuable content, respond to inquiries, and participate in conversations.
- Educate and Inform: Position your brand as a knowledgeable authority in the agriculture sector. Share educational content, tips, and insights that add value to farmers’ lives.
- Use Brand Advocates: Engage satisfied customers as brand advocates. Testimonials and reviews from happy farmers can reinforce your brand’s credibility and attract new customers.
Aligning Marketing Messages with the Brand’s Values
To maintain a unified brand image, it’s essential to align all marketing messages with your brand’s values and personality. Here are some strategies to ensure consistent messaging:
- Develop a Brand Style Guide: Create a brand style guide that outlines the rules for using logos, colors, fonts, and imagery. Share this guide with your marketing team and partners to maintain consistency in all communication efforts.
- Craft a Clear Value Proposition: Clearly communicate your brand’s unique value proposition in all marketing materials. Farmers should understand the benefits of choosing your products or services over competitors.
- Use the Right Tone of Voice: Tailor your tone of voice to match your brand’s personality. Whether it’s friendly, professional, or humorous, the tone should resonate with your target audience.
- Consistent Messaging Across Channels: Whether it’s a social media post, email campaign, or print ad, ensure that the core messaging remains consistent across all channels.
- Integrate Branding in Content Marketing: Your content marketing efforts should reflect your brand’s values. Whether it’s blog posts, videos, or infographics, the content should align with your brand identity.
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor the impact of your marketing messages and gather feedback from farmers. Analyze the performance of different campaigns and adjust your messaging as needed.
By creating a unified brand image and aligning marketing messages with your brand’s values, you can establish a strong and trusted presence in the agriculture market. Consistency in branding will help farmers remember and choose their products or services over competitors, leading to long-term success and growth for your agriculture business.
In the next section, we will explore the role of digital marketing in agriculture and how to leverage digital channels for effective communication with farmers.
Measuring Marketing Success in Agriculture
Measuring marketing success in agriculture is essential to assess the effectiveness of marketing efforts and make informed decisions to optimize future strategies. Here are key steps and metrics to measure marketing success in agriculture:
1. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Agriculture Marketing
Identifying Relevant KPIs to Measure Marketing Effectiveness
Measuring the success of your agriculture marketing efforts is essential for understanding the impact of your strategies and making data-driven decisions. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable metrics that help assess the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns. Here are some relevant KPIs for measuring agriculture marketing success:
- Website Traffic: Track the number of visitors to your agriculture website. Increased traffic indicates higher brand visibility and potential interest from farmers.
- Conversion Rate: Measure the percentage of website visitors who take a desired action, such as filling out a contact form or making a purchase. A higher conversion rate indicates the effectiveness of your website in generating leads or sales.
- Lead Generation: Monitor the number of leads generated through various channels, such as email subscriptions, webinar sign-ups, or downloadable resources. An increase in leads reflects the success of your lead generation efforts.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Calculate the cost of acquiring a new customer through your marketing efforts. Lowering the CAC indicates more efficient marketing spending.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Determine the total value a customer brings to your agriculture business throughout their lifetime. A higher CLV indicates strong customer retention and loyalty.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Measure the profitability of your marketing campaigns by comparing the revenue generated to the cost of marketing. A positive ROI means your marketing efforts are generating revenue.
- Email Open and Click Rates: Track the open and click-through rates of your email campaigns. High engagement indicates the relevance of your content to farmers.
- Social Media Engagement: Measure likes, shares, comments, and clicks on your social media posts. Increased engagement shows that your content resonates with your audience.
- Brand Awareness: Use surveys or social media analytics to gauge the level of brand awareness among farmers. Increased brand recognition indicates effective marketing and visibility.
- Customer Retention Rate: Calculate the percentage of customers who continue to do business with you over time. High retention rates indicate satisfied and loyal customers.
Setting Realistic Goals and Metrics for Agricultural Campaigns
Before implementing any marketing campaign, it’s crucial to set realistic goals and define the metrics that will measure success. Here’s a step-by-step approach to setting achievable goals and metrics:
- Identify Objectives: Determine the primary objectives of your agriculture marketing campaign. Are you aiming to increase sales, generate leads, or enhance brand awareness? Clearly define the desired outcomes.
- Quantify Goals: Set specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for each objective. For example, if your goal is to increase sales, specify the percentage of growth and the timeframe.
- Choose Appropriate KPIs: Select KPIs that align with your objectives and will provide meaningful insights. Each goal may require different KPIs to track progress effectively.
- Benchmark Performance: Establish baseline measurements before launching the campaign. This will help you compare the results and gauge the campaign’s impact.
- Allocate Resources: Determine the budget and resources required to achieve your marketing goals. Ensure that your budget aligns with your objectives and the expected ROI.
- Monitor and Analyze Results: Continuously monitor the performance of your campaigns and track the selected KPIs. Analyze the data regularly to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Adjust Strategies: Based on the insights gained from the data analysis, make data-driven decisions to optimize your marketing strategies. If certain tactics are not delivering results, be willing to adjust and try new approaches.
- Communicate with Stakeholders: Keep all relevant stakeholders informed about the progress and results of your agriculture marketing campaigns. Transparency and communication are essential for alignment and support.
Remember that marketing success is an ongoing process of continuous improvement. Regularly review your goals and metrics, adjust your strategies as needed, and stay up-to-date with industry trends and farmer preferences.
In the next section, we will explore the importance of integrating digital marketing channels into your agriculture marketing strategy and how to effectively leverage them to reach farmers.
2. Analyzing Data and Making Informed Decisions
Utilizing Data Analytics in Agriculture Marketing
Data analytics plays a crucial role in agriculture marketing as it allows you to gain valuable insights into farmer behavior, preferences, and trends. By leveraging data analytics, you can make informed decisions and optimize your marketing strategies for better results. Here’s how to effectively utilize data analytics in agriculture marketing:
- Data Collection: Gather data from various sources, such as website analytics, social media metrics, email engagement, customer surveys, and sales data. The data should cover aspects like farmer demographics, behavior, preferences, and interactions with your brand.
- Data Processing and Cleaning: Clean and organize the collected data to ensure accuracy and consistency. Eliminate duplicate or irrelevant entries, and correct any errors in the dataset.
- Data Analysis Tools: Utilize data analysis tools and software to process and analyze the data effectively. There are various tools available, ranging from basic spreadsheets to advanced data analytics platforms.
- Identify Patterns and Trends: Analyze the data to identify patterns, trends, and correlations. Look for insights on which marketing strategies are most effective, which products resonate with specific farmer segments, and when farmers are most receptive to marketing messages.
- Segmentation Refinement: Use data-driven insights to refine your market segmentation. Identify new customer segments and tailor your marketing messages to address their specific needs and preferences.
- Performance Metrics: Define key performance metrics (KPIs) that align with your marketing objectives. Regularly track these metrics to measure the success of your marketing campaigns.
- A/B Testing: Conduct A/B tests to compare the performance of different marketing strategies. Test variations of ads, content, and emails to determine which ones generate the best response from farmers.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring of your marketing efforts to identify any issues or opportunities as they arise. This allows you to make quick adjustments to improve performance.
- Customer Journey Analysis: Map out the customer journey from the initial contact with your brand to the final conversion. Understand the touchpoints where farmers interact with your marketing content and optimize those touchpoints for maximum impact.
Adapting Strategies Based on Performance Insights
Data analytics provides valuable insights into the performance of your agriculture marketing strategies. Based on these insights, you can adapt and optimize your strategies to achieve better results. Here’s how to adapt your strategies:
- Identify High-Performing Tactics: Analyze the data to identify which marketing tactics are driving the highest engagement, leads, and conversions. Focus your resources on these successful tactics.
- Address Weak Points: Identify areas where your marketing efforts may be underperforming. It could be low email open rates, high bounce rates on your website, or ineffective ad placements. Address these weak points and experiment with alternative approaches.
- Refine Targeting: Use data analytics to refine your audience targeting. Identify the segments that respond best to your marketing messages and concentrate on reaching those farmers.
- Optimize Content: Analyze the performance of your marketing content, such as blog posts, videos, and social media posts. Optimize content based on what resonates most with your audience.
- Responsive Campaigns: Be responsive to market changes and farmer preferences. If data reveals shifts in demand or interests, adapt your campaigns accordingly.
- Budget Allocation: Allocate your marketing budget based on the data-driven performance of each tactic. Invest more in strategies that deliver better ROI and adjust spending on less effective ones.
- Continuous Improvement: Use data analytics as part of a continuous improvement process. Regularly assess the performance of your marketing efforts and make iterative changes to improve outcomes.
- Stay Updated: Stay informed about the latest trends and innovations in data analytics and marketing technologies. Embrace new tools and methodologies that can enhance your marketing effectiveness.
By using data analytics to inform your decision-making, you can create more targeted, relevant, and successful agriculture marketing campaigns. Remember that data analysis is an ongoing process, and the ability to adapt based on performance insights will lead to continuous improvement in your marketing strategies.
Conclusion
Data-driven marketing is the key to thriving in today’s competitive agriculture landscape. Understanding farmers’ needs and preferences allows agribusinesses to create meaningful connections and achieve higher ROI. To stay ahead, continuous improvement and adaptability are crucial. Embrace sustainability and integrated marketing approaches to resonate with environmentally-conscious farmers. By combining these strategies, agribusinesses can grow sustainably and make a lasting impact in the agriculture industry. Stay informed, embrace innovation, and connect with farmers on a deeper level to pave the way for a successful future in agriculture.
