Primary Market Research Advantages And Disadvantages
Are you looking to gather firsthand insights and data to drive your business decisions? Primary market research could be the answer. In this article, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of primary market research. This informative guide will help you understand the benefits and potential challenges of conducting your own research, empowering you to make informed choices and gain a competitive edge in your industry. So, let’s dive into the world of primary market research and uncover its key aspects!
What is Primary Market Research?
Primary market research refers to the process of collecting original data directly from the source, typically from target customers or potential consumers. Unlike secondary research, which involves analyzing existing data and sources, primary research involves firsthand data collection through surveys, interviews, focus groups, observations, or experiments.
Importance of Primary Market Research in Business
Primary market research holds immense importance for businesses across industries. Here are some key reasons why it is a critical component of the decision-making process:
- Understanding Customer Needs: Primary research allows businesses to gain deep insights into customer preferences, pain points, and expectations. By directly engaging with the target audience, companies can tailor their products and services to meet specific demands effectively.
- Identifying Market Opportunities: Conducting primary research helps businesses identify untapped market opportunities and unmet needs. By understanding consumer behavior and preferences, companies can develop innovative solutions and gain a competitive edge in the market.
- Validating Business Ideas: Before investing significant resources into a new product or service, conducting primary research can provide validation for the feasibility and potential success of the idea. This reduces the risk of launching offerings that may not resonate with the target market.
- Evaluating Marketing Strategies: Primary research is instrumental in evaluating the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. By collecting feedback directly from customers, businesses can assess the impact of their promotional efforts and make data-driven adjustments for better results.
- Assessing Customer Satisfaction: Understanding customer satisfaction is essential for maintaining a loyal customer base. Primary research methods, such as customer surveys and feedback forms, provide valuable insights into customer experiences, enabling businesses to enhance their offerings and improve customer retention.
- Staying Ahead of Competitors: In a rapidly evolving market, staying ahead of the competition is crucial. Primary research allows businesses to monitor their competitors and identify their strengths and weaknesses, enabling them to fine-tune their own strategies and gain a competitive advantage.
- Supporting Business Expansion: For businesses looking to expand into new markets or launch in different regions, primary research helps assess market potential and customer preferences in those areas. This information is invaluable for successful expansion planning.
Primary market research serves as a cornerstone for informed decision-making in the business world. By directly engaging with target audiences, companies can gain unique and valuable insights that drive growth, innovation, and long-term success. Embracing primary research as a core strategy empowers businesses to adapt to changing market dynamics and meet the ever-evolving needs of their customers.
Advantages of Primary Market Research

Primary market research offers several advantages that can provide valuable insights for businesses and organizations. Here are some of the key advantages of conducting primary market research:
I. Accurate and Reliable Data Collection
Primary market research provides businesses with the advantage of collecting accurate and reliable data directly from the target audience. By engaging directly with customers or potential consumers, businesses can ensure that the data they gather is firsthand and unbiased. This accuracy and reliability in data collection are crucial for making informed decisions and developing effective strategies.
II. Tailored to Specific Research Objectives
Another significant advantage of primary market research is its ability to be tailored to the specific research objectives of a business. Unlike secondary research, which may not address the exact needs of a company, primary research allows businesses to design surveys, interviews, or focus groups that align precisely with the information they seek. This customization ensures that the research results directly address the questions at hand, making the data more relevant and actionable.
III. In-depth Understanding of Customer Needs
Primary market research goes beyond surface-level insights and offers businesses an in-depth understanding of customer needs. By directly interacting with participants, companies can delve into the motivations, preferences, and pain points of their target audience. This deeper understanding enables businesses to develop products and services that resonate with their customers on a profound level, ultimately driving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
IV. Real-time and Current Information
The timeliness of data is critical in the fast-paced business environment. Primary market research provides real-time and current information because the data is collected directly from consumers in the present moment. This up-to-date data ensures that businesses have the most relevant and accurate information at their disposal when making critical decisions.
V. Opportunity for Direct Interaction with Participants
One of the unique advantages of primary research is the opportunity for direct interaction with participants. Whether through face-to-face interviews or online focus groups, this direct engagement allows businesses to build a rapport with their target audience, encouraging open and candid responses. The personal touch fosters a deeper connection, leading to more valuable insights from participants.
VI. Scope for Exploratory Research
Primary market research offers the scope for exploratory research, where businesses can delve into new areas and gain unanticipated insights. This open-ended approach allows researchers to explore different angles and perspectives, which may lead to the discovery of valuable opportunities or trends that were previously unknown. Exploratory research paves the way for innovative strategies and unique market offerings.
VII. Control Over the Research Process
When conducting primary market research, businesses have complete control over the research process. They can design the research instruments, select the participants, and choose the data collection methods that align with their specific needs and goals. This control ensures that the research is conducted with precision and efficiency, maximizing the relevance and usefulness of the gathered data.
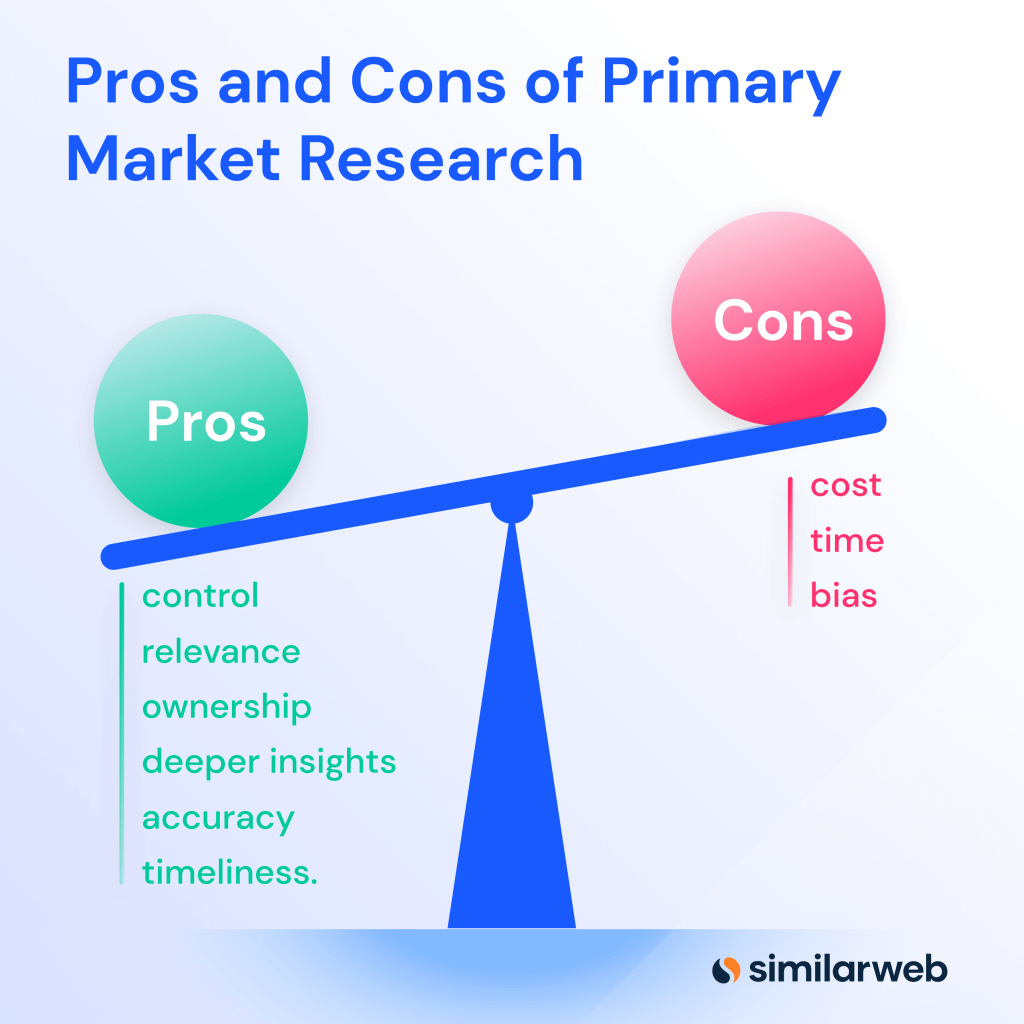
In conclusion, primary market research offers businesses a range of advantages that contribute to better decision-making, improved customer understanding, and increased competitive advantage. The accurate and tailored data, real-time information, and direct interaction with participants all contribute to the effectiveness of primary research in shaping successful marketing strategies and business growth.
Disadvantages of Primary Market Research
While primary market research offers valuable insights, it also comes with some disadvantages and challenges that businesses should be aware of when conducting their research. Here are some of the key disadvantages of primary market research:
I. Time-Consuming and Costly
One of the significant disadvantages of primary market research is that it can be time-consuming and costly. Planning and executing primary research involve careful consideration of research objectives, designing appropriate methodologies, recruiting participants, and collecting data. Depending on the scale and scope of the research, this process can take weeks or even months to complete. Additionally, primary research may require specialized tools, hiring research professionals, or outsourcing the research, all of which can contribute to higher costs.
II. Potential for Bias
Primary market research is susceptible to bias, both from the researchers conducting the study and the participants providing the data. Researchers’ preconceived notions or personal opinions can unintentionally influence the research process and skew the results. Similarly, participants may provide biased responses based on their own perceptions or preferences. Minimizing bias in primary research requires careful design, well-structured questions, and an unbiased approach during data collection and analysis.
III. Challenges in Recruiting Participants
Recruiting participants for primary research can be challenging, especially for niche or specialized target audiences. Finding willing participants who fit specific criteria can be time-consuming and may require incentives to encourage participation. The difficulty in recruitment can lead to limited sample size, potentially affecting the representativeness and generalizability of the research findings.
IV. Data Collection and Analysis Complexity
Collecting and analyzing primary research data can be complex, especially when dealing with large datasets or qualitative data. Depending on the research methods used, data entry, coding, and analysis may require specialized skills and software. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data can be a labor-intensive process, and errors in data collection or analysis can compromise the validity of the research outcomes.
V. Limited Scope for Large-Scale Studies
Primary research may face limitations when conducting large-scale studies. As the process involves direct engagement with participants, scaling up the research to cover a significant population can be challenging and resource-intensive. Large-scale primary research may require substantial time, budget, and manpower, making it less feasible for some projects.
VI. Ethical Considerations and Privacy Concerns
Ethical considerations and privacy concerns are paramount in primary market research. Researchers must ensure that participants’ rights and confidentiality are protected throughout the research process. Obtaining informed consent, ensuring anonymity, and safeguarding sensitive data are critical ethical obligations. Failure to address these concerns can lead to ethical violations and damage a company’s reputation.
In conclusion, while primary market research offers valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, it also comes with its share of disadvantages. The time and cost involved, potential for bias, challenges in participant recruitment, complexity in data collection and analysis, limited scope for large-scale studies, and ethical considerations must be carefully addressed when designing and conducting primary research. By understanding and mitigating these challenges, businesses can make the most of primary market research and use it strategically to inform their decision-making and improve their offerings.
Best Practices for Conducting Primary Market Research
Conducting primary market research requires careful planning, execution, and analysis to ensure accurate and valuable insights. Here are some best practices to follow when conducting primary market research:
I. Defining Clear Research Objectives
Before embarking on primary market research, it is essential to define clear and specific research objectives. What do you want to achieve through the research? Are you looking to understand customer preferences, test a new product concept, or evaluate the effectiveness of a marketing campaign? Defining clear research objectives will guide the entire research process and ensure that the collected data aligns with your business goals.
II. Choosing the Right Research Methodology
There are various primary market research methodologies available, such as surveys, focus groups, interviews, observation, and field research. Each methodology has its strengths and limitations, and the choice of the appropriate one depends on your research objectives, target audience, and the nature of the data you seek. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each method and select the one that best suits your research goals.
III. Designing Effective Survey Questions
If you decide to use surveys as your primary research method, pay special attention to the design of the survey questions. Ensure that your questions are clear, concise, and unbiased. Avoid leading questions that may influence respondents’ answers. Use a mix of multiple-choice questions, open-ended questions, and rating scales to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. Pilot-test the survey with a small group to identify any issues with the questions before conducting the full-scale survey.
IV. Ensuring Data Validity and Reliability
Data validity refers to the extent to which the research data measures what it intends to measure, while data reliability refers to the consistency and stability of the results. To ensure data validity, use well-established research instruments and methodologies. Triangulate data by using multiple sources or methods to cross-validate findings. To ensure data reliability, employ standardized data collection procedures and maintain consistency throughout the research process.
V. Sample Selection and Size Considerations
The selection of the right sample is crucial for the accuracy and representativeness of the research findings. Define your target population and select a sample that is a true representation of your target audience. Consider factors such as demographics, geographic location, and customer behavior when selecting the sample. Additionally, determine an appropriate sample size based on statistical significance to ensure the reliability of the results.
VI. Ethical Guidelines for Research Conduct
Adhering to ethical guidelines is essential in primary market research. Obtain informed consent from all participants, clearly explaining the purpose and nature of the research. Ensure participant confidentiality and anonymity to protect their privacy. Avoid any deceptive practices in data collection. Be transparent about the research objectives and any potential risks or benefits to the participants. Lastly, obtain necessary approvals and permissions before conducting the research, especially when dealing with sensitive topics or vulnerable populations.
By following these best practices, businesses can conduct primary market research effectively and gather valuable insights that inform their decision-making processes. Well-designed and well-executed primary research can provide businesses with a competitive edge, helping them better understand their customers, identify market trends, and develop products and services that meet customer needs and preferences.
Comparative Analysis: Primary vs. Secondary Market Research
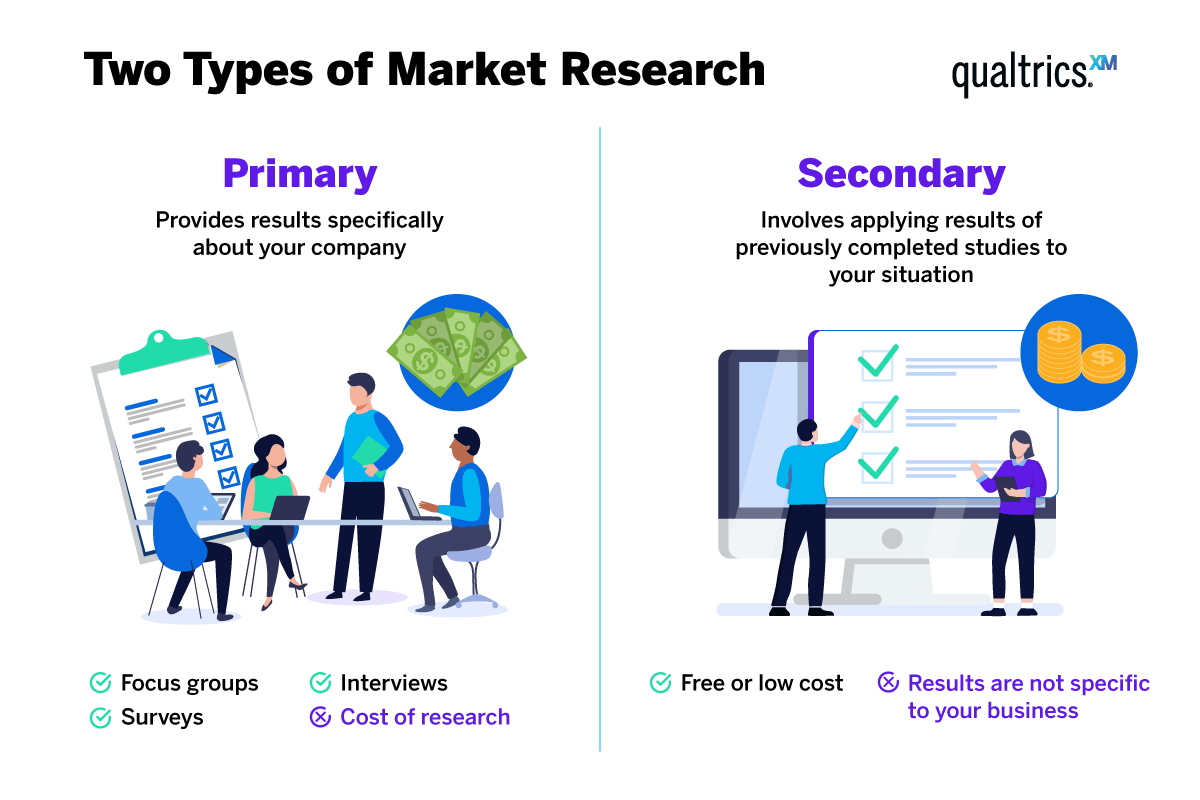
Comparative analysis of primary and secondary market research helps businesses understand the differences and benefits of each research method. Both primary and secondary research are valuable in gathering information, but they have distinct characteristics and purposes. Here’s a comparison of primary and secondary market research:
Understanding Secondary Market Research
Secondary market research involves the use of existing data and information that has been collected by someone else for purposes other than the current research project. This data can include reports, studies, surveys, government publications, industry statistics, and more. Secondary research is valuable because it provides a foundation of knowledge and can help businesses understand the broader market context before conducting primary research.
Pros and Cons of Secondary Market Research
Pros of Secondary Market Research:
- Time-saving and Cost-effective: Since the data already exists, businesses can access it without the need for primary data collection, which saves time and resources.
- Historical Data: Secondary research often provides historical data, allowing businesses to analyze trends and patterns over time.
- Large Sample Size: Secondary data sources may have larger sample sizes than what businesses can achieve in primary research, providing a more comprehensive view of the market.
- Access to Specialized Data: Some data, such as industry reports or government publications, may be difficult or expensive to obtain through primary research but are readily available as secondary data.
Cons of Secondary Market Research:
- Relevance and Accuracy: The data may not be directly aligned with the specific research objectives, leading to potential limitations in its relevance.
- Outdated Information: Since secondary data is not collected for the current research project, it may not reflect the most up-to-date market conditions or consumer behaviors.
- Lack of Control: Businesses have no control over how the data was collected in secondary research, and therefore, the methods or measures used may not align perfectly with their needs.
- Potential Bias: The original data sources may have had biases or limitations, which can impact the reliability of the findings.
Complementary Roles of Primary and Secondary Research
Primary and secondary market research are not mutually exclusive; in fact, they often complement each other. By combining both approaches, businesses can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the market and its dynamics.
Complementary Roles:
- Exploratory Insights: Secondary research can provide initial insights and background information, helping businesses identify knowledge gaps and refine their research objectives before conducting primary research.
- Benchmarking: Secondary data can be used as a benchmark to compare and validate findings from primary research, enhancing the credibility of the research outcomes.
- Contextual Understanding: Secondary research offers a broader context for primary research findings, helping businesses interpret and contextualize their own data.
- Cost Efficiency: By using secondary data for foundational information, businesses can optimize their primary research efforts, focusing on specific areas that require deeper insights.
Both primary and secondary market research have their strengths and weaknesses. While primary research provides customized and specific data directly from the target audience, secondary research offers historical and broader market information. The combination of both approaches can lead to a more well-rounded and insightful market research process, helping businesses make informed decisions and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Case Studies: Successful Primary Market Research Examples
Case Study 1: Product Launch Assessment
Scenario: A technology startup is developing a new fitness-tracking device that they plan to launch in the market. Before the launch, they want to ensure that the product meets the needs and preferences of their target customers. To achieve this, they decide to conduct primary market research.
Primary Research Method: The company uses a combination of online surveys and focus groups to gather feedback from potential users. The online survey allows them to reach a large number of respondents efficiently, while the focus groups provide in-depth insights into users’ opinions and experiences.
Results: Through the online survey, the company learns about customers’ preferences for features, design, and price range for fitness tracking devices. The focus groups reveal additional information about user habits, motivations, and pain points related to fitness tracking. Armed with this information, the company makes necessary adjustments to the product, such as adding new features and refining the design. As a result, they launch a fitness tracking device that resonates with their target audience, leading to strong initial sales and positive reviews.
Case Study 2: Consumer Behavior Analysis
Scenario: A fashion retail chain is experiencing a decline in sales and wants to understand why customers are not visiting their stores as frequently as before. They decide to conduct primary market research to gain insights into consumer behavior.
Primary Research Method: The company uses observational research and interviews to understand customer shopping patterns and preferences. They hire researchers to observe customer behavior in their stores, noting factors like time spent browsing, items tried on, and purchase decisions. Additionally, they conduct interviews with a sample of customers to explore the reasons behind their shopping choices.
Results: Through observational research, the retail chain identifies that certain areas of the store receive less foot traffic, indicating possible layout and merchandising issues. The interviews reveal that customers feel the store lacks the latest fashion trends and that the pricing is perceived as too high. Armed with this information, the retail chain revamps its store layout, brings in more trendy fashion items, and introduces targeted promotions. As a result, customer footfall increases, and sales start to rebound.
Case Study 3: Competitive Landscape Analysis
Scenario: A fast-food restaurant chain is planning to expand its business into a new city. Before doing so, they want to understand the competitive landscape and identify opportunities for differentiation.
Primary Research Method: The company conducts field research by sending mystery shoppers to competitor restaurants in the new city. The mystery shoppers observe and document factors like menu offerings, pricing, service quality, cleanliness, and customer experience.
Results: The field research reveals that the competing restaurants in the new city primarily offer traditional fast food options with limited healthy choices. Additionally, the service quality in some competitors’ restaurants is below par. Armed with this information, the restaurant chain decides to focus on offering a diverse menu with healthier options and emphasizing exceptional customer service. This strategic approach sets them apart from the competition and helps attract new customers to the new city.
In these case studies, primary market research played a crucial role in helping businesses make informed decisions and achieve success. By directly gathering data from their target audience and the market environment, these companies were able to tailor their products, services, and strategies to meet customer needs and preferences effectively. Primary research provided them with valuable insights that secondary data alone could not have provided, making it a powerful tool for businesses seeking to gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Integrating Primary Market Research into Business Strategy

Integrating primary market research into business strategy is essential for making informed decisions, developing effective marketing plans, and staying competitive in the market.
I. Leveraging Research Findings for Decision Making
Scenario: A retail chain is facing increased competition in the market and wants to find ways to attract more customers and increase sales. They decide to conduct primary market research to gain insights into customer preferences and shopping behaviors.
Primary Research Method: The retail chain conducts online surveys and in-store observations to collect data from their customers. The online surveys ask customers about their shopping habits, preferences, and suggestions for improvement. The in-store observation tracks customer flow, browsing behavior, and interactions with products and displays.
Research Findings: Through primary market research, the retail chain discovers that customers are looking for more personalized shopping experiences and prefer stores with a wide variety of product options. They also find that certain areas of the store are underutilized and could be optimized to increase customer engagement.
Decision Making: Armed with these findings, the retail chain decides to implement a customer loyalty program that offers personalized discounts and rewards based on customers’ purchase history. They also introduce new product categories based on customer demands and reorganize the store layout to improve customer flow and highlight popular products. These decisions are based on direct feedback from customers, helping the retail chain align its business strategy with customer needs.
II. Implementing Changes Based on Research Insights
Scenario: An e-commerce company is experiencing a high cart abandonment rate on its website and wants to understand the reasons behind it. They decide to conduct primary market research to identify pain points in the online shopping process.
Primary Research Method: The e-commerce company conducts a combination of online surveys and user testing sessions. The online surveys are sent to customers who abandoned their carts, asking them about the reasons for not completing their purchase. The user testing sessions involve observing participants as they navigate the website and complete a mock purchase.
Research Findings: Through the primary market research, the e-commerce company finds that customers are abandoning their carts due to unexpected shipping costs, a complicated checkout process, and concerns about the security of their payment information.
Implementing Changes: Based on these insights, the e-commerce company takes immediate action to address the issues. They offer free shipping for orders above a certain threshold and provide clear shipping cost information upfront. They also simplify the checkout process, reducing the number of steps required to complete a purchase. Additionally, they implement additional security measures and display trust symbols to reassure customers about the safety of their payment information. As a result of these changes, the cart abandonment rate decreases, and online sales improve.
III. Continual Research for Business Growth
Scenario: A software development company is planning to release a new version of its flagship product. They want to ensure that the new features and improvements align with customer expectations and needs. To achieve this, they decide to conduct primary market research.
Primary Research Method: The software development company uses a combination of focus groups and beta testing to gather feedback from users. The focus groups allow them to have in-depth discussions with a select group of customers, while the beta testing involves releasing a test version of the product to a larger group of users for real-world usage.
Research Findings: Through primary market research, the software development company identifies areas where the new version can be further improved based on customer feedback. They discover that certain features need refinement and that additional functionalities are desired.
Business Growth: By incorporating the feedback from the primary market research, the software development company releases an updated version of the product that better meets customer expectations. The improvements lead to positive word-of-mouth from satisfied users, attracting new customers and contributing to the business’s growth.
In these scenarios, integrating primary market research into the business strategy proves to be invaluable for decision-making, implementing effective changes, and achieving business growth. By directly gathering insights from customers and target audiences, businesses can make informed decisions that align with customer needs and preferences. Continual research ensures that businesses stay relevant and responsive to changing market demands, enabling them to maintain a competitive edge and drive growth in the long run.
Conclusion
Primary market research offers invaluable insights to tailor products and strategies effectively. Its advantages include specific, up-to-date data for accurate decision-making. However, it can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. By planning objectives and methodologies carefully, businesses can maximize benefits and thrive in a competitive marketplace. Knowledge is power, and with the right approach, primary research can unlock a business’s full potential.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main advantages of primary market research?
A: Primary market research offers several advantages that make it a valuable method for businesses seeking to gain insights directly from their target audience:
- Customized Data: Primary research provides specific information tailored to a company’s unique needs and questions. It allows businesses to gather data that is directly relevant to their marketing objectives.
- Up-to-date Information: Primary research provides the most current and relevant data since it involves collecting data directly from consumers or potential customers. This ensures that businesses are working with the most recent information available.
- Problem-Focused Data: Primary research enables businesses to focus on specific marketing problems or objectives. It helps in gaining a deeper understanding of customer behavior, preferences, and needs related to a particular product or service.
Q2: How can I conduct primary market research on a limited budget?
A: Conducting primary market research on a limited budget requires careful planning and resource management. Here are some cost-effective methods to consider:
- Online Surveys: Online surveys are relatively inexpensive to conduct and allow you to reach a large audience quickly. There are several free or low-cost survey platforms available that can help you collect data from your target audience.
- Focus Groups: Organizing small focus groups can be a cost-effective way to gather qualitative insights from a diverse group of participants. Consider recruiting participants from your local community to minimize travel costs.
- In-house Interviews: If possible, conduct in-house interviews with your own team members, employees, or colleagues who can provide valuable insights related to your research objectives.
- Social Media Listening: Monitor social media platforms to gather valuable customer feedback and insights without incurring any direct costs.
- Online Analytics: Utilize website analytics and online tracking tools to gather data on customer behavior and preferences on your website or digital platforms.
Q3: What are some common mistakes to avoid in primary research?
A: When conducting primary market research, it’s essential to be aware of common mistakes that could impact the validity and reliability of your findings. Some mistakes to avoid include:
- Biased Questioning: Ensure that your survey or interview questions are neutral and unbiased to avoid leading respondents to a particular answer.
- Small Sample Size: Ensure your sample size is large enough to draw meaningful conclusions. A small sample size may not be representative of your target audience.
- Overlooking Data Privacy: Protect respondents’ data privacy and confidentiality. Obtain consent before collecting any personal information and use secure data storage methods.
- Survey Design Errors: Design your survey or research instrument carefully to avoid confusion, ambiguity, or double-barreled questions.
- Selection Bias: Be cautious of selecting participants or respondents in a way that may introduce bias into your data.
Q4: Is primary market research suitable for all types of businesses?
A: While primary market research can be highly valuable for businesses seeking to gather specific and relevant insights directly from their target audience, it may not be suitable for all types of businesses or research objectives. Factors to consider include:
- Budget: Conducting primary research can be costlier than using existing secondary data. Businesses with limited budgets may need to prioritize their research needs.
- Time Constraints: Primary research can be time-consuming, especially when conducting in-depth interviews or focus groups. Businesses with urgent research needs may need to consider quicker alternatives.
- Research Objectives: Assess whether primary research aligns with your specific research objectives. Sometimes, existing secondary data may be sufficient for certain research questions.
- Data Availability: Evaluate if the data you need is readily available through existing sources or if you need to collect it directly from your target audience.
Q5: How can I ensure data privacy and confidentiality during research?
A: Ensuring data privacy and confidentiality is crucial to maintain ethical research practices and building trust with respondents. Here are some steps to ensure data privacy:
- Obtain Informed Consent: Before collecting any personal data, inform respondents about the purpose of the research, how their data will be used, and obtain explicit consent.
- Anonymity and Confidentiality: Guarantee anonymity to respondents by avoiding the collection of any identifying information. If confidentiality is necessary, store data securely and restrict access to authorized personnel only.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhere to data protection regulations and privacy laws applicable in your country or region. For example, in the European Union, comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Secure Data Storage: Ensure that all data collected is stored securely and protected from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Data Destruction: Once the research is complete and no longer needed, dispose of data appropriately and securely.
By following these practices, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to protecting respondents’ privacy and maintaining ethical standards in their research activities.



